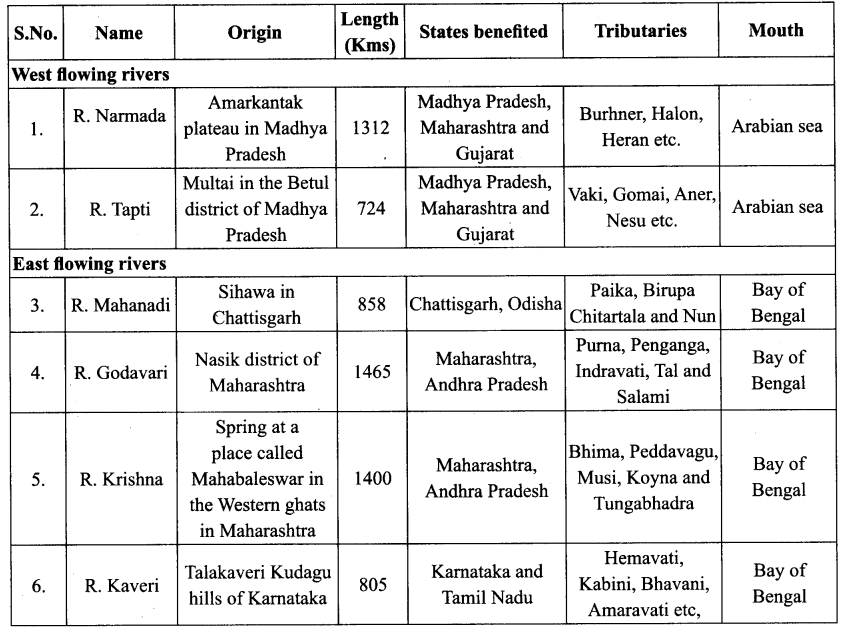
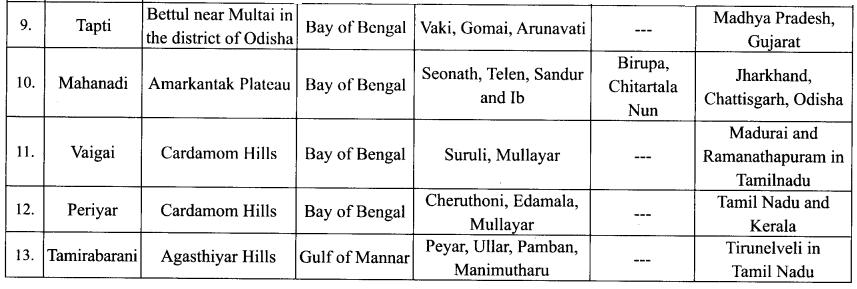
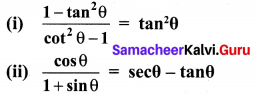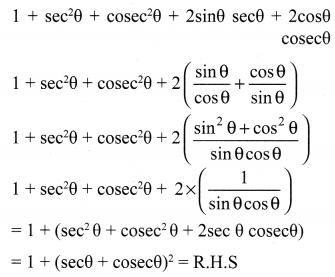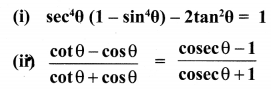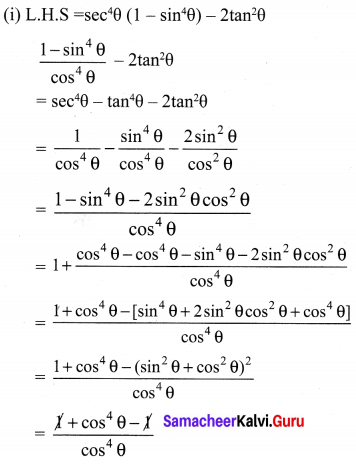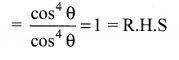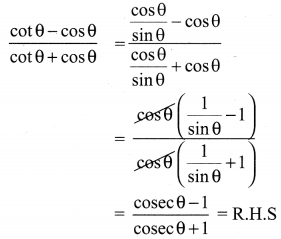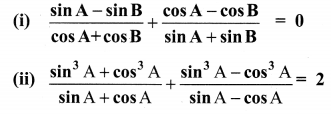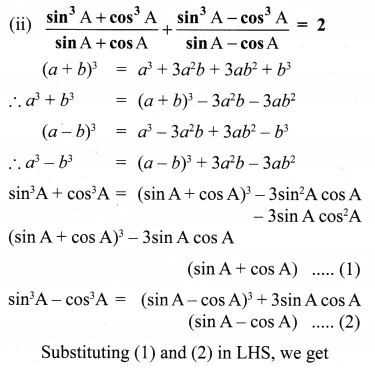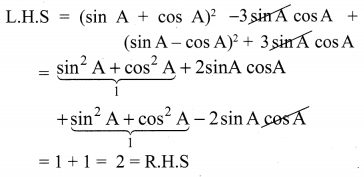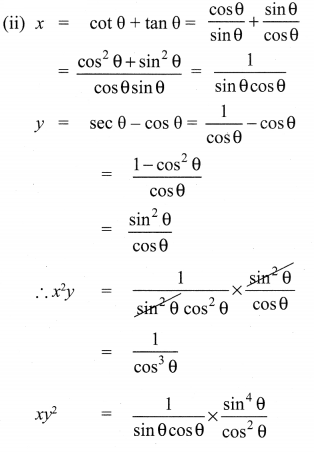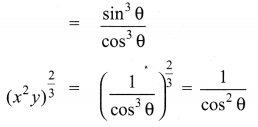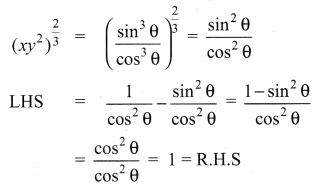You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.6
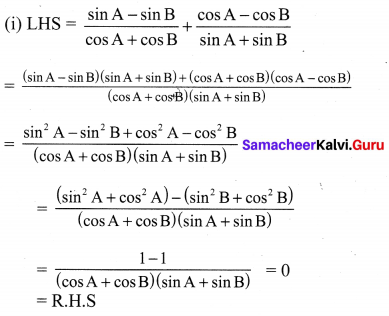
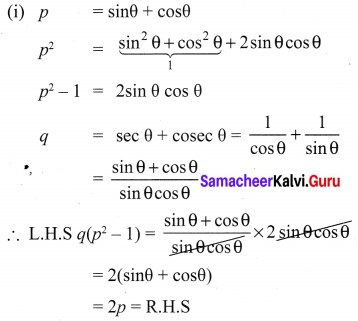
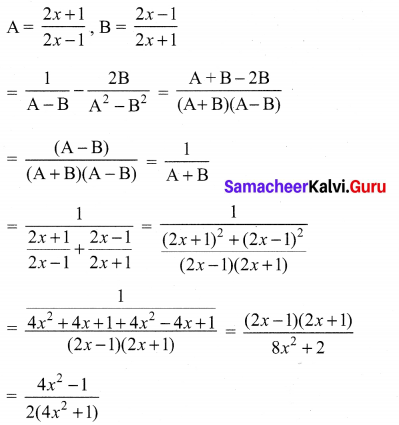
10th Maths Exercise 3.6 Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
Simplify
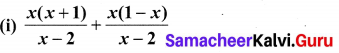
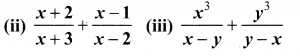
Solution:
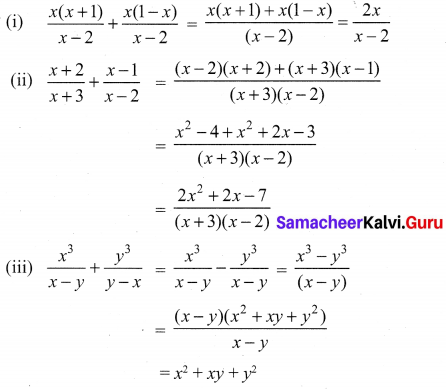
Ex 3.6 Class 10 Samacheer Question 2.
Simplify
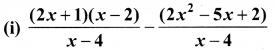

Solution:
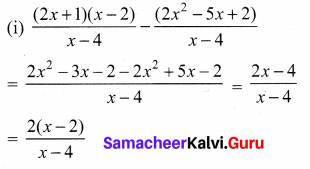
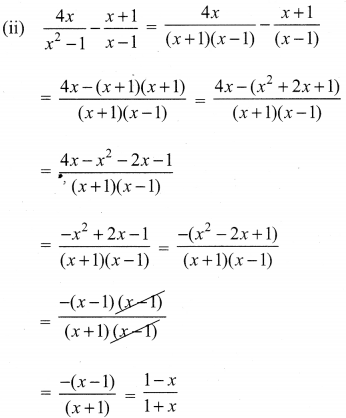
Exercise 3.6 Class 10 Samacheer Kalvi Question 3.
Subtract \(\frac{1}{x^{2}+2}\) from \(\frac{2 x^{3}+x^{2}+3}{\left(x^{2}+2\right)^{2}}\)
Solution:
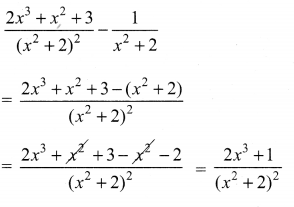
10th Maths Exercise 3.6 Question 4.
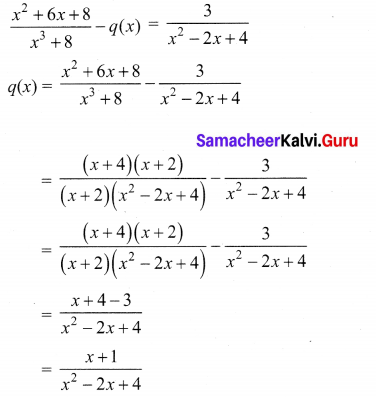
Which rational expression should be subtracted from \(\frac{x^{2}+6 x+8}{x^{3}+8}\) to get \(\frac{3}{x^{2}-2 x+4}\)
Solution:
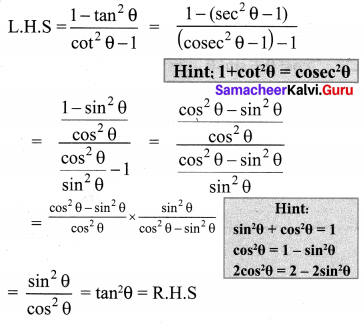
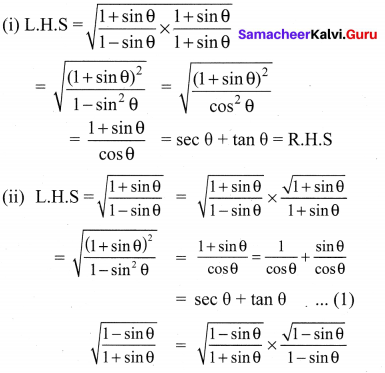
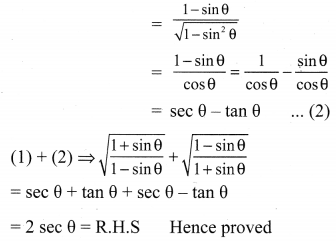
Exercise 3.6 Class 10 Maths Samacheer Question 5.
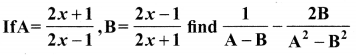
Solution:
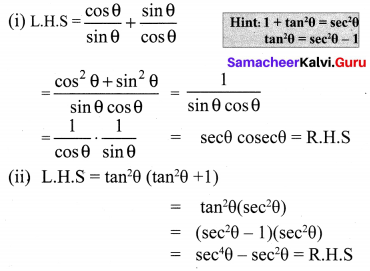
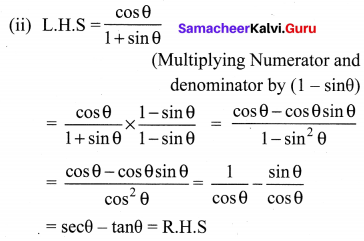
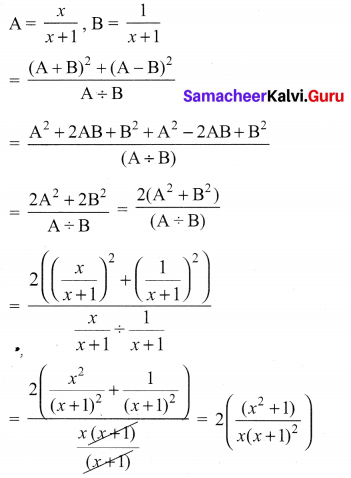
10th Maths Exercise 3.6 In Tamil Question 6.
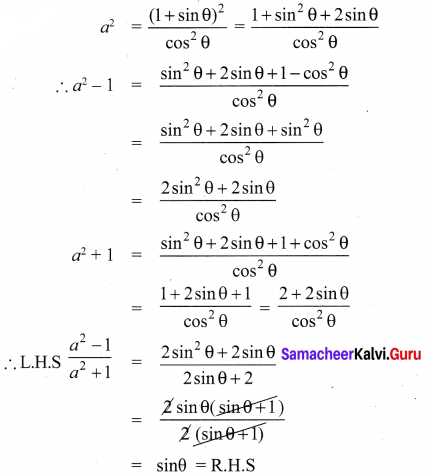
If A = \(\frac{x}{x+1}\), B = \(\frac{1}{x+1}\), prove that
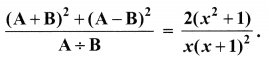
Solution:
10th Maths 3.6 Question 7.
Pari needs 4 hours to complete a work. His friend Yuvan needs 6 hours to complete the same work. How long will be take to complete if they work together?
Answer:
Let the work done by Pari and Yuvan together be x
Work done by part = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)
Work done by Yuvan = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 } \)
By the given condition
\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ x } \) ⇒ \(\frac { 3+2 }{ 12 } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ x } \)
\(\frac { 5 }{ 12 } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ x } \)
5x = 12 ⇒ x = \(\frac { 12 }{ 5 } \)
x = 2 \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 } \) hours (or) 2 hours 24 minutes
10th Maths Algebra Question 8.
Iniya bought 50 kg of fruits consisting of apples and bananas. She paid twice as much per kg for the apple as she did for the banana. If Iniya bought Rs. 1800 worth of apples and Rs. 600 worth bananas, then how many kgs of each fruit did she buy?
Answer:
Let the quantity of apples and bananas purchased be ‘x’ and ‘y’
By the given condition
x + y = 50 ………(1)
Cost of one kg of apple = \(\frac { 1800 }{ x } \)
Cost of one kg of banana = \(\frac { 600 }{ y } \)
By the given condition
One kg of apple = \(2 \frac{(600)}{y}\)
Total cost of fruits purchased = 1800 + 600
x × 2 \(\frac{(600)}{y}\) + y \(\frac{(600)}{y}\) = 2400
\(\frac { 1200x }{ y } \) = 2400 – 600
\(\frac { 1200x }{ y } \) = 1800
1200 x = 1800 × y
x = \(\frac { 1800x }{ 1200 } \) = \(\frac { 3y }{ 2 } \)
Substitute the value of x in (1)
\(\frac { 3y }{ 2 } \) + y = 50
\(\frac { 5y }{ 2 } \) = 50
5y = 100 ⇒ y = \(\frac { 100 }{ 5 } \) = 20
x = \(\frac { 3y }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac{3 \times 20}{2}\)
= 30
The quantity of apples = 30 kg
The quantity of bananas = 20 kg

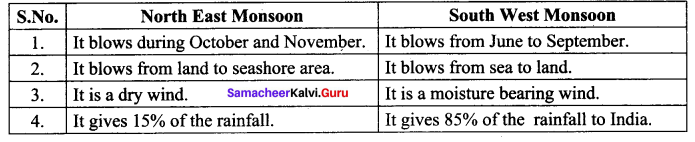
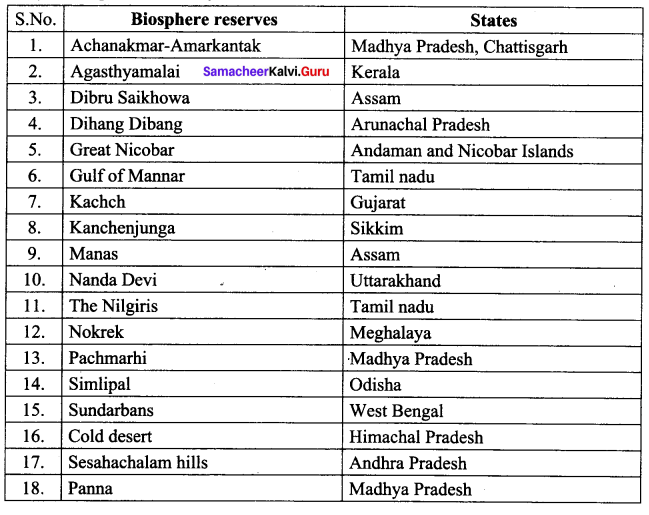
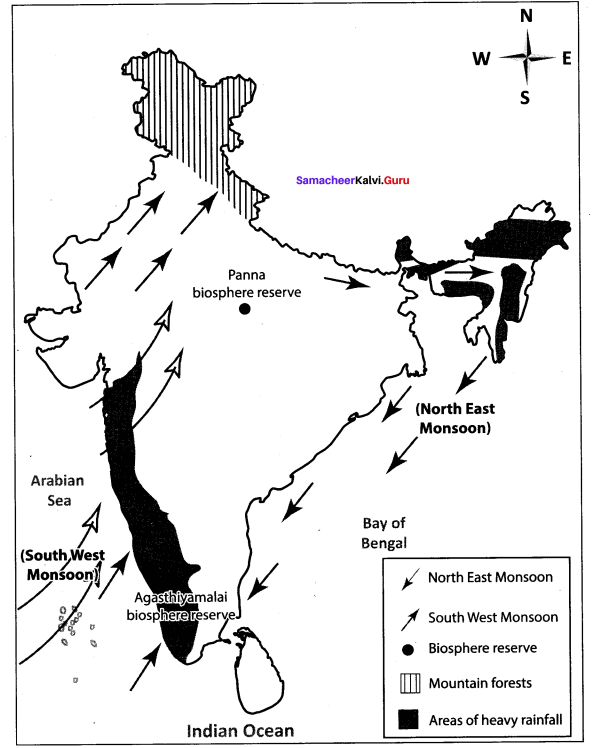







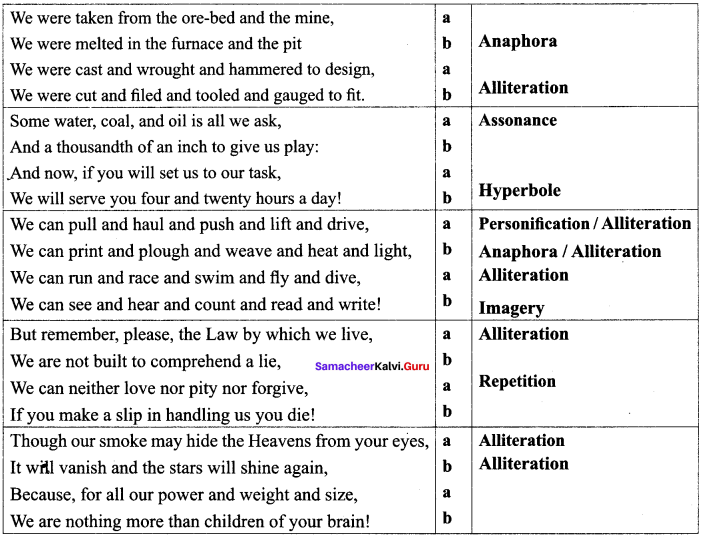










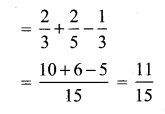


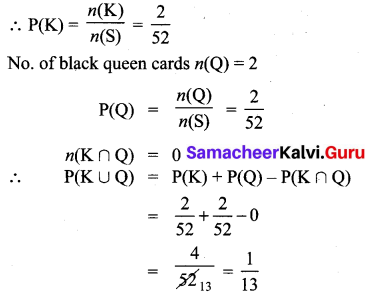
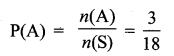

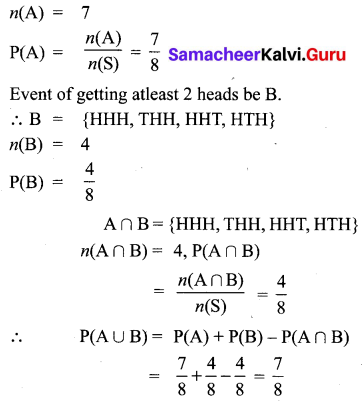
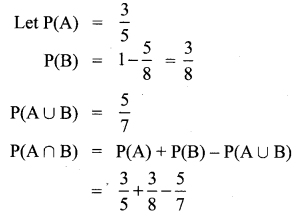
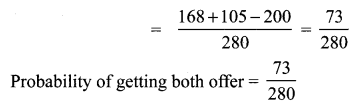

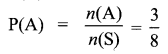

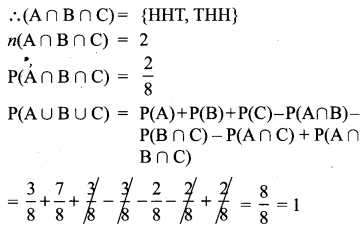
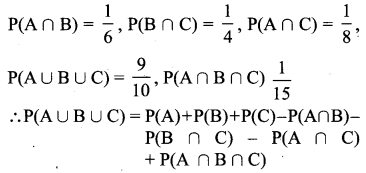
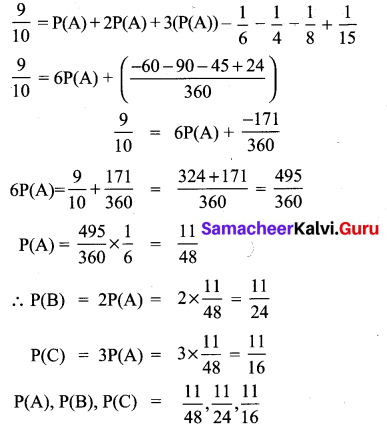
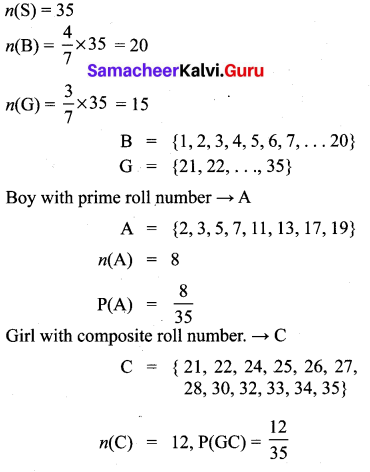



 Answer:
Answer: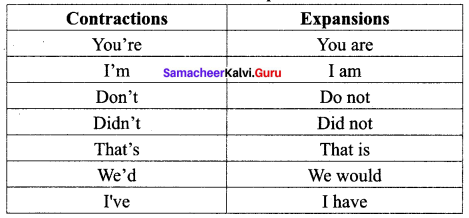














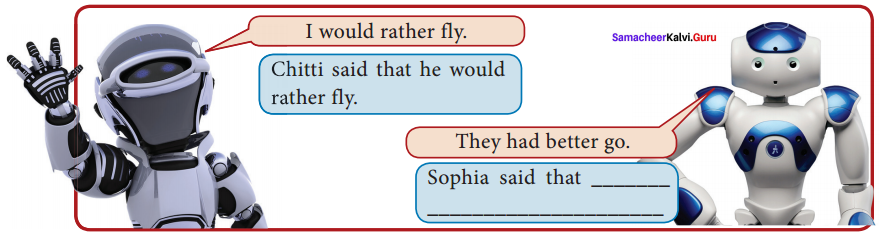
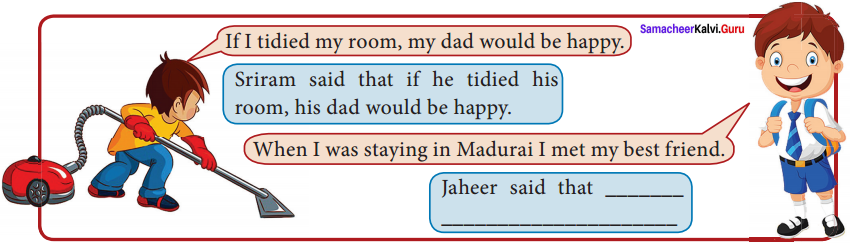

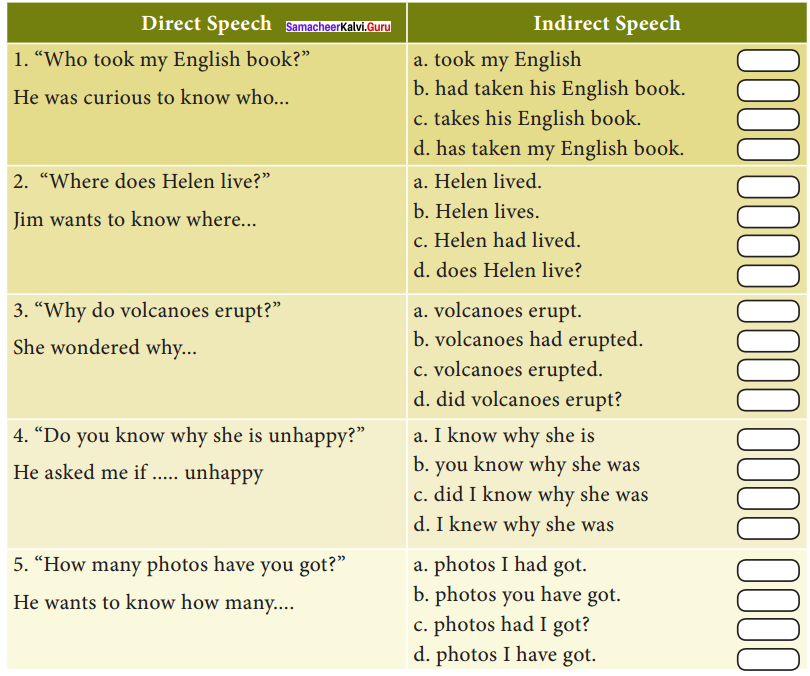 Answer:
Answer: