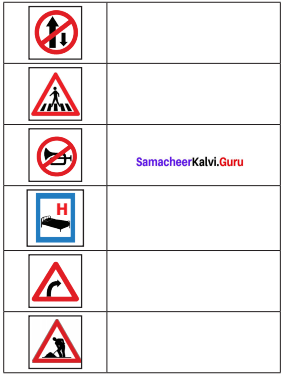
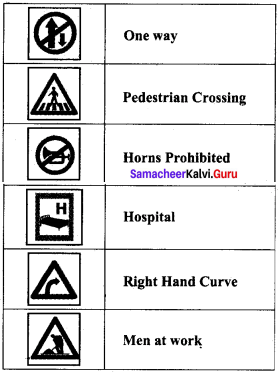
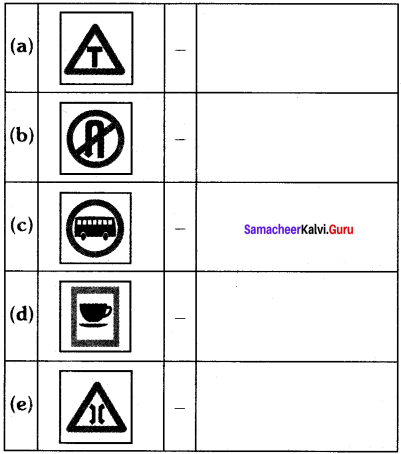
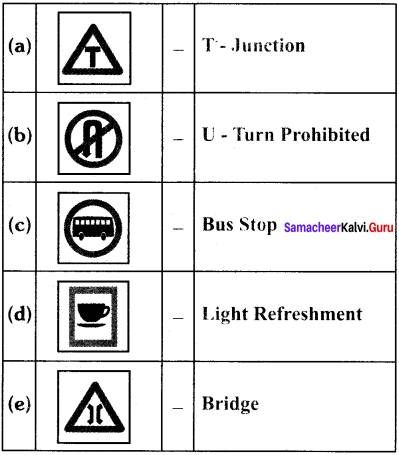
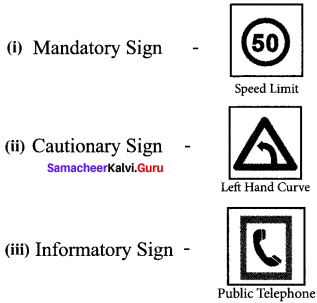
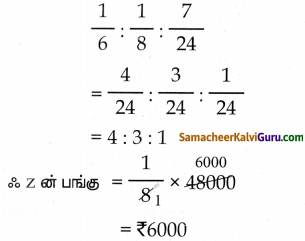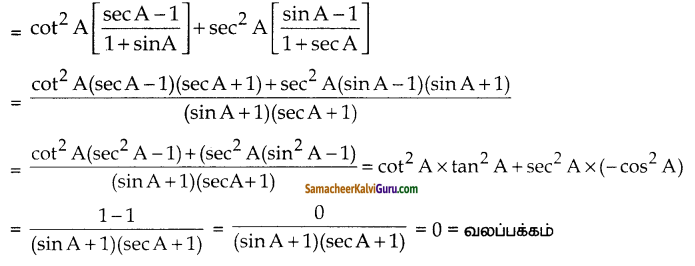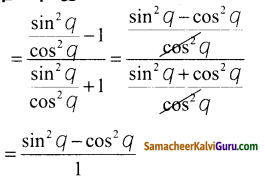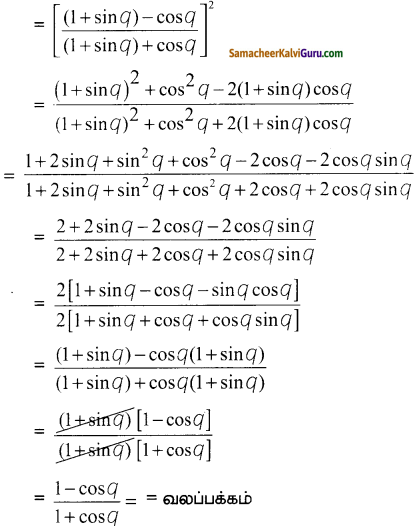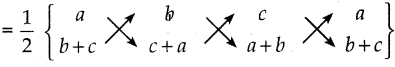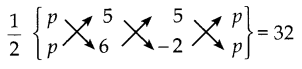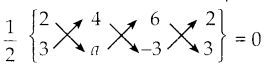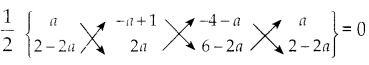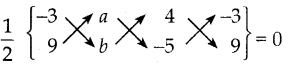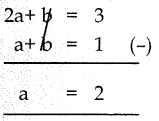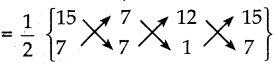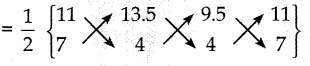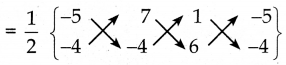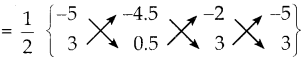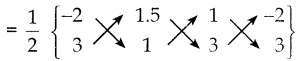Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 4 வாழ்வியல் கணிதம் Ex 4.5 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
TN Board 8th Maths Solutions Chapter 4 வாழ்வியல் கணிதம் Ex 4.5
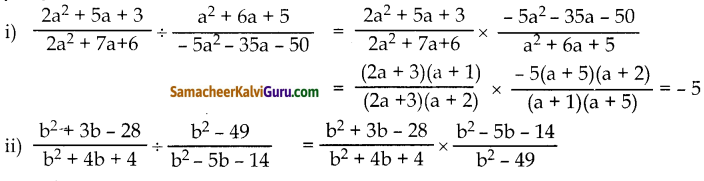
கேள்வி 1.
ஒரு பழ வியாபாரி வாங்கிய மாம்பழங்களில் 10% அழுகியிருந்தன. மீதமிருந்த மாம்பழங்களில் 33\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)% -ஐ விற்றுவிட்டார். தற்போது 240 மாம்பழங்கள் தொடக்கத்தில் இருக்கின்றன எனில், முதலில் அவர் வாங்கிய மொத்த மாம்பழங்களின் எண்ணிக்கையைக் காண்க.
தீர்வு:
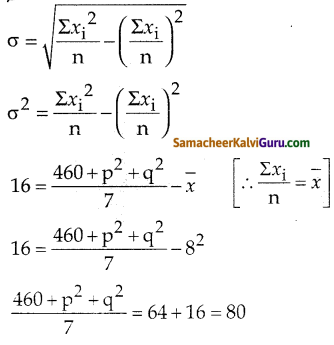
x என்பது மொத்த மாம்பழங்களின் எண்ணிக்கை என்க.
அழுகிய மாம்பழங்கள் = 10% x x
= \(\frac{10 x}{100}=\frac{x}{10}\)
அவரிடம் உள்ளது = 240
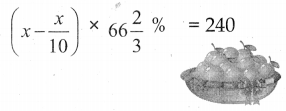
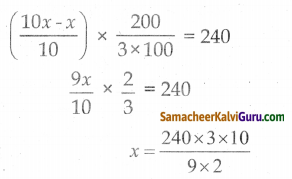
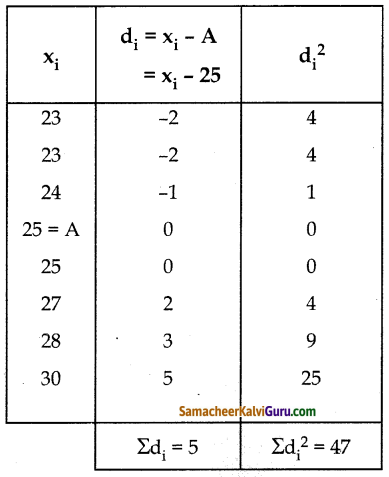
மொத்த மாம்பழங்களின் எண்ணிக்கை 400 ஆகும்.
![]()
கேள்வி 2.
ஒருமாணவர் 31% மதிப்பெண்களைப் பெற்று 12 மதிப்பெண்கள் குறைவாக பெற்றதால் தேர்வில் தேர்ச்சி பெறவில்லை . தேர்ச்சி பெற 35% மதிப்பெண்கள் தேவை எனில், தேர்வின் மொத்த மதிப்பெண்களைக் காண்க.
தீர்வு :
மதிப்பெண்ணை x என்க
தேர்ச்சி பெறுவதற்கான மதிப்பெண் = \(\frac{35 x}{100}\) = 35%
பெற்ற மதிப்பெண்கள் = \(\frac{31 x}{100}\)
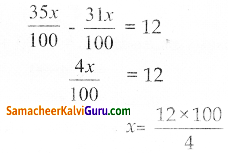
x = 300
அதிகபட்ச மதிப்பெண் 300 ஆகும்.
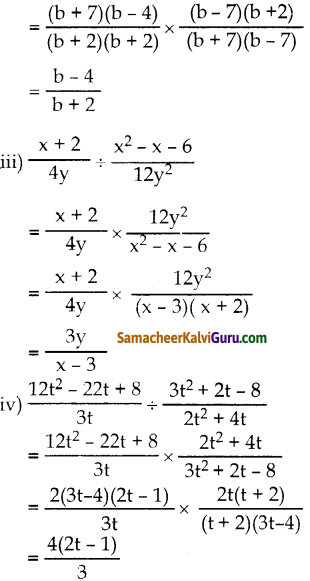
கேள்வி 3.
சுல்தானா, ஒரு பொது அங்காடியில் பின்வரும் – பொருள்களை வாங்கினார். அவர் செலத்திய மொத்த இரசீதுத் தொகையைக் கணக்கிடுக.
i) 5% சரக்கு மற்றும் சேவை வரியுடன் ₹800 மதிப்பிலான மருந்துகள்.
ii) 12% சரக்கு மற்றும் சேவை வரியுடன் ₹650 மதிப்பிலான அழகு சாதனப்பொருள்கள்.
iii) 0% சரக்கு மற்றும் சேவை வரியுடன் ₹900 மதிப்பிலான தானியங்கள்
iv) 18% சரக்கு மற்றும் சேவை வரியுடன் ₹1750 மதிப்பிலான கருப்புக் கண்ணாடி
v) 28% சரக்கு மற்றும் சேவை வரியுடன் ₹28500 மதிப்பிலான காற்றுப் பதனி (AC)
தீர்வு:

(i) மொத்த ரசீது
தொகை = மருந்து மதிப்பு+ ச.சேவை .வரி 5%
= 800 + 800 x \(\frac { 5 }{ 100 }\)
= 800 + 40 = ₹840
(ii) மொத்த ரசீது தொகை
= அழகுசாதன
பொருளின் விலை + ச.சேவை .வரி 12%
= 650 + 650 x \(\frac { 12 }{ 100 }\)
100 = 650 + 78 = ₹728
(iii) மொத்த ரசீது தொகை = தானியங்களின் மதிப்பு + ச.சேவை. வரி 0%
= 900 + 900 x \(\frac { 0 }{ 100 }\)
= 900 + o = ₹900
(iv) மொத்த ரசீது தொகை = கருப்பு கண்ணாடியின் மதிப்பு + ச.சேவை. வரி 18%
= 1750 + 1750 x \(\frac { 18 }{ 100 }\)
= 1750 + 315
= ₹2065
(v) மொத்த ரசீது தொகை = காற்றுப் பதினியின் மதிப்பு + ச.சேவை.வரி 28%
= 28500 + 28500 x \(\frac { 28 }{ 100 }\)
= 28500 + 7980
= ₹36480
![]()
கேள்வி 4.
P இன் வருமானம் Q ஐக் காட்டிலும் 25% அதிகம் எனில், Q இன் வருமானம் P ஐக் காட்டிலும் எத்தனை சதவீதம் குறைவு?
தீர்வு :
Qன் வருமானம் x என்க
P = x + xன் 25%
= x + \(\frac{25}{100}\)x
= x + \(\frac{x}{4}\)
P = \(\frac{5 x}{4}\)
Pன் வருமான சதவீதம் = \(\frac{5 x}{4}\) x 100
= 125x
Qன் வருமான சதவீதம் = 100x
வித்தியாசம் = 125x – 100x
= 25x
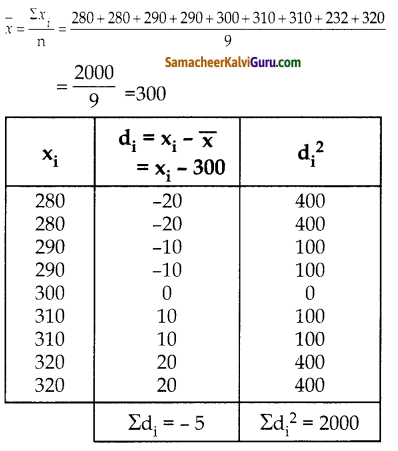
Qன்வருமானம் Pன்வருமானத்தை விட 25% குறைவு.
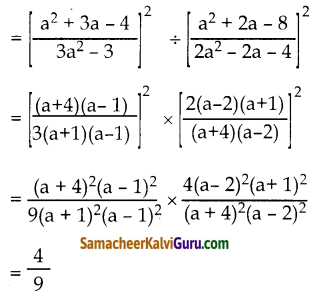
கேள்வி 5.
வைதேகி, இரு சேலைகளை தலா ₹2200 இக்குவிற்றாள். ஒன்றின் மீது 10% இலாபத்தையும் மற்றொன்றின் மீது 12% நட்டத்தையும் அடைந்தாள் எனில், சேலைகளை விற்றதில் அவளின் இலாபம் அல்லது நட்டம் சதவீதத்தைக் காண்க.

தீர்வு:
ஒரு சேலையின் விலை = ₹ 2200
இரு சேலைகளின் விலை = ₹2200 x 2
= ₹ 4400
அடக்க விலை = 10%, வி.வி =₹ 2200
im 16
100x வி.வி அ.வி =
” 100+ இலாபம்% _ 100 x 2200 _ 100 x 2000
100 + 10 110
அ.வி = =₹ 2000
நட்டம் = 12%
im 17
= ₹ 2500
மொத்த அடக்கவிலை = 2000 + 2500
=₹4500
நட்டம் = அ.வி – வி.வி
= 4500 – 4400
= ₹100
im 18
= 2.22%
![]()
கேள்வி 6.
32 ஆண்கள் நாளொன்றுக்கு 12 மணி நேரம் வேலை செய்து ஒரு வேலையை 15 நாள்களில் முடிப்பர் எனில், அந்த வேலையின் இரு மடங்கை எத்தனை ஆண்கள் நாளொன்றுக்கு 10 மணி நேரம் வேலை செய்து 24 நாள்களில் முடிப்பர்?
தீர்வு :
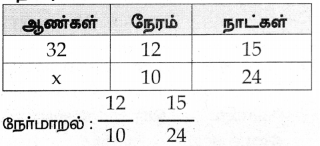
ஆண்கள் செய்யும் வேலை
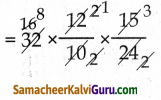
= 8 x 3
= 24 ஆண்கள்
வேலையின் இருமடங்கை செய்யும் ஆண்கள் எண்ணிக்கை இருமடங்காகும்.
= 2 x 24
= 48 ஆண்கள்
கேள்வி 7.
அமுதா, ஒருசேலையை 18 நாள்களில் நெய்வார். அஞ்சலி, அனிதாவை விட நெய்வதில் இரு மடங்கு திறமைசாலி . இருவரும் இணைந்து நெய்தால், அந்தச் சேலையை எத்தனை நாள்களில் நெய்து முடிப்பர்?
தீர்வு :
அமுதா நெய்த வேலை = 18 நாட்கள்
அஞ்சலி நெய்த சேலை = 9 நாட்கள்
இருவரும் சேர்ந்து = \(\frac{a b}{a+b}\)
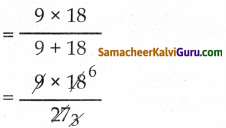
= 6 நாட்கள்
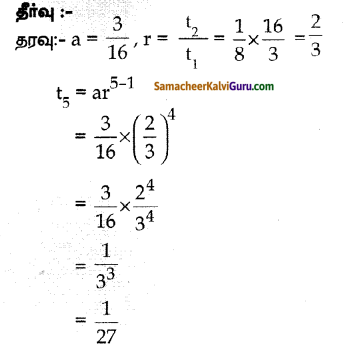
கேள்வி 8.
P மற்றும் Q ஆகியோர் ஒரு வேலையை முறையை 12 மற்றும் 15 நாள்களில் முடிப்பர். P ஆனவர் அந்த வேலையைத் தனியேத் தொடங்கிய பிறகு, 3 நாள்கள் கழித்து Q ஆனவர் அவருடன் சேர்ந்து வேலையானது முடியும் வரை அவருடன் இருந்தார் எனில், வேலையானது எத்தனை நாள்கள் நீடித்தது?
தீர்வு :
P மற்றும் Q செய்த மொத்த வேலை = 60
P மட்டும் செய்த வேலை = \(\frac { 60 }{ 12 }\) = 5
Q மட்டும் செய்த வேலை = \(\frac { 60 }{ 15 }\) = 4
P ஆனவர் கூடுதலாக 3 நாட்கள் செய்த வேலை = 3 x 5 = 15
P மற்றும் Q விட்டுவிட்ட வேலை = 60 – 15 = 45
P மற்றும் Q சேர்ந்து செய்த வேலை = 5 + 4 = 9
P மற்றும் Q சேர்ந்து செய்த வேலையின்
45 நேரம் = \(\frac { 45 }{ 9 }\) = 5 நாட்கள்
நீடித்த நாட்கள் 5 + 3 = 8 நாட்கள்
![]()
மேற்சிந்தனைக் கணக்குகள்
கேள்வி 9.
ஒரு பின்னத்தின் தொகுதியை 50% அதிகரித்தும் பகுதியை 20% குறைத்தால், அந்த பின்னமானது \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 }\) ஆக மாறுகிறது எனில், அசல் பின்னத்தைக் காண்க.
பின்னத்தை \(\frac { x }{ y }\) என்க.
தொகுதி :
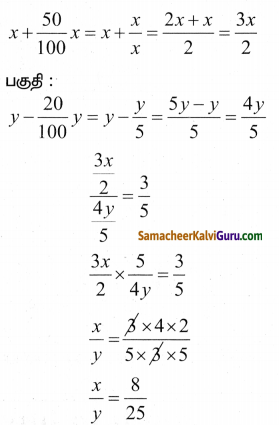
கேள்வி 10.
கோபி, ஒரு மடிக்கணினியை 12% இலாபத்திற்கு விற்றார். மேலும், அதை ₹1200 இக்கு கூடுதலாக விற்றிருந்தால், இலாபம் 20% ஆக இருந்திருக்கும். மடிக்கணினியின் அடக்க விலையைக் காண்க.
தீர்வு :
பொருளின் விலை 100% என்க.
விற்பனை இலாபம் 12% எனில் மொத்த இலாபம் 112% மற்றும்

20% இலாபம் எனில் மொத்த இலாபம் 120%
எனவே 120% – 112% =₹1200
8% = 1200
எனவே 100% = \(\frac{1200}{8}\) x 100
= ₹ 15000
∴ மடிக்கணினியின் அடக்கவிலை ₹15000
![]()
கேள்வி 11.
₹ 180 ஐக் குறித்த விலையாகவும், ₹108ஐ விற்பனை விலையாகவும் கொண்ட ஒரு பொருளுக்கு கடைக்காரர் இரண்டு தொடர் தள்ளுபடிகளை அளிக்கிறார். இரண்டாவது தள்ளுபடியின் 8% எனில், முதல் தள்ளுபடியின் சதவீதத்தைக் காண்க.
தீர்வு :
x என்பது முதல் தள்ளுபடி சதவீதம் என்க.
குறித்த விலை = ₹ 180
முதல்தள்ளுபடி x % =180 x \(\frac { x }{ 100 }\) = ₹ 1.8x
வி.வி = கு.வி – தள்ளுபடி
= 180 -1.8x
இரண்டாவது தள்ளுபடி 25% = (180-1.8.x) x \(\frac { 25 }{ 100 }\)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) (180 – 1.8x) = வி.வி
வி.வி = (180 -1.8 x) – (180 – 1.8x)\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
=(180-1.8x) \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
(180 – 1.8x) x \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) = ₹ 108
(180 – 1.8x) = \(\frac{108 \times 4}{3}\) = 144
180 – 1.8x = 144
1.8x = 180 – 144 = 36
x = \(\frac { 36 }{ 1.8 }\)
x = 20%
கேள்வி 12.
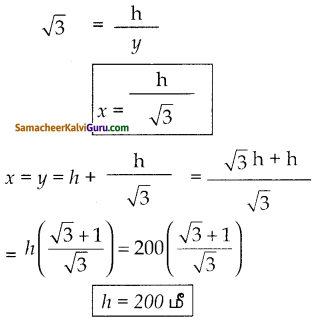
ஒர் அசலானது, கூட்டு வட்டி முறையில் 2 ஆண்டுகளில் அதைப்போன்று 1.69 மடங்கு ஆகிறது எனில் வட்டி வீதத்தைக் காண்க.
தீர்வு :
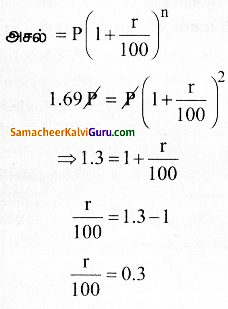
r = 0.3 x 100
r = 30%
கேள்வி 13.
ஒரு சிறு தொழில் நிறுவனம், 40 ஆண்களைப் பணியமர்த்தி 150 நாள்களில் 540 விசைப்பொறி இறைப்பிகளைத் (Motor Pumps) தயாரித்து வழங்க ஓர் ஒப்பந்தத்தை எடுத்துக்கொள்கிறது. 75 நாள்களுக்குப் பிறகு, அந்நிறுவனத்தால் 180 விசைப்பொறி இறைப்பிகளை மட்டுமே தயாரிக்க முடிந்தது. வேலையானது ஒப்பந்தத் தின்படி நேரத்திற்கு முடிய வேண்டுமெனில், கூடுதலாக எத்தனை ஆண்களை அந்நிறுவனம் பணியமர்த்த வேண்டும்?
தீர்வு :
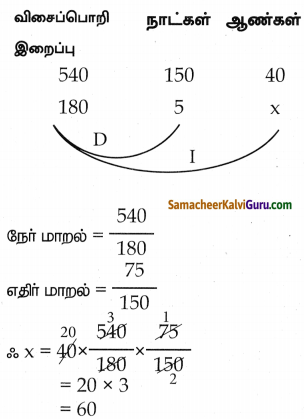
கூடுதலாக 20 ஆண்களை பனியமர்த்த வேண்டும்.
![]()
கேள்வி 14.
P என்பவர் தனியே ஒரு வேலையின் \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) பகுதியை 6 நாள்களிலும், Q என்பவர் தனியே அதே வேலையின் \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) பகுதியை 4 நாள்களிலும் முடிப்பர். இருவரும் இணைந்து அந்த வேலையின் \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) பகுதியை எத்தனை நாள்களில் முடிப்பர்?
தீர்வு :
P என்பவர் தனியே ஒரு வேலையில் \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) பகுதியை = 6 நாட்கள்
முழுவேலையை = \(\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{6}\)
= \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Q என்பவர் தனியே செய்த வேலையின் நாட்கள்
= \(\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{1}{4}=\frac{1}{6}\)
P + Q இருவரும் இணைந்து செய்த வேலை
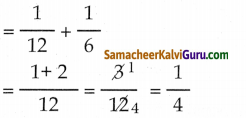
ஆனால் \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) பகுதியின் வேலையை செய்து முடிக்க ஆகும் காலம் = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) x 4
= 3 நாட்கள்
கேள்வி 15.
X என்பவர் தனியே ஒரு வேலையை 6 நாள்களிலும், Y என்பவர் தனியே அதே வேலையை 8 நாள்களிலும் முடிப்பர். X மற்றும் Y ஆகியோர் இந்த வேலையை ₹48000 இக்கு ஒப்புக் கொண்டனர். Z என்பவரின் உதவியுடன், அவர்கள் அந்த வேலையை 3 நாள்களில் முடித்தனர் எனில், தொகையில் Z இன் பங்கு எவ்வளவு? தீர்வு :
(x + y + z) ன் ஒரு நாள் வேலை = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) —— (1)
X தனியே செய்த வேலை = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
Y தனியே செய்த வேலை = \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\)
(X + Y) ன் ஒரு நாள் வேலை = \(\frac{1}{6}+\frac{1}{8}\)
= \(\frac{8+6}{6 \times 8}\)
= \(\frac{14}{48}=\frac{7}{24}\) ——– (2)
(2) ஐ (1) ல் பிரதியிட
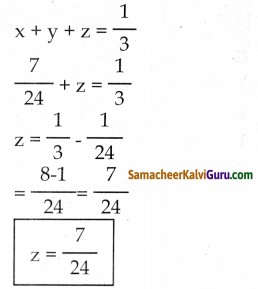
ஒரு நாள் செய்த வேலை அளவு =