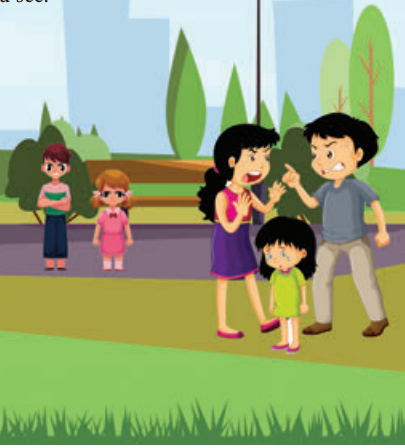
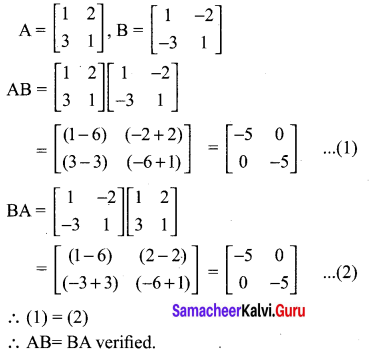
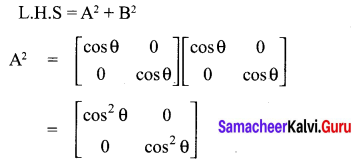
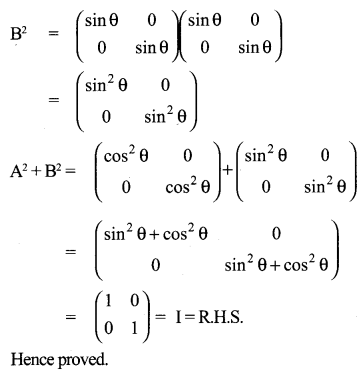
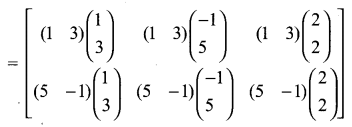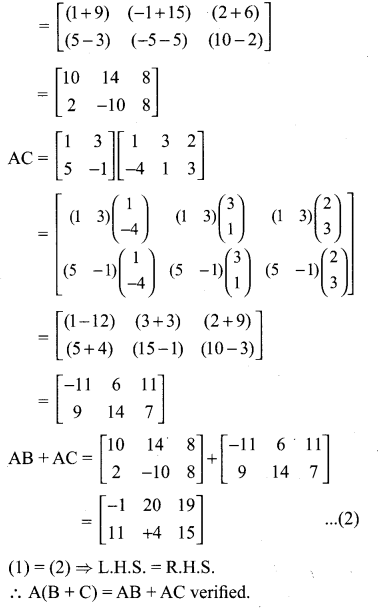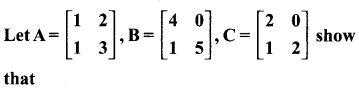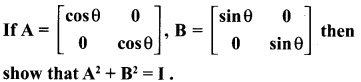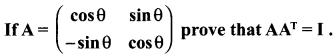Looking to improve English skills and gain more subject knowledge then the best resources that you can use here is Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Solutions for Prose Chapter 2 The Night the Ghost Got in Questions and Answers.
In the Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Guide for Chapter 2 The Night the Ghost Got in textbook solutions, subject experts covered all types of questions and answers related to the topics, quick notes, summary, solved & unsolved exercises, etc. If you are planning to prepare Chapter 2 The Night the Ghost Got in via textbook, then you’re suggested to go with this Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Book Solutions Questions and Answers PDF for better understanding and preparation.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Solutions Prose Chapter 2 The Night the Ghost Got in
English Subject experts who are having max years of experience prepared this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 10th English Prose Chapter 2 The Night the Ghost Got in Questions and Answers. They have explained all the topics covered in the board prescribed latest syllabus in a simple way to understand easily. So, students can prepare Chapter 2 English from this Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Book Questions and Answers PDF. Download the Tamilnadu State Board 10th English Chapter 2 The Night the Ghost Got in Workbook Solutions PDF by accessing the below links and learn properly for the final exams to score well.
The Night the Ghost Got in warm up:
Use the following tongue twisters in a ‘Game of Telephone: where each student whispers the phrase to the next. The student who finishes the last says it aloud to the class. Let the students fill in the table given with what they listen to. They can get the help of their teacher
- Six sleek swans swam swiftly southwards.
- Four furious friends fought ur the phone.
- Green glass globes glow greenly.
- Six slimy snails sailed silently.
- Scissors sizzle, thistles sizzle.
- He threw three free throws.
- Tommy Tucker tried to tie Tammys Turtles tie.
- I wish you were a fish in my dish.
- Five frantic frogs fled from fifty fierce fishes.
- black bugs bleed blue black blood but baby black bugs bleed blue blood.
- Red blood blue blood
- Fresh registration… Fresh registration
- She sells seashells at the seashore
- Fred fed Ted bread, and Ted fed Fred bread
 Answer:
Answer:

I hope you ended with a delightfully tangled whole new tongue twisters.
The Night the Ghost Got in InText Questions
a. Where was the author when he heard the noise?
Answer:
The author had just stepped out of the bathtub, when he heard the noise.
b. What did the narrator think the unusual sound was?
Answer:
At first, he thought it was his father or his brother Roy. Next, he suspected that it was a burglar. Later on, he thought that it was a ghost.
c. What were the various sounds the brothers heard when they went downstairs?
Answer:
The brothers heard like a man running and started up the stairs towards them. They thought that they were coming two at a time. They saw nothing, but only heard the steps.
d. Who were the narrator neighbors?
Answer:
The narrator’s neighbors were a retired engraver named Bodwell and his wife.
e. How did the Bodwells react, when a shoe was thrown into their house?
Answer:
Mr. Bodwell was shouting, frothing a little and shaking his fist. Mrs. Bodwell wanted to sell their house and go back to Peoria. For some years, he had been in a bad way and was subjected to mild attacks.
f. What did the Bodwells think when they heard the mother shout?
Answer:
Bodwell thought that there were burglars in his house when they heard the mother shout.
g. What was the grandfather wearing?
Answer:
The narrator’s grandfather was wearing a long flannel nightgown over long woollen pants, a nightcap and a leather jacket around his chest.
h. What conclusions did grandfather jump to when he saw the cops?
Answer:
His grandfather was going through fits where he believes he is in the war. He thinks that General Meade’s men are deserting under fire from Stonewall Jackson.
i. Were the policemen willing to leave the house?
Answer:
No, the policemen were not willing to leave without getting their hand on somebody besides grandfather.
j. What made the reporter gaze at the author?
Answer:
The author had put on one of his mother’s dress, as he couldn’t find anything else. The reporter looked at him with mingled suspicion and interest.
The Night the Ghost Got in Textual Questions
A. Answer the following questions in a sentence or two.
The Night The Ghost Got In Questions And Answers Question 1.
Why was the narrator sorry to have paid attention to the footsteps?
Answer:
The imagination of the ghost getting into his house lead to a commotion. It caused his mother to throw a shoe through a window of the neighbouring house. It ended with his grandfather shooting a policeman. So the narrator was sorry to have paid attention to the footsteps.
The Night The Ghost Got In Summary Question 2.
Why did Herman and the author slam the doors?
Answer:
Herman and the author slammed the doors because they thought that someone was coming up their stairs. They were scared as they heard the steps of someone.
10th English Unit 2 Prose Question Answer Question 3.
What woke up the mother?
Answer:
The slamming of the doors had awakened their mother.
10th English The Night The Ghost Got In Question Answer Question 4.
What do you understand by the mother’s act of throwing the shoe?
Answer:
His mother enormously fancied the thrill of throwing a shoe through a glass window of her neighbour. She is a highly excitable woman.
The Night The Ghost Got In Question 5.
Why do you think Mrs. Bodwell wanted to sell the house?
Answer:
Mrs. Bodwell wanted to sell the house, as she wanted to go back to Peoria, due to the frequent mild attacks.
10th English The Night The Ghost Got In Question 6.
How did the cops manage to enter the locked house?
Answer:
The cops managed to enter the locked house by breaking the glass of the front door.
The Night The Ghost Got In Paragraph Question 7.
Why were the policemen prevented from entering grandfather’s room?
Answer:
The policemen were prevented from entering into grandfather’s room because the narrator realized that it would be bad if they do so. His grandfather was going through a phase, in which he believed that General Meade’s men were beginning to retreat. They were under the control of Stonewall Jackson.
The Night The Ghost Got In Pdf Question 8.
Who used the zither and how?
Answer:
Zither was used by the guinea pig to sleep on it. It would never sleep anywhere except on the zither.
Question 9.
Mention the things that the grandfather imagined.
Answer:
His grandfather imagined that the cops were deserters from Meade’s army. He thought that they were trying to hide away in his attic.
Additional Questions
Question 1.
Who is Mr. Bodwell?
Answer:
Bodwell is Thurber family’s neighbour, a retired engineer. He is “subject to mild ‘attacks,’” like most people whom the family knows.
Question 2.
How does Mr. Bodwell react to the shoe thrown by Mrs. Thurber?
Answer:
When the narrator’s mother throws a shoe through the Bodwells’ window and says there are burglars in the house, Bodwell is momentarily confused, thinking that the burglars are in his house, before understanding the truth and alerting the police.
Question 3.
Who is the only cop referred by name and what does he do?
Answer:
The only policeman referred to by name is Joe. He examines an old zither with another policeman.
Question 4.
Why does Joe mock the policeman who wants to retrieve his gun from the grandfather?
Answer:
When the policeman talks bravely about going to retrieve his gun from the grandfather, Joe mocks him because he feels it’s dangerous to approach an armed and unstable suspect.
Question 5.
Who is Herman? Comment on his personality.
Answer:
Herman is the brother of the narrator, James Thurber. He generally sleeps uneasily, always fearful that something might come and “get him” in the night. When the narrator wakes him and he hears the sounds in the dining room, he runs back into his room and slams the door showing what a timid boy he can be.
Question 6.
Who is the Zither-cop? Why is he called so?
Answer:
One of the policemen who search through the house finds an old zither and strums it in curiosity. The story later refers to this officer as “Zither,” as well as “the zither- cop.”
Question 7.
Why were the policeman prevented from entering grandfather’s room?
Answer:
The zither-cop was shot at by the grandfather because he was the first to go up the stairs when they heard the sound of a creaking in the attic caused by the grandfather turning in the bed.
B. Answer the following questions in about 100-150 words.
Question 1.
Describe the funny incident that caused the confusion in the house.
Answer:
James, the author comes out of the bathroom, drying him she dining table. He wakes up his brother Herman. They both listen to the footsteps and gets scared. Their mother wakes up. When she comes to know lf. At that moment, he hears the footsteps of someone walking downstairs near the she alerts her neighbour to call the police. The police arrive with some reporters.
They search all over, upstairs and downstairs. When they find nothing, they rush to the attic. The narrator’s grandfather believes that he is still in the war. He thinks that the policemen are deserters. So he starts shooting at them. The policemen leave their house immediately, creating a lot of confusion everywhere.
Question 2.
Narrate the extensive search operation made by the policemen in the house.
Answer:
The police were on hand in a commendably short time. They began banging at the narrator’s front door. When nobody responded, they broke into the house. They searched downstairs and upstairs messing up everything. They opened all the doors and windows. They pulled the drawers and furniture. They began to ransack the floor, pulled beds away from the walls, tore clothes off the hooks in the closets.
They also pulled suitcases and boxes off the shelves. Later, they heard some creaking in the attic. They stepped into the attic. As his grandfather thought that they were the deserters from Meade’s army, so he started shooting at them. Then he went back to bed. The cops were unwilling to leave without getting their hand on somebody. They felt it was a defeat for them. They began to poke into things again and finally left the place.
Additional:
Question 1.
What do you know about James Thurber, the narrator?
Answer:
The narrator James Thurber, presents himself as acting judiciously, although his actions are uncommon to raise the uncertainties of the policemen. He is the first person in the household to hear the mysterious sound, as he is stepping out of the bathtub at 1:15 a.m. on November 17th. After waking his brother Herman, he is the one who resolves that the reason of the sound downstairs must be an apparition.
When his hasty mother decides that the sounds must be caused by intruders, the narrator thinks that she is past reasoning. Even when the cops arrive, he is still wrapped in a towel from his bath. Later, when the reporter comes around asking questions, the narrator puts on one of his mother’s blouses, explaining that it is the only thing that he can find at the moment.
He chooses to be honest with the reporter and tell him that the problem was caused by ghosts, but the reporter does not take him earnestly. Later, when the policeman who has been shot by Grandfather wants to challenge him and take his gun back, the narrator mediates with composed receptivity and offers to take the gun over to the police station in the morning.
“A judicious reticence is hard to learn, but it is a lifetime lesson.”
Question 2.
What is the theme of the story, ‘The Night the Ghost got in’ by James Thurber?
Answer:
The theme of the story, ‘The Night the Ghost got in’ by James Thurber is surely of a supernatural kind. This story asks readers to accept the existence of the ghost mentioned in the title as a believable one. Many a time, ghost stories offer readers a sign for a common explanation for the events that the characters themselves trust are triggered by the bizarre scenario.
Although it seems very unlikely that a real ghost would have generated a commotion in the house, Thurber gives readers distressing indication that the sounds that he heard were undeniably supernatural. For example, the police thoroughly investigate the house and say that all the doors and windows are locked from inside and nothing in the house is said to have been taken by burglars. The father and brother Roy, who are at first expected do have come home from Indianapolis early, do not feature in the play and are just characters mentioned during conversations.
“The human mind delights in grand conceptions of supernatural beings.”
Question 3.
Bring out the character of the grandfather and the mother in the lesson, ‘The Night the Ghost got in’.
Answer:
The narrator’s grandfather is an old- timer of the Union army of the Civil War, which terminated about fifty-two years ago. His bedroom is in the attic. When the police come to the house to search for the burglar, the grandfather thinks that they are militaries who are abandoning because they are losing to the South. The grandfather calls them “cowardly dog” and “lily-livered cattle” and then fetches a policeman’s holster and shoots a man with his own gun.
The police retreat, terrified of the irrational old man but at the breakfast table the next morning, Grandfather seems impeccably conscious of the previous night’s situation, asking why so many police had been “tanyhootin” around the house. On the contrary, the narrator’s mother, Mrs Thurber is a highly excitable woman, scatter brained yet practical at times.
Hearing a sound in her house and suspecting a burglar, she thinks of the clever plan of alerting Mrs and Mr. Bodwell the neighbours by throwing a shoe through his closed window. After he goes to alert the police, she considers throwing the matching shoe, a thrill and fanciful act. She is surprised to hear that Grandfather has shot a policeman, not because of the courageous ferocity of the act, but because the cop was such a nice-looking young man.
“Great powers don’t get angry Nor do they act in haste!”
Vocabulary:
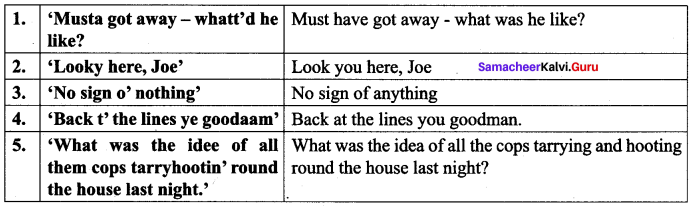
C. Look at the following expressions from the text. With the help of your teacher rewrite them in standard English. One has been done for you.

Answer:
D. Complete the given tabular column with the suitable plural forms.
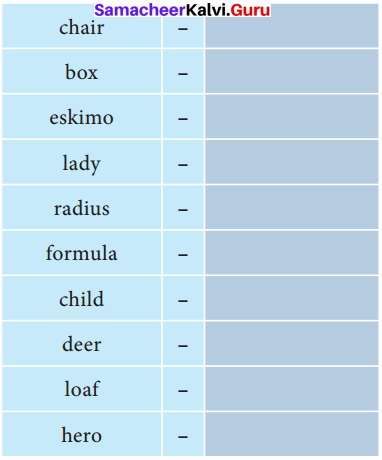
Answer:
Listening Activity:
E. Listen to the story and answer the following.
A Short Story : Three Simple Rules This Short Story Three Simple Rules is quite interesting to all the people. Enjoy reading this story. Once there was a rich man in Thailand. His name was Chulong. He was a very rich man. Yet he wanted more riches, more money. One day he was walking in his garden. He saw a strange bird in a bush. It was very small. But it had very beautiful and colorful features. Its voice was also very sweet. Chulong had never seen such a bird in his life. He slowly went near the bush unseen. He caught the bird. Now the bird began to speak.
“Why have you caught me?” the bird asked. “I want to make money. I can sell you for a big amount,” replied Chulong. “But you are already rich. Why do you want more?” asked the bird. “Because I want to become richer and richer,” replied Chulong. “But do not dream of making .
money through me!” said the bird. It further added, “You cannot sell me. Nobody will buy me, because, in imprisonment, I lose my beauty and my sweet voice.” Then it slowly turned into a black bird. The beautiful features were now looking like the feathers of a crow. Chulong hopes of making money were shattered. He said angrily, “I will kill you, and I will eat your meat.” “Eat me! I am so small. You will not get any meat out of me,” replied the bird.
Chulong could not answer. The bird then suggested, “Well set me free. In return I shall teach you three simple but useful rules.” “What is the use of the rules? I want only money,” said Chulong. He was irritated. “But these rules can profit you greatly,” added the bird. “Profit me! Really? Then I shall set you free. But how can I trust you? You may fly away,” said Chulong. “I give you my word. And I always keep my word,” said the bird. Chulong wanted to take a chance.
He released the bird. It flew up at once. Then it sat on the branch of a tree. Its color started changing. It became beautiful again. Chulong asked, “Now teach me the rules.” “Certainly,” said the bird. Then it added, “The first rule is Never Believe everything others say. The second rule is Never be sad about something you do not have. The third rule is Never throw away what you have in your hand.” “You silly bird,” shouted Chulong. And he added, “These three rules are known to everyone.
You have cheated me.” But the bird said, “Chulong, just sit down for ” a while. Think about all your actions of today. You had me in your hands, but you threw me away (released me). You believed all that I said. And you are sad about not having me. The rules are simple. But you never followed them. Now do you see the value of the rules?” so saying the bird Threw away and disappeared from his sight.
Question 1.
The rich man was from
(a) Nagaland
(b) Thailand
(c) Finland
Answer:
(b) Thailand
Question 2.
Where did Chulong catch the bird?
Answer:
Chulong caught the bird in a bush in his garden.
Question 3.
Why did Chulong catch the bird?
Answer:
Chulong caught the bird because it was strange and small and would surely fetch him good •money.
Question 4.
What will happen to the bird in imprisonment?
Answer:
The bird in imprisonment will lose its beauty and sweet voice.
Question 5.
What did the bird suggest Chulong, in exchange for its freedom?
Answer:
The bird in exchange for its freedom suggested to Chulong three simple, yet useful rules.
Question 6.
Does Chulong want to earn money honestly?
Answer:
No, he did not want to earn money honestly.
Question 7.
What were Chulongs plans for the bird?
Answer:
Chulong wanted to sell the bird and earn good money.
Question 8.
Who is wise according to you?
Answer:
The bird is wise according to me.
Question 9.
Is the bird a crow?
Answer:
No, the bird isn’t a crow.
10. What are the three rules given by the bird?
Answer:
The three rules given by the bird are:
- Never believe everything others say.
- Never be sad about something you do not have.
- Never throw away what you have in your hand.
Speaking Activity
F. Quiz: Who am I ?
Sample questions to ask. Answers must be ‘yes’ or ‘no’ only.
- Are you a male (female)?
- Are you young (old)?
- Are you a famous personality?
- Are you alive now?
- Are you a singer (dancer, actor)?
- Does your name start with ‘……………’ ?
- Are you a historical figure?
- Is he/she ………………. ?
G. Use this passage to play the game. You can collect information on other famous personalities and play too.

Charlie Chaplin was bom on April 16, 1889, in London England. His birth name was Charles ‘ Spencer Chaplin, though he had many nicknames growing up such as Charlie, Chariot, and The Little Tramp. His father, Charles Chaplin, and his mother, Hannah Chaplin, were inducted into the music hall of fame, leading the way to his exposure even as a young boy.
His first on stage moment was when he was 5 years old; he sang a song that was intended to be sung by his own mother; she had become ill at the time of the performance, so little Charlie Chaplin stood instead and performed for his mother. Charlie Chaplin came to the United States in 1910, at the age of 21. He was brought to New York, which was known to be a great place to start out for anyone trying to become a professional actor. Two years later, in 1913, Chaplin signed his very first contract at Keystone and it was no time before he headed to Hollywood. His first movie premiered in 1914, “Making a Living,” and went on to make over 35 movies total in that year alone.
Charlie Chaplin grew to become one of the most popular and successful actors of all time. The moment that really kicked off his long career was in 1921 when he starred in, and produced, his first full length film called “The Kid.” From then on, most people all over the world knew Charlie Chaplin and loved his movies. He had a great career and life, dying on December 25, 1977, in Vevey, Switzerland. He had apparently died of natural causes in his sleep from old age.
Give Answers:
Is the personality a female character? No
Is he a political figure? No
Is he from the Film Industry? Yes
Is he a comedian? Yes
Is he from India? No
Is the person alive? No
Is he an artist from his childhood? Yes
Reading:
H. Read the following incident carefully to answer the questions that follow.
The tie that does not bind
“Oh, so you’re going abroad? Can you bring me back ?” I’ve been asked to bring back a vaccine for a course. Once I searched the suburbs of Paris for two days for a special brand of ceramic paint. Having spent a lot of money for Cartier lighter refills, I had them confiscated at the airport just before boarding because the gas might be dangerous in the air.
Now, two months before a trip, I stop talking to people so they won’t suspect I’m about to travel. But someone always catches me.” I’ve heard you’re going to New York, and I want you to get something for me. It’s just a little thing you can find anywhere. I don’t know exactly how much it costs, but it shouldn’t be much. We’ll settle up when you get back”.
What Gilson asked me to buy was, in fact a little thing: a tie. But not just any tie. He wanted a tie with a small embroidered G. Any colour would do, as long as it had his initial. Look , this is a special flight, I explained . We are only staying Saturday through Tuesday. On the day we arrived I didn’t have time to think about the tie, but strolling around on Sunday I did see ties bearing various letters in more than one shop window. They were cheap, just a dollar, but all the shops were closed.
On Monday, lunch lasted the whole afternoon. Then it was Tuesday morning, time to leave. It was only when I saw our airport bus waiting outside the hotel that I remembered the tie. I told the group to go on. I would get a taxi to the airport. And so I went in search of a nearby shop where I had seen ties.
But I couldn’t find it. I walked further down the street-one, two, three blocks – all in vain. Back at the hotel, a bit anxious now, I took my suitcase, got a taxi and asked the driver to rush to the street where I had seen them. The driver stopped at each shop we passed so I could look from the window.
The stores had all sorts of ties, but not the kind I was looking for. When I finally thought I had located the right shop, I decided to go in and check. The driver refused to wait. Parking was prohibited, he said. I promised to double the fare, jumped out and ran into the shop. Was I going to miss the plane just for a damned tie?
The salesman was unbearably slow. When I realized that the smallest change I had was a ten dollar note , I grabbed ten ties of different colours so I wouldn’t have to wait for change. I rushed out with the ties in a paper bag. On the street I looked around. The taxi had vanished, taking my suitcase. What is more, I was going to miss the plane.
I ran to the comer, and hope flared up again: the taxi was waiting in the next street. Quick to the airport! As I settled down inside the taxi. I sighed with relief. Gilson was going to have enough initialized ties to last him a lifetime.
When I reached the airport, I paid the taxi driver the double fare and grabbed my suitcase. Panting, I boarded the plane under the reproachful gaze of the other passengers, all primly seated with their seat belts fastened. Ready to take off. Departure had been delayed because of me.
“At least I hope you found your tie”, said one who knew the story.
“I did”, I answered triumphantly.
After making myself comfortable, I reached for the paper bag to show the ties.
I had left it behind; in the taxi.
Question 1.
What was the writer always asked to do whenever he planned to go abroad?
Answer:
Whenever the writer planned to go abroad, he was always asked to buy something or the other like a vaccine for a course, a special brand of ceramic paint, Cartier lighter refills and so on.
Question 2.
What did Gilson want the writer to bring for him?
Answer:
Gilson wanted the writer to bring a tie with a small embroidered G on it.
Question 3.
When did the writer remember the fact that he had to buy something for Mr. Gilson? The writer remembered the fact that he had to buy
Answer:
something for Mr. Gilson only on Tuesday when it was time to leave.
Question 4.
Why were the other passengers in the flight gazing at the writer?
Answer:
The other passengers in the flight gazed at the writer since the flight was delayed because of him.
Question 5.
What is the humour element in the above incident?
Answer:
The humour element in the above accident is that after all the frantic search for the tie and purchasing ten of them to avoid the trouble of getting back the change, the writer had left it – behind in the taxi for which he had also paid double the fare.
I. Suggesting titles.
Title summarises the story. Each paragraph is a part of the story. Look at the following expressions and find out the paragraphs that best suit these expressions.
- Oh, No! But it happens! Paragraph 1
- Don’t let out your travelling dates Paragraph 2
- Anyway, people will be people Paragraph 3
- Search begins Paragraph 6
- Things are not that easy Paragraph 7
- Hurry invites worry Paragraph 10
J. Look at the following situations the writer was in. He could have avoided the situation and saved himself. Glance through the write up again and comment on what the writer should have done in the following situations.
1. Gilson asked the writer to bring a tie.
He should have politely refused stating it was a business trip.
2. On the day of arrival, the writer had no time to think about the tie.
The writer should not have felt guilty since he was busy.
3. The writer remembered about the tie when the bus was leaving for the airport.
He should have stopped being courteous and proceeded to the airport with others.
4. The writer walked down in search of the shop.
When he couldn’t find the shop with ties he was looking for, he should have not searched for it in other shops.
5. The writer rushed out with the tie in a paper bag.
The writer should have kept the paper bag inside his suitcase as soon as he got into the taxi.
K. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The narrator searched for three days to buy ceramic paint. [False]
- The author was going to New York. [True]
- Gilson asked the narrator to buy a tie. [True]
- The taxi driver took away the narrator’s suitcase. [False]
- Departure was delayed because of the author. [True]
- The author left the ties in the taxi. [True]
M. Write a speech for your school Literary Association celebration with the given lead.
Writing:
Good morning to one and all present here, it is indeed my privilege to stand before you as the Secretary of the Literary Association. It was formed to stimulate and motivate the young minds to perform challenging activities and become good orators, dramatists, poets and also be short story writers. The purpose is mainly to enhance the literary, aesthetic and communicative skills among students. You are the pillars of the future society. The advancement of the society lies in your hands.
Communication skills is vital for the development of an individual or a society. Thereby, every year informative programmes are conducted to enhance the language skills and dramatic talents. Students are provided a platform to nurture and exhibit their innate potentials. We request you to unleash the hidden potentials and bring out the latent abilities. Explore the world around and experience a different environment. I am sure, each one of you will have a story to share about the learning experiences in this Literary Association. Wishing you a challenging journey for a lifetime experience. Thank you.
Grammar:
A. Na’garajan and Dhanalakshmi want to buy a new house. They have come to see a house for sale. Complete the conversation below by adding a, an or the.
Nagarajan : Well, here we are, No. 8, Kaveri Street. I think this is …………………. (a)…………… house we saw online. What do you think of ………….. (b) ………….. location?
Dhanalakshmi : It is in …………….. (c) ……………….. nice neighbourhood. And it’s close to the railway station.
Nagarajan : And …………….. (d) …………….. bus stop is not too far away
Dhanalakshmi : How many rooms are there?
Nagarajan : There are three rooms, ………………….. (e) kitchen and ……………….. (f) …………………balcony.
Dhanalakshmi : There is ………………….. (g) ………………. lawn behind ………….. (h) …………………. house, right?
Nagarajan That’s right …………….. (i) ……………….. lawn is actually quite large. Did you see any photos of ……………… (j) ……………….. living room, online? What does it look like?
Dhanalakshmi : …………………. (k) ………………… living room looks great. It looks bright and airy. It has …………………. (l) …………………. nice view of ………………… (m) ………………… hills. But …………….. (n) …………. kitchen looks ……………… (o) …………….. little small.
Nagarajan : And, I remember you said there isn’t …………… (p) ………….. store room, right?
Dhanalakshmi : No, but there is …………… (q) …………… attic, where we can store things.
Nagarajan : I hope this house is ……………(r) ……………. better option.
Dhanalakshmi : let’s wait for …………(s) ……………….. real estate agent. She said, she would be here at three o’clock.
Nagarajan : Look there she is!
Answers:
(a) the, (b) the, (c) a, (d) the, (e) a, (f) a, (g) a, (h) the, (i) The, (j) the, (k) The, (l) a, (m) The, (n) the, (o) a, (p) a, (q) an, (r) a, (s) the
B. Few articles are missing in the given passage. Edit the passage given below by adding suitable articles wherever necessary.
My neighbourhood is very interesting place. My house is located in apartment building downtown near many stores and offices. There is small supermarket across street, where * my family likes to go shopping. There is also post office and bank near our home. In our neighbourhood there is small, Green Park where my friends and I like to play on weekends and holidays. There is small pond near park and there are many ducks in park. We always have great time. In addition there is elementary school close to our home where my little brother studies in third grade. There are so many things to see and do in my neighbourhood that’s why I like it. It’s really great place.
Answer:
My neighbourhood is a very interesting place. My house is located in an apartment building downtown near many stores and offices. There is a small supermarket across the street, where my family likes to go shopping. There is also a post office and a bank near our home. In our neighbourhood there is a small, Green Park where my friends and I like to play on weekends and holidays. There is a small pond near the park and there are many ducks in the park. We always have a great time. In addition there is an elementary school close to our home where my little brother studies in third grade. There are so many things to see and do in my neighbourhood. That’s why I like it. It’s really a great place.
C. Refer to the dictionary to find out the meaning of the following prepositions and match them with the correct meaning.
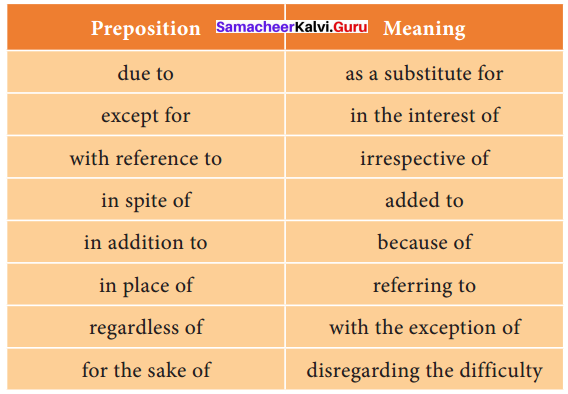
D. Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate prepositional phrase from the given options.
1. Everything falls to the ground …………………. earth’s gravitational pull.
(a) in addition to
(b) because of
(c) cause of
Answer:
(b) because of
2. The trial was conducted ………………. the procedure of law.
(a) in accordance with
(b) due to
(c) despite of
Answer:
(a) in accordance with
3. There is a temple right …………. my house.
(a) in back of
(b) apart from
(c) in front of
Answer:
(c) in front of
4. As a ……………….. of his hard work, he achieved the target.
(a) instead of
(b) result of
(c) apart from
Answer:
(b) result of
5. Failure is often the ………………. negligence.
(a) effect of
(b) consequence of
(c) reason of
Answer:
(b) consequence of
6. Children are given toys ………………. sweets on Children’s day.
(a) on top of
(b) in addition to
(c) due to
Answer:
(b) in addition to
7. The parents must be informed …………………… any indiscipline conduct of their wards.
(a) because of
(b) in case of
(c) in spite of
Answer:
(b) in case of
8. He didn’t turn up ……………………… his busy schedule.
(a) consequence of
(b) due to
(c) except for
Answer:
(b) due to
9. Global warming is ……………………. the green house emission.
(a) an effect of
(b) in spite of
(c) in addition to
Answer:
(a) an effect of
10. ……………… several warnings, he continued to swim.
(a) due to
(b) in spite of
(c) because of
Answer:
(b) in spite of
E. Edit the following passage by replacing the underlined incorrect words with correct prepositional phrases.
1. Janu is studying in class X. In the event of the teachers.
According to the teachers, Janu is studying in Class X.
2. she is a disciplined student. In addition to her poverty, she …………….. .
In spite of her poverty, she is a disciplined student.
3. is always neat. Many students like her in case of …………….. .
Because of her neatness, many students like her.
4. her simplicity. According to her studies, she also ………………. .
Apart from her studies, she is also known for her simplicity.
5. participates in sports. She gets on with everyone in case of ………….. .
She gets on with everyone in spite of her participation in sports.
6. age and gender in the school. In opposition to taking leave, she ensures …………….. .
Due to her opposition to take leave, she ensures her age and gender in the school.
7. that she completes the work given before she goes to school next day.
On account of completing the work given before, she goes to school the next day.
The Night the Ghost Got in by James Thurber:
James Thurber was born on December 8, 1894, in Columbus, Ohio. He was an American cartoonist, author, humourist, journalist, playwright, and celebrated wit. He worked for the New Yorker from 1927 to 1933 and continued contributing stories and drawings to it for the rest of his life, becoming one of America’s most treasured humourists. He was best known for, “The Catbird Seat”. As the sight in Thurber’s good eye failed, his literary production dwindled. Thurber fell into alcoholism in his later years and died of pneumonia following a stroke on November 2, 1961.
The Night the Ghost Got in Summary:

Introduction:
Imagination of odd things leads to absolute humourous drama making everybody confused. This story makes us laugh at the confused family members whose imagination creates a chaos ultimately for nothing that made everyone spend a sleepless night. Let us enjoy the sequence that happened inside a house due to each persons’ different imaginations.

Confusion over foot steps:
The narrator, James Thurber, comes out of his bathtub in the bathroom at 1:15 a.m. in the morning, on November 17th, 1915 and hears footsteps going round and round the dining room, downstairs. At first, James thinks the footsteps might belong to his father and brother Roy, who had been traveling in Indianapolis and were supposed to be back late in the evening. James quickly realizes that it isn’t his father and brother.

Brother Herman Wakes Up
After a few minutes, he fears something strange and goes to wake up his brother, Herman. Waking up all of a sudden in the middle of the night, Herman is frightened to know of someone downstairs as stated by his brother. He goes back to bed, slamming the door.

Mother’s fear for Burglar’s
The slamming of the door makes their mother come out of her room. The mother asks them about the footsteps she has heard and then comes to the conclusion that there are burglars inside their house.

Agitated neighbours
As the telephone is in the dining area, she plans to contact the police through her neighbour and throws a shoe through the window of the Bodwell’s. They are cross with her behavior. However, Mr.Bodwell mistakes for burglars in his house. The confusion is cleared and he calls the police and tells them about the burglars in Thurber house.

Arrival of Police
A whole lot of police in a Ford Sedan, two on motorcycles, and a patrol wagon with about eight policemen and a few reporters creates more chaos and confusion. They call out for the inmates and when no one responds, they break in. They find the narrator upstairs with a towel round his waist and the mother who is certain of burglars in the house. Though all doors and windows are bolted from inside, to justify their trip, the police set about searching the house, moving furniture and cleaning closets.

Police are suspicious
At one point, a policeman’s inquisitiveness gets the best of him, and he points out a rare old musical instrument, a zither, to another officer. The narrator adds to the confusion with the inadequate information about the family’s old guinea pig which used to sleep on the zither. The police are suspicious of this strange family.

Grandfather’s obsession
Just when the police decide to retire, the narrator’s grandfather sleeping in the attic makes a slight noise and the policemen spring into action. They race upstairs to catch the culprit. The narrator knows that this will lead to worry because his grandfather thinks that the Civil War is still going on. Grandfather is obsessed with the retreat of the army under General George Meade. When the policemen arrive at his door, he is convinced that they are Meade’s army. He calls them cowards and tells them to go back to the battle.

Grandpa shoots a Policeman
Grandpa slaps one of the policemen across the back of the head, sending him to the floor and as the others leave their fallen companion and run away, he takes the man’s gun from his holster and shoots at him, hitting him in the shoulder. He fires twice more and then goes back to bed. Back downstairs, the police are upset that there is nobody to arrest, but they are not willing to go back to the attic and risk being shot at. The wounded officer’s shoulder is bandaged and they start looking around the house \ again.

Reporter gazes at narrator’s stupidity
A reporter approaches the narrator who is wearing one of his mother’s outfit since he doesn’t find his nightdress. When the reporter asks him about the commotion, the narrator admits the presence of ghosts in the house. It is indeed a comedy, when the narrator’s mother is informed about Grandfather shooting a policeman and she is concerned about a nice-looking young man being shot at.

Unraveled Mystery
The next morning, the grandfather comes down for breakfast looking cheery. James, Herman, and their mother all think that the grandfather has forgotten the whole scene. However, the story ends with the grandfather asking, with a smirk on his face, what on earth the police had been doing raiding the house the night before. He chided them that none of them left a bottle beside his head and told them that they did not realize how hard it was for a thirsty man to look for water in the dining room. Now the family had him there; it was the grandpa who was going around the dining room last night.

Conclusion:
This story thus ended as a humourous drama, each one assuming that there is a ghost, a burglar and Meade’s army men inside the house. Author has sequenced the scenes as a lively comedy show that one will roar with laughter at the stupidity of each person in the story.

The Night the Ghost Got in Glossary:
Textual:


Additional:
Synonyms:
Choose the most appropriate synonym of the underlined word.
1. ‘Burglars!’ she shouted, intuitively.
(a) intentionally
(b) thoughtfully
(c) knowingly
(d) instinctively
Answer:
(d) instinctively
2. ‘He thinks you’re deserter.’
(a) absconder
(b) camel
(c) convict
(d) dessert-monger
Answer:
(a) absconder
3. ‘Nothing.’ he said, gruffly.
(a) sadly
(b) grievously
(c) angrily
(d) carefully
Answer:
(c) angrily
4. ‘Open up!’ cried a hoarse voice.
(a) sharp
(b) haughty
(c) soft
(d) trough
Answer:
(d) rough
5. ‘What’s that?’ snapped Joe.
(a) retorted
(b) smiled
(c) mocked
(d) photographed
Answer:
(a) retorted
6. A board creaked, when it was trod upon.
(a) weary
(b) worn
(c) walked
(d) opened
Answer:
(c) walked
7. A half-dozen policemen emerged out of the darkness.
(a) appeared
(b) exit
(c) charged
(d) jumped
Answer:
(a) appeared
8. A reporter, a thin-faced, wispy man, came up to me.
(a) considerable
(b) significant
(c) substantial
(d) delicate
Answer:
(d) delicate
9. Before I could intervene, the cops were in the attic.
(a) interfere
(b) interrogate
(c) instigate
(d) investigate
Answer:
(a) interfere
10. Finally the cops broke the thick bevelled glass.
(a) rough
(b) thin
(c) oblique
(d) hovelled
Answer:
(c) oblique
11. Five or six cops sprang for the attic door.
(a) leaped
(b) water
(c) spring
(d) sprout
Answer:
(a) leaped
12. Flashlights shot streaks of gleam up and down the walls.
(a) glows
(b) signals
(c) strains
(d) splashes
Answer:
(d) splashes
13. Glass tinkled into the bedroom.
(a) jingled
(b) placed
(e) tinged
(d) sparked
Answer:
(a) jingled
14. Grandfather had evidently jumped to a conclusion.
(a) immediately
(b) earnestly
(c) obviously
(d) drastically
Answer:
(c) obviously
15. He gazed at me a long time.
(a) gawked
(b) stared
(c) glared
(d) shouted
Answer:
(b) stared
16. Herman looked at me in some alarm.
(a) apprehension
(b) excitement
(c) intuition
(d) bell
Answer:
(a) apprehension
17. Herman rushed to his room’and slammed the door.
(a) altered
(b) banged
(c) sliced
(d) dug
Answer:
(b) banged
18. Herman ventured out of his room.
(a) volunteered
(b) venerated
(c) visioned
(d) vagaries
Answer:
(a) volunteered
19. I can see their viewpoint – phony.
(a) deceptive
(b) sounding
(c) clear
(d) phonetic
Answer:
(a) deceptive
20. T could hear a rending of wood.
(a) shredding
(b) breaking
(c) rubbing
(d) rushing
Answer:
(a) shredding
21. I could see the faint shine of plates on the plate-rail.
(a) tired
(b) feeble
(c) weary
(d) track
Answer:
(b) feeble
22. I gripped his arm.
(a) cut
(b) grieved
(c) grasped
(d) damaged
Answer:
(c) grasped
23. I prevented her.
(a) legitimate
(b) prohibited
(c) presumed
(d) deserted
Answer:
(b) prohibited
24. I suspected next that it was a burglar.
(a) alerted
(b) blamed
(c) called
(d) doubted
Answer:
(d) doubted
25. Instantly the steps began again.
(a) blatantly
(b) callously
(c) suddenly
(d) definitely
Answer:
(c) suddenly
Antonyms:
Choose the most appropriate antonym of the underlined word.
1. Imagination of odd things always leads to absolute humour.
(a) tragedy
(b) beauty
(c) comedy
(d) danger
Answer:
(a) tragedy
2. The ghost raised such a hullabaloo of misunderstandings.
(a) misinterpretation
(b) calculations
(c) silence
(d) tumult
Answer:
(c) silence
3. Its advent caused my mother to throw a shoe.
(a) initiation
(b) departure
(c) calmness
(d) dawn
Answer:
(b) departure
4. They began about a quarter past one o’clock in the morning.
(a) started
(b) culminated
(c) culminated
(d) brought
Answer:
(b) culminated
5. My mother was asleep in one room upstairs.
(a) lethargic
(b) brimming
(c) awake
(d) dozing
Answer:
(c) awake
6. The old walnut bed, you will remember, fell on my father.
(a) agree
(b) blame
(c) forget
(d) daring
Answer:
(c) forget
7. They were the steps of a man walking rapidly.
(a) forcibly
(b) speedily
(c) hurriedly
(d) leisurely
Answer:
(d) leisurely
8. The steps kept going round and round at regular intervals.
(a) unvarying
(b) irregular
(c) consistent
(d) reckless
Answer:
(b) irregular
9. It did not enter my mind until later that it was a ghost.
(a) fixture
(b) earlier
(c) advanced
(d) latter
Answer:
(b) earlier
10. The steps had ceased.
(a) stopped
(b) seized
(c) begun
(d) terminated
Answer:
(c) begun
11. The slamming of the doors had aroused mother.
(a) dampened
(b) below
(c) above
(d) finite
Answer:
(a) dampened
12. ‘What was all that running around downstairs?’ said mother.
(a) stairway
(b) attic
(c) dining
(d) upstairs
Answer:
(d) upstairs
13. Bodwell was subject to mild ‘attacks’.
(a) trivial
(b) serious
(c) insignificant
(d) meagre
Answer:
(b) serious
14. The police were on hand in a commendably short time.
(a) laudably
(b) outrageously
(c) committedly
(d) admirably
Answer:
(b) outrageously
15. They came in a patrol wagon with a few reporters.
(a) meagre
(b) limited
(c) many
(d) scarce
Answer:
(c) many
16. Finally the cops put their shoulders to our big heavy front door.
(a) light
(b) substantial
(c) hefty
(d) dense
Answer:
(a) light
17. He believed that General Meade’s men, were beginning to retreat.
(a) rejoice
(b) advance
(c) evacuation
(d) withdrawal
Answer:
(b) advance
18. The; cops were reluctant to leave.
(a) indisposed
(b) settle
(c) keen
(d) lazy
Answer:
(c) keen
19. The night had been distinctly a defeat for them.
(a) victory
(b) setback
(c) conquest
(d) destiny
Answer:
(a) victory
20. The reporter was a thin-faced, wispy man.
(a) fine
(b) flimsy
(c) thin
(d) substantial
Answer:
(d) substantial
We hope the data given here will benefit you to the fullest extent at the time of preparation. For better understanding of English subject this Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Solutions for Class 10th English Prose Chapter 2 The Night the Ghost Got in PDF is the best resource. Download & ace up your preparation. Keep in touch with us and get the latest information on Tamilnadu State board Textbook Solutions PDF.