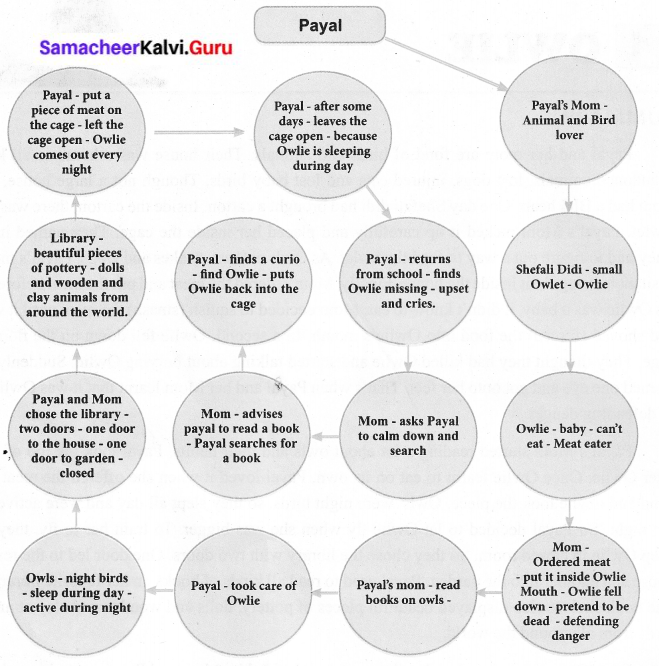
Students can Download English Poem 1 The Crocodile Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Solutions Term 1 Poem Chapter 1 The Crocodile
The Crocodile Poem Questions And Answers Poem Overview
| No. | Poem Line | Explanation |
| 1-2 | Ham doth the little crocodile improve Ms shining tail | The poet questions how the little crocodile uses water from its tears to improve the shining of its tail. The tail is already shining because of the water poured on its scales. |
| 3-4 | Ami pour dm water of ike Nile On emeny golden scale | The poet jokes that the crocodile secretes enough teardrops for them to seem like they equal all the water in the River Nile. |
| 5-6 | How cheerful he seems to grin, How neatly spreads his claws , | The crocodile seems to start grinning, as if it were welcoming its fellow creatures of the sea onto land along with itself .The crocodile also spreads his claws out on the sand, as if to create space for the fish to move in. |
| 7-8 | And welcomes little fishes in, With gently smiling jaws | In fact, all these actions on the crocodile’s part are designed to trick them and to trap them. When it opens its shining mouth, it in fact gobbles up all the fish that come swimming up towards its body. |
The Crocodile Poem Summary Glossary
doth – an expression of old English for ‘does’
Improve – to become better than before
cheerful – happy
gently – softly, mildly
scale – thin horny things on the skin of crocodile
grin – smile meaninglessly showing the teeth
A. Read the poem aloud in pairs.
To be done by the students
B. Choose the rhyming words from the box and write thehn in the correct blanks.
file, din, caws, nail, while, paws, mail, thin
- claws, jaws, _______ , _______
- grin, in, _______ , _______
- crocodile, Nile, _______ , _______
- tail, scale, _______ , _______
Answers:
- caws, paws
- din, thin
- file,while
- nail, mail
C. Read these lines and answer the questions given below.
The Crocodile Poem 6th Standard Question 1.
How cheerful he seems to grin
Who does ‘he’ refer to?
Answer:
He refers to the crocodile.
Crocodile Poem Summary Question 2.
And pour the water of the Nile
What does the Nile refer to? Where is it?
Answer:
The Nile is the longest river in the world. It flows in Northeastern Africa, covering eleven countries, including Egypt.
The Crocodile – Poem Summary Question 3.
And welcomes little fishes in
With gently smiling jaws!
a. Who welcomes the fish? Why?
Answer:
The Crocodile welcomes the fish. It welcomes the fish as they would become its food.
b. Which line tells you that the crocodile is hungry?
Answer:
The line ‘when you can smell the grass from your garden seat’ tells us The second line “with gently smiling jaws”
D. Work in pairs. Share your answers with your partner.
Crocodile Poem Question 1.
What is the poem about?
Answer:
The poem is about a crocodile.
Crocodile Poem In English Question 2.
How does the crocodile’s tail look?
Answer:
The tail looks shining.
The Crocodile Poem Question 3.
What does ‘improve his tail’ mean?
Answer:
To become better than before.
Crocodile Questions And Answers Question 4.
How does he spread his claws?
Answer:
He spreads his claws neatly.
6th Standard English Poem The Crocodile Question 5.
Why does he welcome little fishes?
Answer:
He is hungry and he feeds on them. So he welcomes them.
Question 6.
Which line talks about the crocodile’s mouth and his shape?
Answer:
The last line with gently smiling jaws.
Writing
E. What does the poet say about the crocodile? Write in your own words, (in about fifty words).
Answer:
“How doth the little crocodile” is a children’s poem by Lewis Carroll. It discusses the looks of a crocodile. It uses rhyming words. In the first stanza, the poet talks about the tail of the crocodile and the scales of it. The scales are so, shiny like the waters of the river Nile. The second stanza speaks of the crocodile’s smile (grin) and claws. The crocodile is cheerful to welcome the little fishes to consume them.
The Crocodile Additional Questions
I. Poem Comprehension.
1. And Pour the water of the Nile
On every golden scale !
(a) What Is rafarrad as water of tha Nile ?
Answer:
The tears of the crocodile is referred as water of the Nile.
(b) Why Is the scale golden ?
Answer:
The scale in the tail is shining like gold due to water poured on it.
2. How cheerful he seems to grip
How neatly spreads its claws
(a) Who is’he’referred here?
Answer:
The crocodile.
(b) Why is he cheerful ?
Answer:
He is cheerful because he is onto the land and going to eat the fishes.
II. Poetic Devices.
1. How cheerful he seems to grin
How neatly spreads his claws
What Is the poetic device used In this line ? Explain your answer.
Answer:
Personification. He refers to the crocodile with the word “he” rather than the word “it”. He acknowledges that the crocodile’s tears are not the result of emotional distress, but also shows how the crocodile generates them with the intention of capturing his prey.
2. And pour the water of the Nile
On every golden scale !
What is the poetic device used in this line ? Explain your answer
Answer:
Metaphor: This poetic device is used when a covert comparison is made between two different things or ideas. Here the poet compares the tears of the crocodile with the waters of the River Nile.
III. Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
What does the crocodile uses to improve the shining of Its tall?
Answer:
It uses its tears to spread over its back, so that it can improve the shining of its tail.
Question 2.
How does the poet comment on the crocodile’s tear drops?
Answer:
He says that the crocodile secrets enough tear drops, so that they seem to equal all the water in the river Nile‘
Question 3.
What does the poet say in the second stanza?
Answer:
The poet describes what the crocodile does, when it spots the fish in the water, tries to swim near the shore.
Question 4.
How does the crocodile create space for the fish to move in?
Answer:
It spreads his claws out on the sand, as if to create space for the fish to move in.
Question 5.
What actions are being designed by the crocodile to trick and trap the fish?
Answer:
It welcomes the fish by grinning at it and also spreads his claws out on the sand, as if to create space for the fish to move in.
IV. Paragraph Questions.
Question 1.
The crocodile seems to have cruet intentions. Justify.
Answer:
The crocodile does have cruel intentions of using deception (cheating) and tricking its prey. It fakes the tears as if the killing of the prey is causing it emotional distress. However it isn’t so. The crocodile is a crafty creature that tricks its prey into surrendering itself. The shedding of tears is not related to emotional status in any way as the poet shows us in the poem. Rather it is aimed at enhancing the physical appearance of the crocodile so that it can attract its prey and deceive the prey into offering itself up for the crocodile’s consumption. Thus crocodile has cruel intentions to cheating and tricking its prey.
The Crocodile Summary
Stanza 1
In this stanza, the poet describes how a crocodile may enhance the physical appearance of its tail. The crocodile has come up out of the water and is sitting on the shore. It is evident on a sunny day, for the light of the sun to fall on the scales of the crocodile’s body is making them shine. However, the poet does not seem to be content with just the sunlight brightening up its appearance. He concludes that a certain amount of water poured on its scales would further beautify its appearance. As we know, the eyes of the crocodile are placed in a horizontal relation with its back. Therefore, when it secretes tears, the water from the tears can easily spread over its back.
This is exactly what the crocodile does. The crocodile’s tears are not only caused by emotional distress, as they are in the case of human beings. Hence, it is easy for the crocodile to secrete a large amount of teardrops and have them roll down the scales of its body, making them shine to a larger extent than they naturally would in the sunlight. The poet jokes that the crocodile secretes enough teardrops for them to seem like they equal all the water in the River Nile.
Stanza 2
In this stanza, Alice describes what the crocodile does when it spots the fish in the water trying to swim near the shore. The crocodile seems to start grinning, as if it was welcoming its fellow creatures of the sea oftto land along with itself. The crocodile also spreads his claws out on the sand, as if to create space for the fish to move in. The last thing the crocodile does is to open its mouth wide, as if to utter a kindly word. However, the fish are sorely mistaken if they interpret the crocodile’s actions in this way. In fact, all these actions on the crocodile’s part are designed to trick them and to trap them. When it opens its shining mouth, it infact gobbles up all the fish that come swimming up towards its body
Message: The poem also draws our attention to the various people in the world, who outwardly seem friendly but wait for an opportunity to strike at innocent people who may be unaware of their real malicious intentions.
So the poet is warning us to be very careful while dealing with others and not get carried away by their sweet smile or attractive looks.