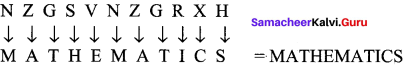
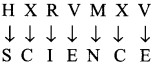
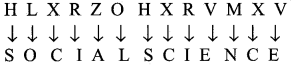
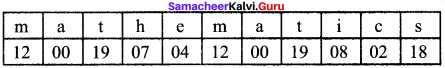
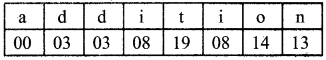
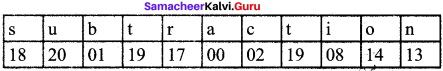
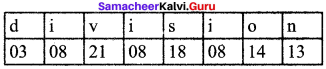
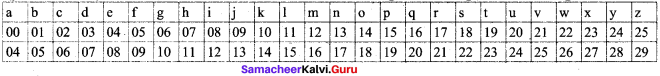
Students can Download Maths Chapter 1 Numbers Intext Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 3 Chapter 1 Numbers Intext Questions
Exercise 1.1
Think (Text book page No. 3)
Question 1.
Is the square of a prime number, prime?
Solution:
No, the square of a prime number ‘P’ has at least 3 divisors 1, P and P². But a prime number is a number which has only two divisors, 1 and the number itself. So square of a prime number is not prime.
Question 2.
Solution:
The sum of two perfect squares, need not be always a perfect square. Also the difference of two perfect squares need not be always a perfect square. Bu the product of two perfect square is a perfect square.
![]()
Try These (Text book Page No. 3)
Consider the following square numbers:
(i) 441
(ii) 225
(iii) 289
(iv) 1089.
Express each of them as the sum of two consecutive positive integers.
Solution:
(i) 441 = 220 + 221
(ii) 225 = 112 + 113
(iii) 289 = 144 + 145
(iv) 1089 = 544 + 545
Think (Text book Page No. 4)
Question 1.
Take an even natural number, say, 46 (or any other even number of your choice). Try to express it as a sum of consecutive odd numbers starting with 1. Do you succeed?
Solution:
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 = 36
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + 13 = 49
So 46 cannot be expressed as a sum of consecutive odd numbers starting with 1. But 36 also an even natural number. It can be expressed as the sum of consecutive odd numbers as 36 = 1 +3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11.
Question 2.
The square of an odd number can always be written as the sum of two consecutive natural numbers. Can the reverse statement be true? Is the sum of any two consecutive natural numbers a perfect square of a number?
Solution:
No, the reverse is not true. The sum of any two consecutive natural numbers need not be a perfect square of a number. Example: 35 + 36 = 71, not a perfect square.
Try These (Text book Page No. 4)
(i) Which among 256, 576, 960, 1025, 4096 are perfect square numbers?
(Hint: Try to extend the table of squares already seen).
Solution:
256 = 16²
576 = 24²
4096 = 64²
∴ 256, 576 and 4096 are perfect squares
(ii) One can judge just by look, that the each of the following numbers (82, 113, 2057, 24353, 8888,1972) is not a perfect square. Explain why?
Solution:
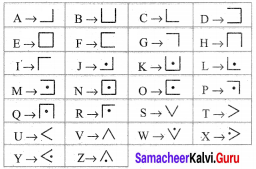
Because the unit digit of a perfect square will be 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, 9. But the given numbers have unit digits 2, 3, 7, 8. So they are not perfect squares.
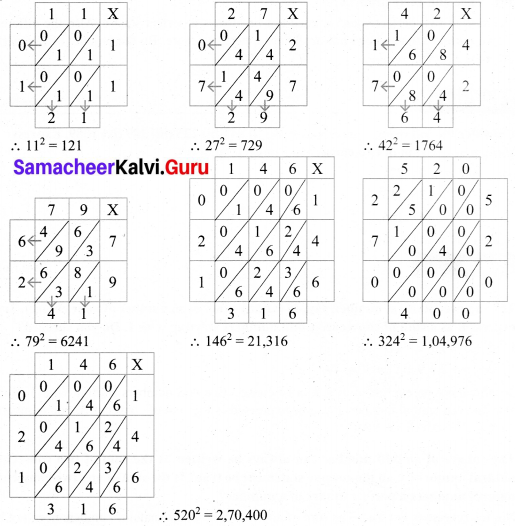
(iii) Find the squares by diagonal method and also the ones digit in the squares of the following numbers: 11, 27, 42, 79, 146, 324, 520.
Solution:
Ones digit is the squares of
Think (Text book Page No. 5)
Consider the claim: “Between the squares of the consecutive numbers n and (n+1), there are 2n non-square numbers”. Can it be true? Find how many non-square numbers are there
(i) between 4 and 9?
(ii) between 49 and 64?
and verify the claim.
Solution:
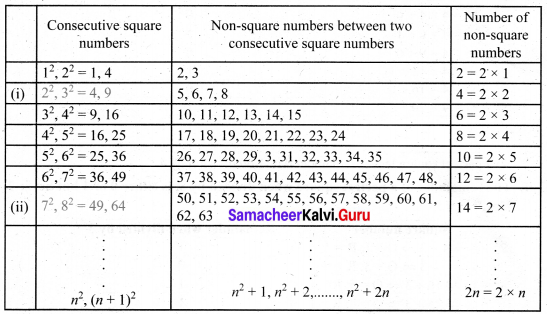
Therefore we conclude that there are 2n non-square numbers between two consecutive square numbers.
![]()
Activity 1. (Text book Page No. 5)
Verify the following statements:
(i) The square of a natural number, other than 1, is either a multiple of 3 or exceeds a multiple of 3 by 1.
Verification
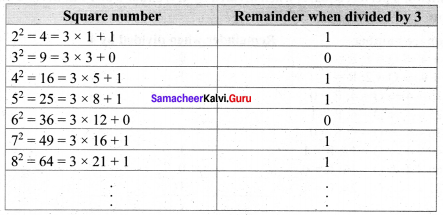
Hence verified that the square of a natural number other than 1, is either a multiple of 3 or exceeds a multiple of 3 by 1.
(ii) The square of a natural number, other than 1, is either a multiple of 4 or exceeds a multiple of 4 by 1.
Verification
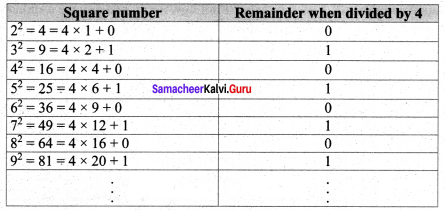
So a perfect square leaves remainder 0 or 1 on division by 4.
(iii) The remainder of a perfect square when divided by 3, is either 0 or 1 but never 2.
Verification
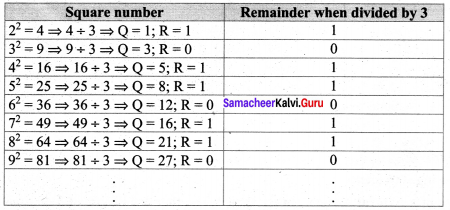
So in all the cases the remainder is either 0 or 1, but not 2. Hence verified.
(iv) The remainder of a perfect square, when divided by 4, is either 0 or 1 but never 2 and 3.
Verification
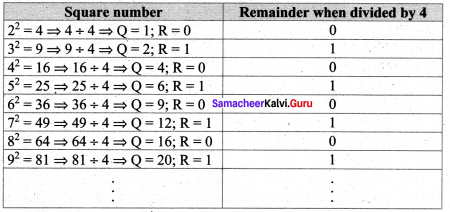
From the table it is verified that the remainder of a perfect square when divided by 4 is either 0 or 1 but never 2 and 3.
(v) When a perfect square number is divided by 8, the remainder is either 0 or 1 or 4, but never be equal to 2, 3, 5, 6 or 7.
Verification
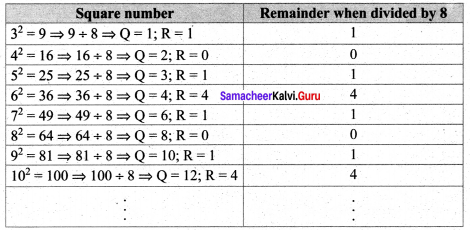
From the table it is verified when a perfect square number is divided by 8, the remainder is 0 or 1 or 4. but never be equal to 2, 3, 5, 6 or 7
Activity 2. (Text book Page No. 6)
Consider any natural number m > 1.We find that (2m, m² – 1, m² + 1) will form a Pythagorean triplet. (A little algebra can help you to verify this!). With this formula, generate a few Pythagorean triplets.
Solution:
For any natural number m, we have 2m, m² – 1, m² + 1 is a Pythagorean triplet.
(i) Consider 2m = 16 ⇒ m = 8
m² – 1 = 64 – 1 = 63
m² + 1 = 64 + 1 = 65
So Pythagorean triplet is 16, 63, 65.
(ii) Consider 2m = 18 ⇒ m = 9
m² – 1 = 81 – 1 = 80
m² + 1 = 81 + 1 = 82
So Pythagorean triplet is 18, 80, 82.
![]()
Try These (Text book Page No. 7)
Use the method of successive subtraction of odd numbers (starting from 1) to examine the following numbers and find if they are perfect squares or not. For perfect square numbers that you find, identify the square root.
(i) 144
(ii) 256
(iii) 360
Solution:
(i) 144
Step 1: 144 – 1 = 143
Step 2: 143 – 3 = 140
Step 3: 140 – 5 = 135
Step 4: 135 – 7 = 128
Step 5: 128 – 9 = 119
Step 6: 119 – 11 = 108
Step 7: 108 – 13 = 95
Step 8: 95 – 15 = 80
Step 9: 80 – 17 = 63
Step 10: 63 – 19 = 44
Step 11: 44 – 21 = 23
Step 12: 23 – 23 = 0.
We get 0 in the 12th step. ∴ 144 is a perfect square and ∴ \(\sqrt{144} \) = 12.
(ii) 256
Step 1: 256 – 1 = 255
Step 2: 255 – 3 = 252
Step 3: 252 – 5 = 247
Step 4: 247 – 7 = 240
Step 5: 240 – 9 = 231
Step 6: 231 – 11 = 220
Step 7: 220 – 13 = 207
Step 8: 207 – 15 = 192
Step 9: 192 – 17 = 175
Step 10: 175 – 19 = 156
Step 11: 156 – 21 = 135
Step 12: 135 – 23 = 112
Step 13: 112 – 25 = 87
Step 14: 87 – 27 = 60
Step 15: 60 – 29 = 31
Step 16: 31 – 31 = 0
We have subtracted odd numbers starting from 1 repeatedly from 256. We get 0 in the 1 step.
∴ 256 is a perfect square and \(\sqrt{256} \) = 16.
(iii) 360
Step 1: 360 – 1 = 359
Step 2: 359 – 3 = 356
Step 3: 356 – 5 = 351
Step 4: 351 – 7 = 344
Step 5: 344 – 9 = 335
Step 6: 335 – 11 = 324
Step 7: 324 – 13 = 311
Step 8: 311 – 15 = 296
Step 9: 296 – 17 = 279
Step 10: 279 – 19 = 260
Step 11: 260 – 21 = 239
Step 12: 239 – 23 = 216
Step 13: 216 – 25 = 191
Step 14: 191 – 27 = 164
Step 15: 164 – 29 = 135
Step 16: 135 – 31 = 104
Step 17: 104 – 33 = 71
Step 18: 71 – 35 = 36
Step 19: 36 – 37 = -1
We have subtracted successive odd numbers starting from 1, repeatedly from 360, we didn’t get zero.
∴ The given number is not perfect square.
Think (Text book Page No. 8)
In this case, if we want to find the smallest factor with which we can multiply or divide 108 to get a square number, what should we do?
Solution:
108 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 2² × 3² × 3
If we multiply the factors by 3, then we get
2² × 3² × 3 × 3 ⇒ 2² × 3² × 3² = (2 × 3 × 3)²
Which is a perfect square.
∴ Again if we divide by 3 then we get 2² × 3² ⇒ (2 × 3 )², a perfect square.
∴ We have to multiply or divide 108 by 3 to get a perfect square.
![]()
Exercise 1.2
Try These (Text book Page No. 11)
Find the square root by long division method.
(i) 400
(ii) 1764
(iii) 4356
Solution:
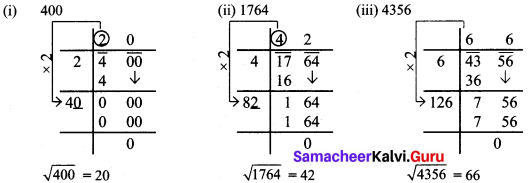
Try These (Text book Page No. 12)
Question 1.
Without calculating the square root, guess the number of digits in the square root of the following numbers:
(i) 14400
(ii) 100000000
(iii) 390625
Solution:
(i) \(\sqrt{14400}=\sqrt{144 \times 100}=\sqrt{144} \times \sqrt{100}\) = 12 x 10 = 120.
(ii) \(\sqrt{100000000}=\sqrt{10000 \times 10000}=\sqrt{10000} \times \sqrt{10000}\) = 100 × 100 = 10,000
(iii) \(\sqrt{390625}=\sqrt{25 \times 25 \times 25 \times 25}=\sqrt{25 \times 25} \times \sqrt{25 \times 25}\) = 25 x 25 = 625
Question 2.
Find the square root of
(i) 19.36
(ii) 1.2321
(iii) 116.64
Solution:
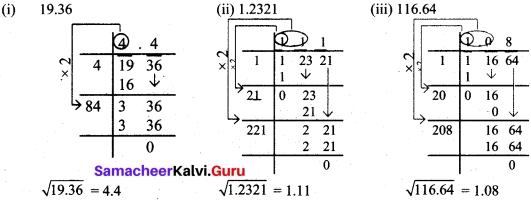
Think (Text book Page No. 13)
Fill up the table:
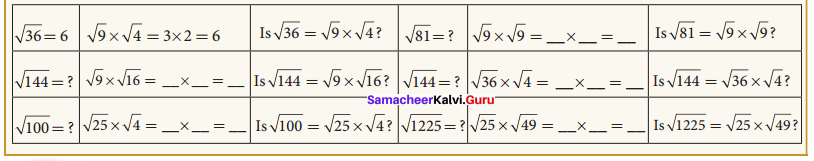
Solution:
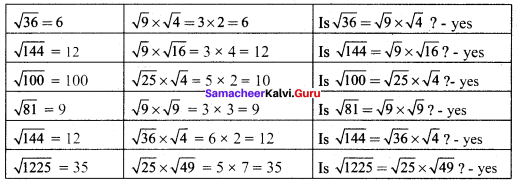
Activity 3. (Text book Page No. 13)
Attempt to prepare a table of square root problems as in the above case to show that if a and b are two perfect square numbers, then \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}}=\frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\) (b ≠ 0) We can use this idea to compute easily certain square-root problems.
Solution:
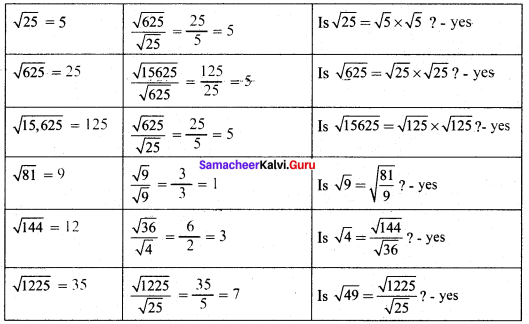
Try These (Text book Page No. 13)
Using the above method, find the square root of 1.2321 and 11.9025.
Solution:
(i) \(\sqrt{1.2321}=\sqrt{\frac{12321}{10000}}=\frac{111}{100}\) = 1.11
(ii) \(\sqrt{11.9025}=\frac{\sqrt{119025}}{\sqrt{10000}}=\frac{345}{100}\) = 3.45
![]()
Try These (Text book Page No. 14)
Put the numbers
(i) 4, \(\sqrt{14} \), 5 and
(ii) 7, \(\sqrt{65} \), 8 in ascending order.
Solution:
(i) 4, \(\sqrt{14} \), 5
Squaring all the numbers we get 4², \((\sqrt{14})^2 \) , 5² ⇒ 16, 14, 25
∴Ascending order: 14, 16, 25
Ascending order: \(\sqrt{14} \), 4, 5
(ii) 7, \(\sqrt{65} \), 8
Squaring 7, \(\sqrt{65} \) and 8 we get 7², \((\sqrt{65})^2 \), 8² ⇒ 49, 65, 64
Ascending order: 49, 64, 65
Ascending order: 7, 8, \(\sqrt{65} \)
Exercise 1.3
Try These (Text book Page No. 17)
Find the ones digit in the cubes of each of the following numbers,
(i) 17
(ii) 12
(iii) 38
(iv) 53
(v) 71
(vi) 84
Solution:
(i) 17
17 ends with 7, so its cube ends with 3. i.e, ones digit in 173 is 3.
(ii) 12
12 ends with 2, so its cube ends with 8. i.e, ones digit in 123 is 8.
(iii) 38
38 ends with 8, so its cube ends with 2. i.e, ones digit in 383 is 2.
(iv) 53
53 ends with 3, so its cube ends with 7. i.e, ones digit in 533 is 7.
(v) 71
71 ends with 1, so its cube ends with 1. i.e, ones digit in 713 is 1
(vi) 84
84 ends with 4, so its cube ends with 4. i.e, ones digit in 843 is 4.
Think (Text book Page No. 17)
Find the smallest number by which 675 must be divided to obtain a perfect cube.
Solution:
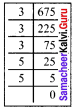
We find that 675 = 3 x 3 x 3 x 5 x 5
= 3 x 3 x 3 x 5 x 5
Here we have an ungrouped 5 x 5.
So if we divide 675 by 5 x 5 then the new number will be a perfect cube.
ie. 675 ÷ 25 = 27
The new number is 27
\(\sqrt[3]{27}=\sqrt[3]{3 \times 3 \times 3}\) = 3
![]()
Exercise 1.4
Try These (Text book Page No. 21)
Expand the following numbers using exponents:
(i) 8120
(ii) 20305
(iii) 3652.01
(iv) 9426.521
Solution:
(i) 8120 = (8 x 1000) + (1 x 100) + (2 x 10) + 0 x 1
= (8 x 103) + (1 x 102) + (2 x 101)
(ii) 20305 = (2 x 10000) + (0 x 1000) + (3 x 100) + (0 x 10) + (5 x 1)
= (2 x 104) + (3 x 102) + 5
(iii) 3652.01 = 3000 + 600 + 50 + 2 + \(\frac{0}{10}+\frac{1}{100}\)
= (3 x 1000) +(6 x 100) + (5 x 10) + (2 x 1) + (1 x \(\frac{1}{100}\))
= (3 x 103) + (6 x 102) + (5 x 101) + 2 + (1 x 10-2)
(iv) 9426.521 = (9 x 1000) + (4 x 100) + (2 x 10) + (6 x 1) + \(\left(\frac{5}{10}\right)+\left(\frac{2}{100}\right)+\left(\frac{1}{1000}\right)\)
= (9 x 103) + (4 x 102) + (2 x 101) + 6 + (5 x 10-1) + (2 x 10-2) + (1 x 10-3)
Try These (Text book Page No. 23)
Verify the following laws (as we did above). Here, a, b are non-zero integers and m, n are any integers.
1. Zero exponent rule: a0 = 1.
2. Product of same powers to power of product rule: am x bm = (ab)m
3. Quotient of same powers to power of quotient rule: \(\frac{a^{m}}{b^{m}}=\left(\frac{a}{b}\right)^{m}\)
Verification:
Let a = 2; b = 3; m = 2
1. a0 = 20 = 1.
2. am x bm = 22 x 32 = 4 x 9 = 36 = (2 x 3)2
3. \(\frac{a^{m}}{b^{m}}=\frac{2^{2}}{3^{2}}=\frac{4}{9}=\left(\frac{2}{3}\right)^{2}\)
Try These (Text book Page No. 26)
Question 1.
Write in standard form: Mass of planet Uranus = 8.68 x 1025 kg.
Solution:
Mass of Planet Uranus = 86800000000000000000000000 kg
[23 zeros after 868]
Question 2.
Write in scientific form:
(i) 0.000012005
(ii) 4312.345
(iii) 0.10524
(iv) The distance between the Sun and the planet Saturn 1.4335 x 1012 miles.
Solution:
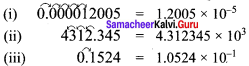
(iv) The distance between Sun and the planet Saturn is 1.4335 x 1012 miles
![]()
Activity 4. (Text book Page No. 29)
Observe that
23 – 13 = 1 + 2 x 1 x 3
33 – 23 = 1 + 3 x 2 x 3
43 – 33 = 1 + 4 x 3 x 3
Find the value of 153 – 143 in the above pattern.
Solution:
153 – 143 = 1 + 15 x 14 x 3
Think (Text book Page No. 29)
13 = 1 = 1
23 = 8 = 3 + 5
33 = 27 = 7 + 9 + 11
Observe and continue this pattern to find the value of 73 as the sum of consecutive odd numbers.
13 = 1 = 1
23 = 8 = 3 + 5
33 = 27 = 7 + 9 + 11
43 = 64 = 13 + 15 + 17 + 19
53 = 125 = 21 + 23 + 25 + 27 + 29
63 = 216 = 31 + 33 + 35 + 37 + 39 + 41
73 = 343 = 43 + 45 + 47 + 49 + 51 + 53 + 55