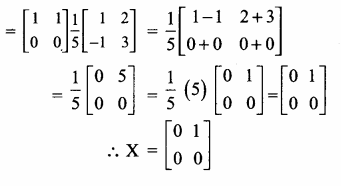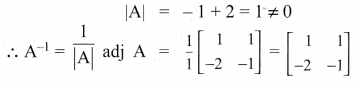Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 1 அணிகள் மற்றும் அணிக்கோவைகளின் பயன்பாடுகள் Ex 1.2 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
TN Board 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 அணிகள் மற்றும் அணிக்கோவைகளின் பயன்பாடுகள் Ex 1.2
கேள்வி 1.
பின்வரும் அணிகளுக்கு சிற்றணிக்கோவையை பயன்படுத்தி அணித்தரம் காண்க:
(i) \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
2 & -4 \\
-1 & 2
\end{array}\right]\)
(ii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
-1 & 3 \\
4 & -7 \\
3 & -4
\end{array}\right]\)
(iii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
1 & -2 & -1 & 0 \\
3 & -6 & -3 & 1
\end{array}\right]\)
(iv) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -2 & 3 \\
2 & 4 & -6 \\
5 & 1 & -1
\end{array}\right]\)
(v) \(\left[\begin{array}{llll}
0 & 1 & 2 & 1 \\
0 & 2 & 4 & 3 \\
8 & 1 & 0 & 2
\end{array}\right]\)
தீர்வு:
(i) \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
2 & -4 \\
-1 & 2
\end{array}\right]\)

A ஒரு 2×2 வரிசை அணி
∴ \(\rho\)(A) ≤ (2, 2) – மீச்சிறு = 2
A-ன் பூச்சியமற்ற சிற்றணிக் கோவைகளின்
உச்ச வரிசை 2 ஆகும்.
இது \(\left|\begin{array}{rr}
2 & -4 \\
-1 & 2
\end{array}\right|\) = 4 – 4 = 0
ஆகையால், \(\rho\)(A)<2
அடுத்து 1 வரிசையுடைய சிற்றணிக்
கோவையை தேர்வு செய்வோம் |2| = 2≠0
∴ \(\rho\)(A) = 1
![]()
(ii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
-1 & 3 \\
4 & -7 \\
3 & -4
\end{array}\right]\)
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
-1 & 3 \\
4 & -7 \\
3 & -4
\end{array}\right]\) என்க .
A ஒரு 3 × 2 வரிசை அணி
∴ ρ(A) ≤ (3, 2) -ன் மீச்சிறு = 2
A -ன் பூச்சியமற்ற சிற்றணிக் கோவைகளின்
உச்ச வரிசை 2 ஆகும்.
அது \(\left|\begin{array}{cc}
-1 & 3 \\
4 & -7
\end{array}\right|\) = 7-12 =-5 ≠ 0
∴ ρ(A) = 2.
(iii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
1 & -2 & -1 & 0 \\
3 & -6 & -3 & 1
\end{array}\right]\)
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
1 & -2 & -1 & 0 \\
3 & -6 & -3 & 1
\end{array}\right]\) என்க.
A ஒரு (2 × 4) வரிசை அணி
∴ ρ(A) ≤ (2, 4) -ன் மீச்சிறு = 2
A-ன்பூச்சியமற்ற சிற்றணிக்கோவைகளின்
உச்சவரிசை 2 ஆகும்.
அது \(\left|\begin{array}{ll}
1 & -2 \\
3 & -6
\end{array}\right|\) = – 6+6 =0
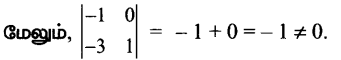
∴ ρ(A) = 2.
(iv) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -2 & 3 \\
2 & 4 & -6 \\
5 & 1 & -1
\end{array}\right]\)
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -2 & 3 \\
2 & 4 & -6 \\
5 & 1 & -1
\end{array}\right]\) என்க.
A ஒரு 3 × 3 வரிசை அணி
∴ ρ(A) ≤ (3, 3) – ன் மீச்சிறு = 3
A-ன் பூச்சியமற்ற சிற்றணிக்கோவைகளின்
உச்சவரிசை 3 ஆகும்.
அது, |1 -2 3)
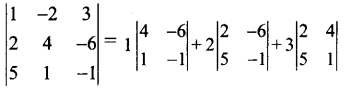
[R1.- ன் மூலம் விரிவுபடுத்தப்பட்டது]
= 1 (-4+ 6) + 2 (- 2 + 30) + 3 (2 – 20)
= 1 (2) + 2 (28) + 3 (- 18) = 2 + 56 – 54 = 58 – 54 = 4≠0
∴ ρ(A) = 3.
![]()
(v) \(\left[\begin{array}{llll}
0 & 1 & 2 & 1 \\
0 & 2 & 4 & 3 \\
8 & 1 & 0 & 2
\end{array}\right]\)
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{llll}
0 & 1 & 2 & 1 \\
0 & 2 & 4 & 3 \\
8 & 1 & 0 & 2
\end{array}\right]\) என்க.
A ஒரு 3 × 4 வரிசை அணி
∴ ρ(A) ≤ (3, 4)- ன் மீச்சிறு = 3
A-ன்பூச்சியமற்ற சிற்றணிக்கோவைகளின்
உச்ச வரிசை 3
=-8 (6 – 4) = – 8(2) =-16≠0
∴ ρ(A) = 3
![]()
கேள்வி 2.
பின்வரும் அணிகளுக்கு ஏறுபடி வடிவத்தைப் பயன்படுத்தி அணித்தரம் காண்க :
(i) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
1 & 1 & 1 & 3 \\
2 & -1 & 3 & 4 \\
5 & -1 & 7 & 11
\end{array}\right]\)
(ii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & 2 & -1 \\
3 & -1 & 2 \\
1 & -2 & 3 \\
1 & -1 & 1
\end{array}\right]\)
(iii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
3 & -8 & 5 & 2 \\
2 & -5 & 1 & 4 \\
-1 & 2 & 3 & -2
\end{array}\right]\)
தீர்வு:
(i) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
1 & 1 & 1 & 3 \\
2 & -1 & 3 & 4 \\
5 & -1 & 7 & 11
\end{array}\right]\)
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cccc}
1 & 1 & 1 & 3 \\
2 & -1 & 3 & 4 \\
5 & -1 & 7 & 11
\end{array}\right]\) என்க
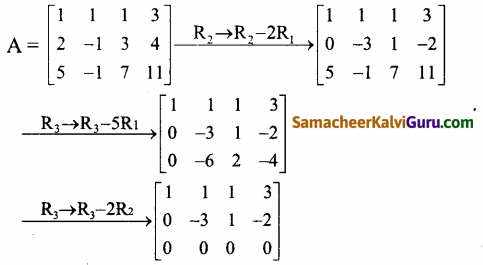
கடைசி சமான அணியானது நிரை ஏறுபடி வடிவத்தில் அமைந்துள்ளது. இரண்டு அபூச்சிய நிரைகளை உடையது.
∴ ρ(A) = 2.
![]()
(ii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & 2 & -1 \\
3 & -1 & 2 \\
1 & -2 & 3 \\
1 & -1 & 1
\end{array}\right]\)
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 2 & -1 \\
3 & -1 & 2 \\
1 & -2 & 3 \\
1 & -1 & 1
\end{array}\right]\) என்க.
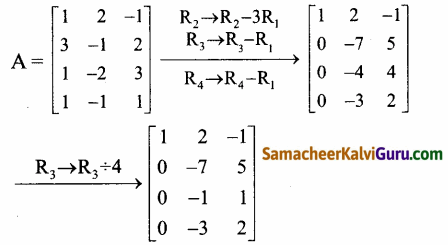
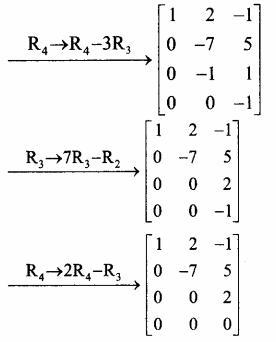
கடைசி சமான அணியானது நிரை ஏறுபடி வடிவத்தில் அமைந்துள்ளது. மூன்று அபூச்சிய நிரைகளை உடையது.
∴ ρ(A) = 3
(iii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
3 & -8 & 5 & 2 \\
2 & -5 & 1 & 4 \\
-1 & 2 & 3 & -2
\end{array}\right]\)
Let A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
3 & -8 & 5 & 2 \\
2 & -5 & 1 & 4 \\
-1 & 2 & 3 & -2
\end{array}\right]\)
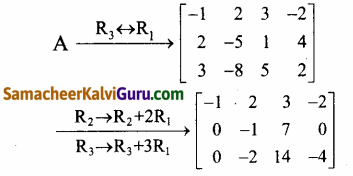
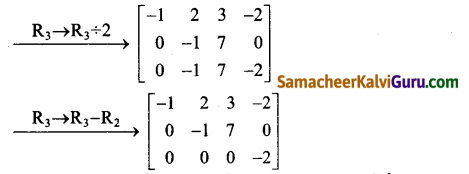
கடைசி சமான அணியானது நிரை ஏறுபடி வடிவில் அமைந்துள்ளது. மூன்று அப்பூச்சிய நிரைகளை உடையது.
∴ ρ(A) = 3
![]()
கேள்வி 3.
பின்வரும் அணிகளுக்கு காஸ்-ஜோர்டன் நீக்கல் முறையைப் பயன்படுத்தி நேர்மாறு காண்க:
(i) \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
2 & -1 \\
5 & -2
\end{array}\right]\)
(ii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -1 & 0 \\
1 & 0 & -1 \\
6 & -2 & -3
\end{array}\right]\)
(iii) \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 2 & 3 \\
2 & 5 & 3 \\
1 & 0 & 8
\end{array}\right]\)
தீர்வு:
(i) \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
2 & -1 \\
5 & -2
\end{array}\right]\)
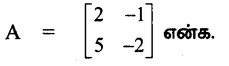
காஸ்-ஜோர்டன் முறையை பயன்படுத்த கிடைப்பது
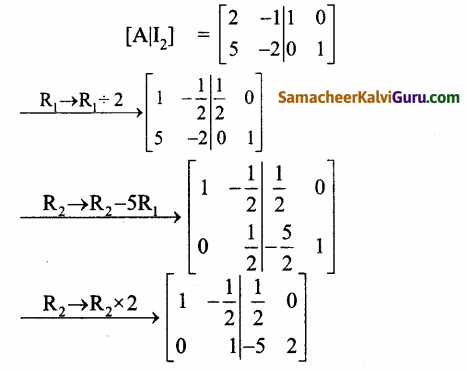
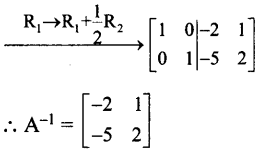
(ii) \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -1 & 0 \\
1 & 0 & -1 \\
6 & -2 & -3
\end{array}\right]\)
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -1 & 0 \\
1 & 0 & -1 \\
6 & -2 & -3
\end{array}\right]\) என்க.
காஸ்-ஜோர்டன் முறையை பயன்படுத்த கிடைப்பது
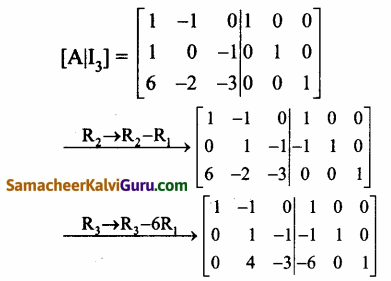
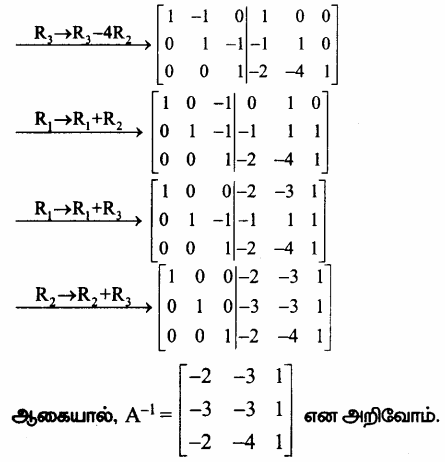
![]()
(iii) \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 2 & 3 \\
2 & 5 & 3 \\
1 & 0 & 8
\end{array}\right]\)
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 2 & 3 \\
2 & 5 & 3 \\
1 & 0 & 8
\end{array}\right]\) என்க
காஸ்-ஜோர்டன் முறையை பயன்படுத்த கிடைப்பது
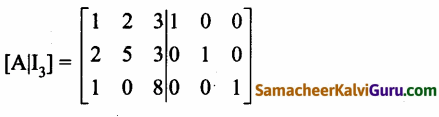
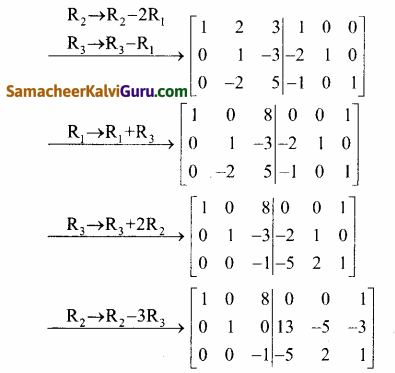
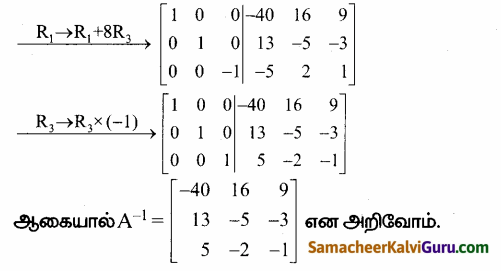
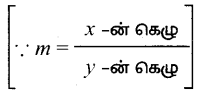
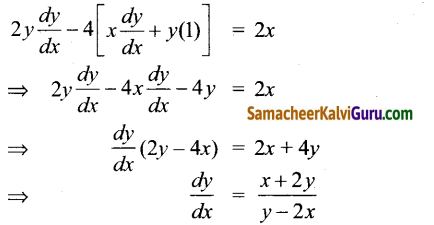
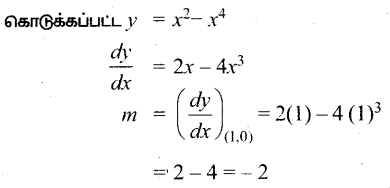

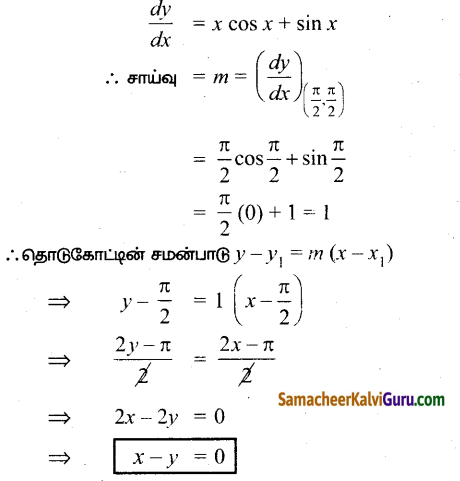
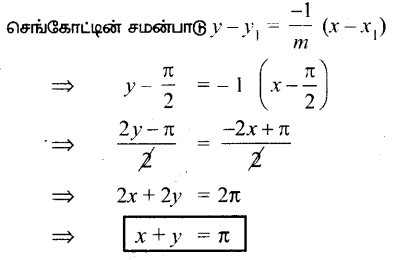
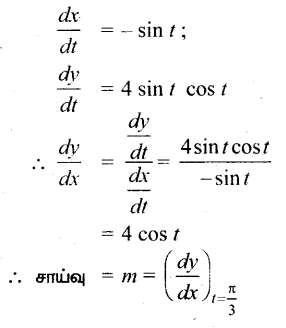
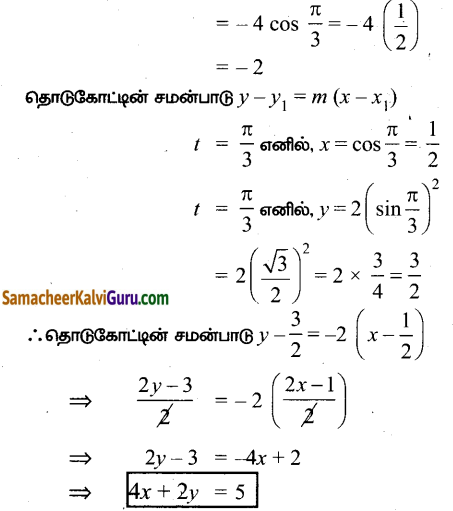
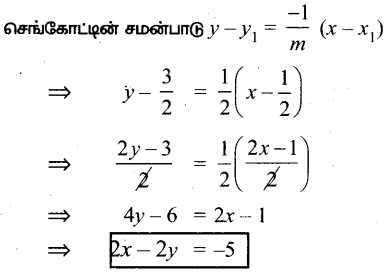
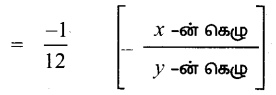
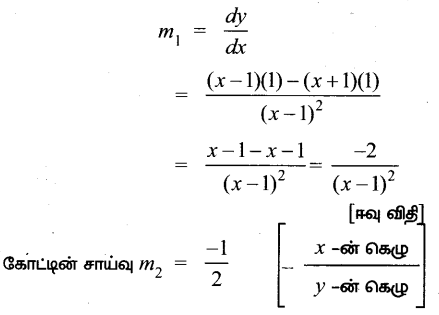
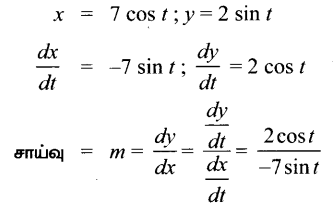
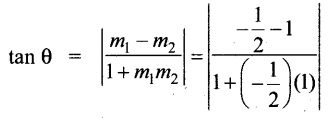
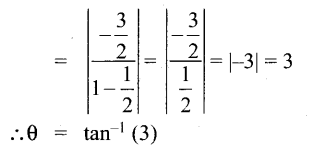
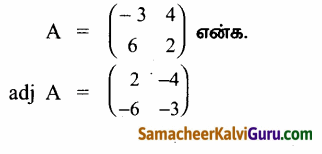
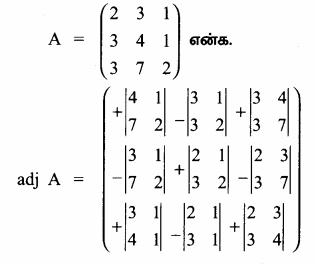
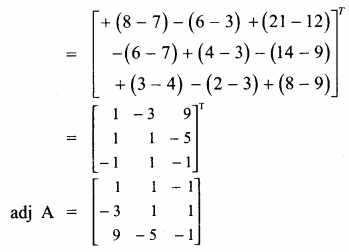
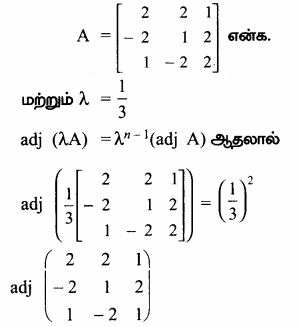
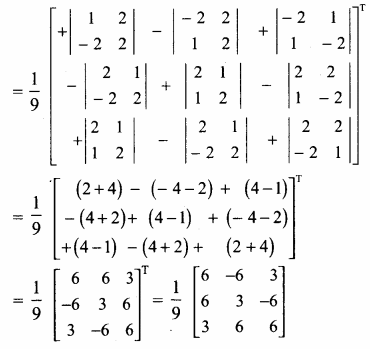
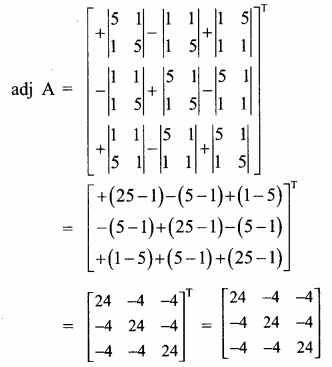
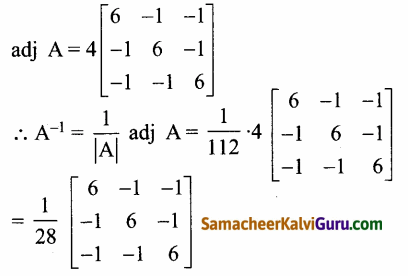
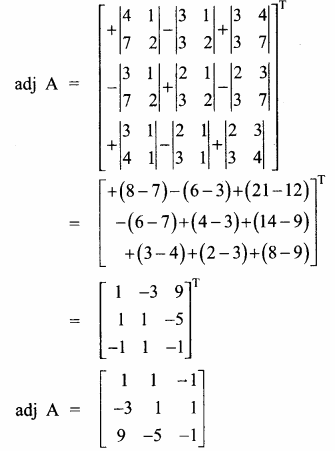
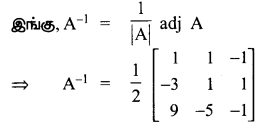
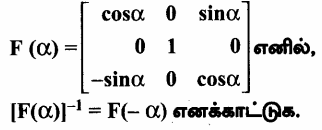
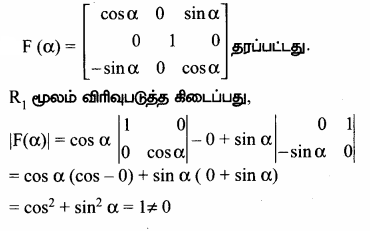
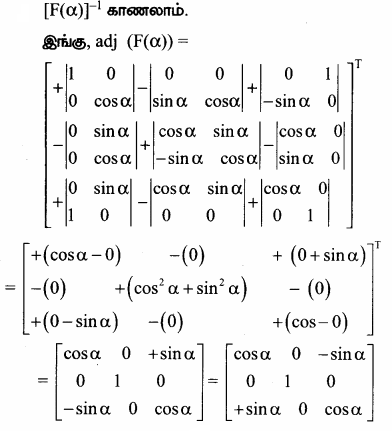
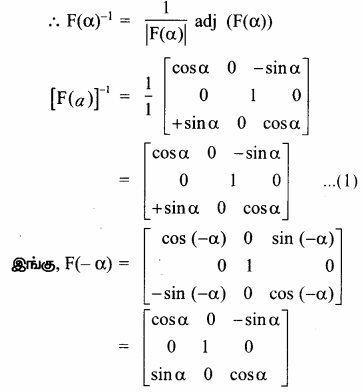

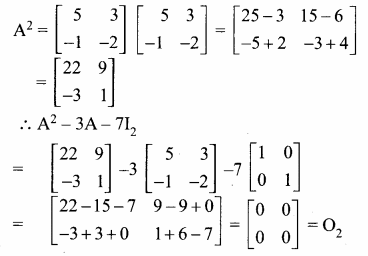
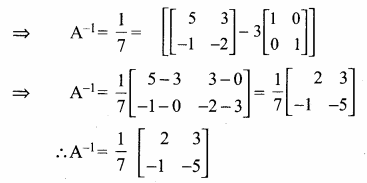
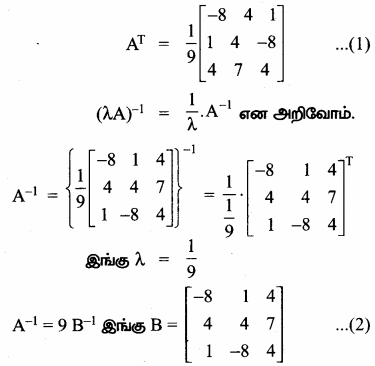
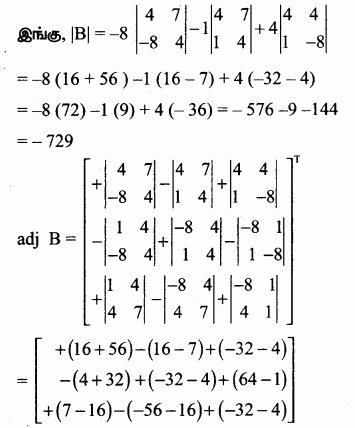
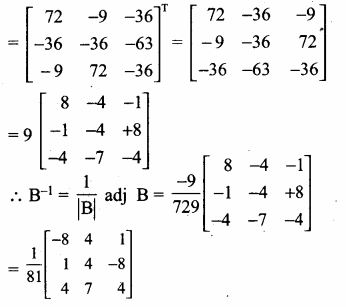
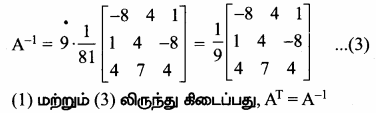
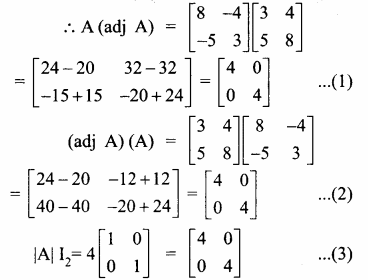
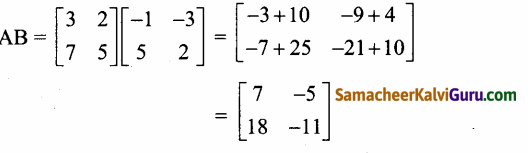
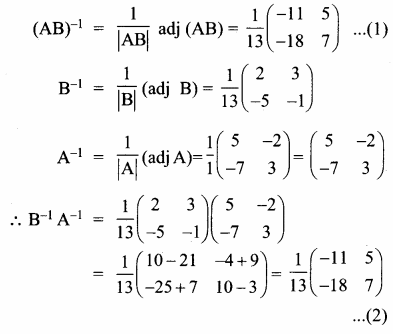
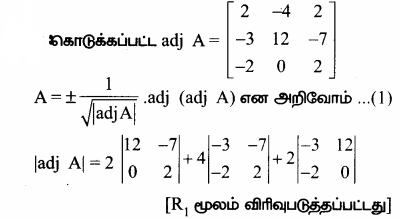
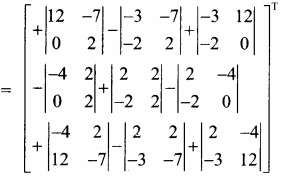
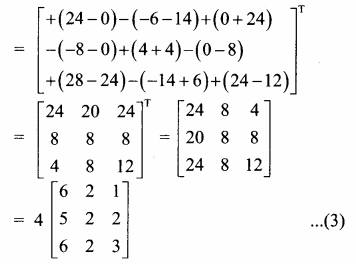
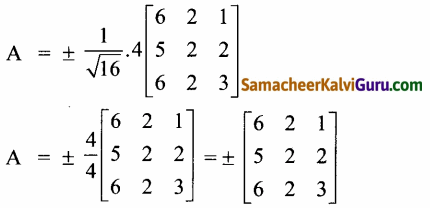

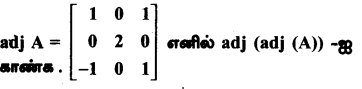
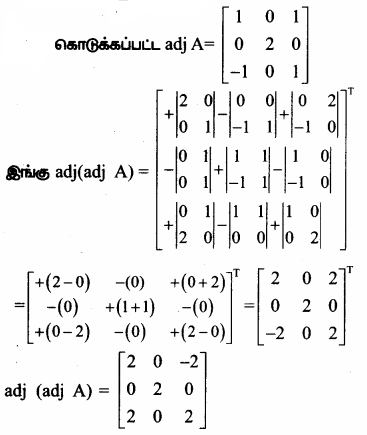
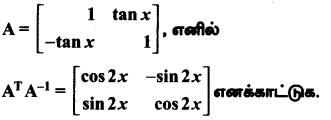
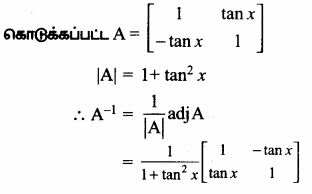
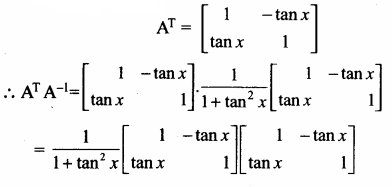
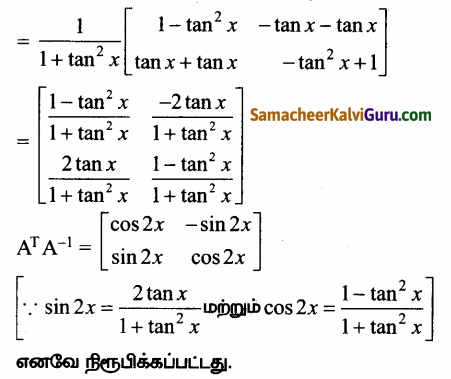
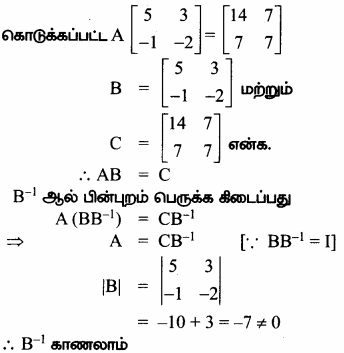
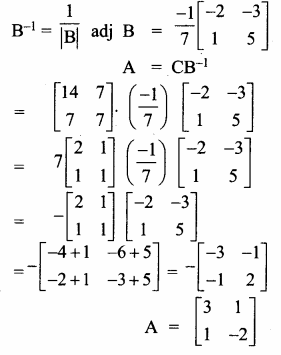
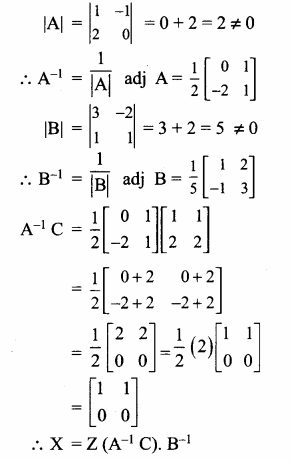
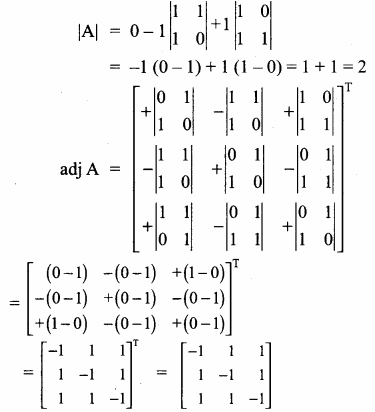
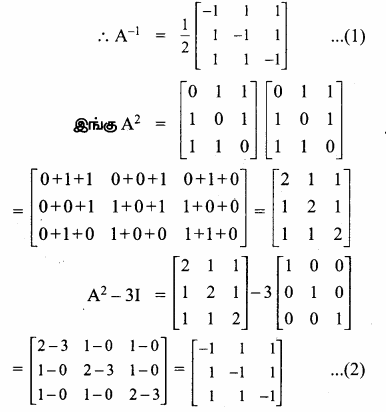
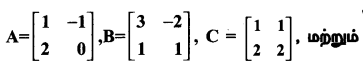 AXB = C எனில், X என்ற அணியைக் காண்க.
AXB = C எனில், X என்ற அணியைக் காண்க.