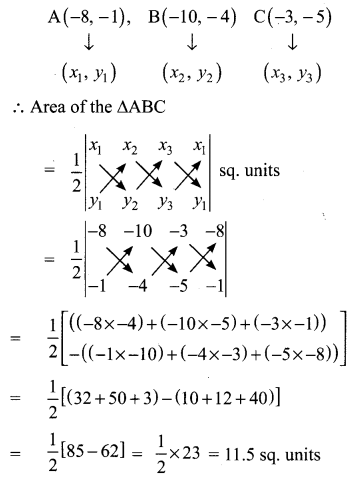
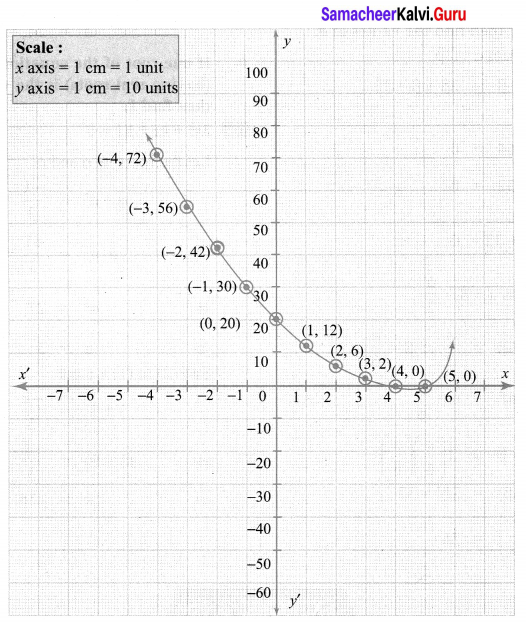
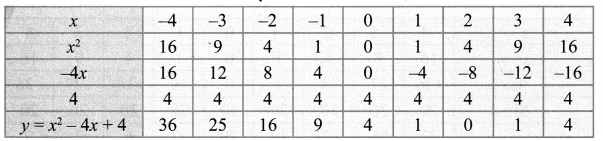
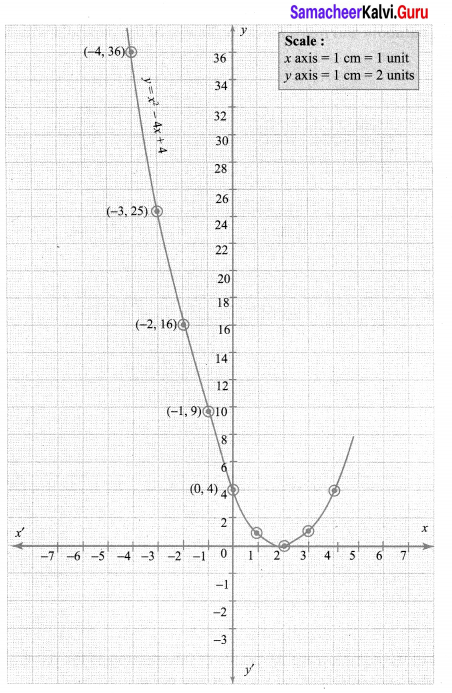
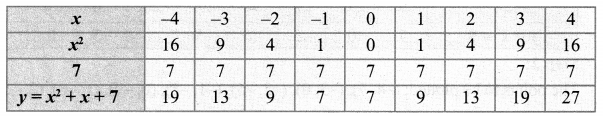
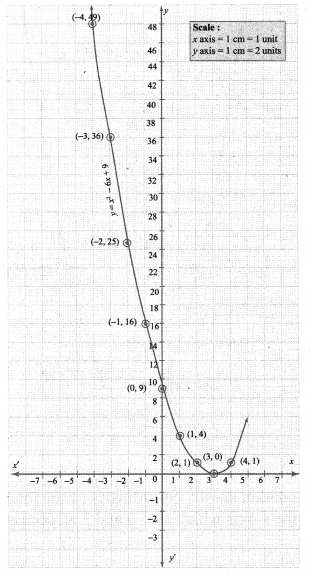
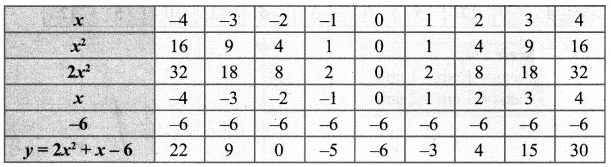
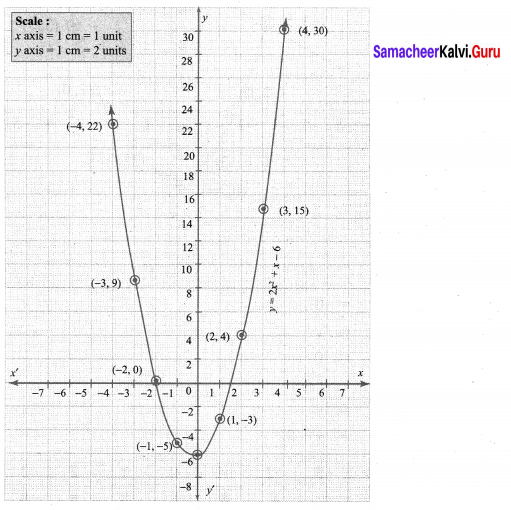
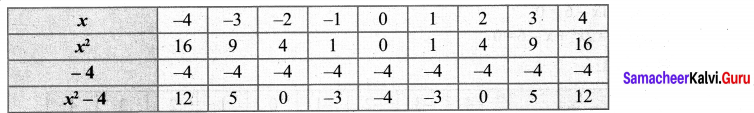
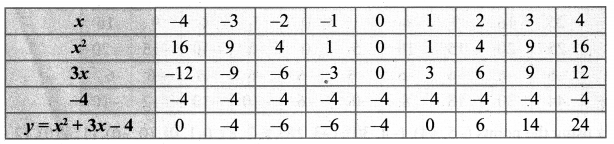
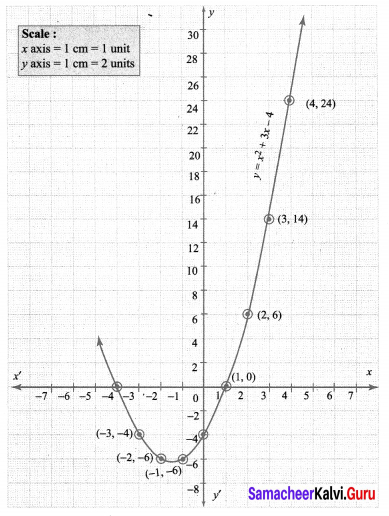
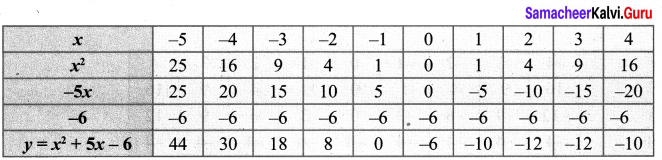
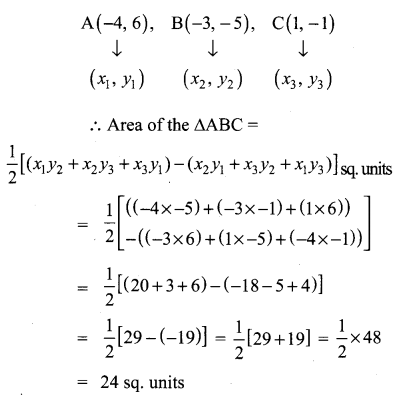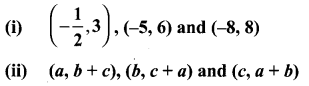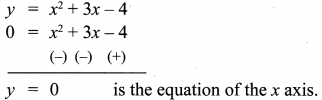Students who are preparing for the Science exam can download this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 10th Science Chapter 1 from here for free of cost. These Tamilnadu State Board Textbook Solutions PDF cover all 10th Science Laws of Motion Book Back Questions and Answers.
All these concepts of Chapter 1 Laws of Motion are explained very conceptually by the subject teachers in Tamilnadu State Board Solutions PDF as per the prescribed Syllabus & guidelines. You can download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Book Solutions Chapter 1 Laws of Motion State Board Pdf for free from the available links. Go ahead and get Tamilnadu State Board Class 10th Science Solutions of Chapter 1 Laws of Motion.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 1 Laws of Motion
Kickstart your preparation by using this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 10th Science Chapter 1 Laws of Motion Questions and Answers and get the max score in the exams. You can cover all the topics of Chapter 1 easily after studying the Tamilnadu State Board Class 10th Science Textbook solutions pdf. Download the Tamilnadu State Board Science Chapter 1 Laws of Motion solutions of Class 10th by accessing the links provided here and ace up your preparation.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Laws of Motion Textual Solved Problems
10th Science Laws Of Motion Book Back Answers Question 1.
Calculate the velocity of a moving body of mass 5 kg whose linear momentum is 2.5 kg ms-1.
Solution:
Linear momentum = mass × velocity
Velocity = \(\frac { linear momentum }{ mass }\)
V = \(\frac { 2.5 }{ 0.5 }\) = 0.5 ms-1.
Laws Of Motion Class 10 Questions And Answers Question 2.
A door is pushed, at a point, whose distance from the hinges is 90 cm, with a force of 40 N. Calculate the moment of the force about the hinges.
Solution:
Formula: The moment of a force M = F × d
Given: F = 40 N and d = 90 cm = 0.9 m.
Hence, moment of the force = 40 × 0.9 = 36 Nm.
Laws Of Motion Class 10 Samacheer Question 3.
At what height from the centre of the Earth the acceleration due to gravity will be \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)th of its value as at the Earth.
Solution:
Data: Height from the centre of the Earth, R’ = R + h
The acceleration due to gravity at that height, g’ = \(\frac { g }{ 4 }\)
Formula:
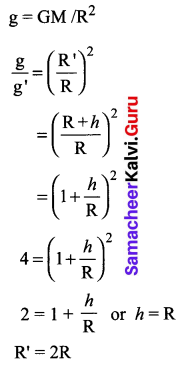
From the centre of the Earth, the object is placed at twice the radius of the earth.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Laws of Motion Textbook Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer.
Laws Of Motion Class 10 Book Back Answers 1.
The inertia of a body depends on _____ .
(a) weight of the object
(b) acceleration due to gravity of the planet
(c) mass of the object
(d) Both a & b.
Answer:
(c) mass of the object
10th Science Unit 1 Question 2.
Impulse is equals to:
(a) rate of change of momentum
(b) rate of force and time
(c) change of momentum
(d) rate of change of mass
Answer:
(c) change of momentum
10th Science Laws Of Motion Question 3.
Newton’s III law is applicable to ______ .
(a) for a body is at rest
(b) for a body in motion
(c) both a & b
(d) only for bodies with equal masses.
Answer:
(c) both a & b
10th Law Of Motion Question 4.
Plotting a graph for momentum on the X-axis and time on Y-axis. The slope of the momentum-time graph gives:
(a) Impulsive force
(b) Acceleration
(c) Force
(d) Rate of force
Answer:
(c) Force
Laws Of Motion – Class 10 New Syllabus Question 5.
In which of the following sport the turning of the effect of force used?
(a) swimming
(b) tennis
(c) cycling
(d) hockey.
Answer:
(c) cycling
10th Physics Laws Of Motion Question 6.
The unit of ‘g’ is ms-2. It can be also expressed as _____ .
(a) cm s-1
(b) N kg-1
(c) Nm2 kg-1
(d) cm2 s-2
Answer:
(b) N kg-1
Laws Of Motion 10th Science Question 7.
One kilogram force equals to:
(a) 9.8 dyne
(b) 9.8 × 104 N
(c) 98 × 104 dyne
(d) 980 dyne
Answer:
(c) 98 × 104 dyne
10th Standard Science Laws Of Motion Question 8.
The mass of a body is measured on planet Earth as M kg. When it is taken to a planet of radius half that of the Earth then its value will be ____ kg.
(a) 4M
(b) 2M
(c) \(\frac { M }{ 4 }\)
(d) M.
Answer:
(c) \(\frac { M }{ 4 }\)
10th Science Law Of Motion Question 9.
If the Earth shrinks to 50% of its real radius its mass remaining the same, the weight of a body on the Earth will _____ .
(a) decrease by 50%
(b) increase by 50%
(c) decrease by 25%
(d) increase by 300%.
Answer:
(c) decrease by 25%
Laws Of Motion Class 10 In Tamil Question 10.
To project the rockets which of the following
principle(s) is /(are) required?
(a) Newton’s third law of motion
(b) Newton’s law of gravitation
(c) Law of conservation of linear momentum
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (c)
II. Fill in the blanks.
10th Science Lesson 1 Question 1.
To produce a displacement _____ is required.
Answer:
force.
10th Science Solution Samacheer Kalvi Question 2.
Passengers lean forward when the sudden brake is applied in a moving vehicle. This can be explained by ____.
Answer:
the inertia of motion.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 10th Science Question 3.
By convention, the clockwise moments are taken as _____ and the anticlockwise moments are taken as _____.
Answer:
negative, positive.
10th Science Solutions Samacheer Kalvi Question 4.
______ is used to change the speed of the car.
Answer:
Acceleration.
10th Science Solutions Samacheer Question 5.
A man of mass 100 kg has a weight of _____ at the surface of the Earth.
Answer:
980 N.
III. State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the statement if it is false:
Class 10 Samacheer Kalvi Science Solutions Question 1.
The linear momentum of a system of particles is always conserved.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The linear momentum of a system of particles is always conserved if no external force acts.
10th Samacheer Kalvi Science Solutions Question 2.
The apparent weight of a person is always equal to his actual weight.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Weight of a body is greater at the equator and less at the polar region.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Weight of a body is lesser at the equator and greater at the polar region.
Question 4.
Turning a nut with a spanner having a short handle is so easy than one with a long handle.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Turning a nut with a spanner having a short handle is so harder than one with a long handle.
Question 5.
There is no gravity in the orbiting space station around the Earth. So the astronauts feel weightlessness.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: There is a gravity in the orbiting space station around the earth. Since space station and astronauts have equal acceleration. Both the astronauts and space station are in the state of weightlessness.
IV. Match the following.
Question 1.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Newton’s I law | (a) Propulsion of a rocket |
| 2. Newton’s II law | (b) Stable equilibrium of a body |
| 3. Newton’s III law | (c) Law of force |
| 4. Law of conservation of linear momentum | (d) Flying nature of a bird |
Answer:
1. (b) Stable equilibrium of a body
2. (c) Law of force
3. (d) Flying nature of a bird
4. (a) Propulsion of a rocket
V. Assertion & Reasoning
Mark the correct choice as
(a) If both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion: The sum of the clockwise moments is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments.
Reason: The principle of conservation of momentum is valid if the external force on the system is zero.
Answer:
(b) If both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 2.
- Assertion: The value of ‘g’ decreases as height and depth increase from the surface of the Earth.
- Reason: ‘g’ depends on the mass of the object and the Earth.
Answer:
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
VI. Answer briefly.
Question 1.
Define inertia. Give its classification.
Answer:
Inertia: The inherent property of a body to resist any change in its state of rest or the state of uniform motion, unless it is influenced upon by an external unbalanced force, is known as ‘inertia’.
Types of Inertia
- Inertia of rest
- Inertia of motion
- Inertia of direction
Question 2.
Classify the types of force based on their application.
Answer:
- Like parallel forces
- Unlike parallel forces
Question 3.
If a 5 N and a 15 N forces are acting opposite to one another. Find the resultant force and the direction of action of the resultant force.
Solution:
The two forces are unlike parallel forces
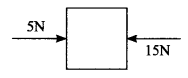
Let P = 5N, Q = 15N
Resultant force (R) = P – Q = 5 + (-15) = -10N
R = -10N.
The resultant force acting along the direction of “Q”.
Question 4.
Differentiate mass and weight.
Answer:
| Mass | Weight |
| The quantity of matter contained in the body | The gravitation force exerted on it due to the Earth’s gravity alone. |
| Scalar quantity | Vector quantity |
| Unit: Kg | Unit: N |
| Constant at all the places | Variable with respect to gravity. |
Question 5.
Define moment of a couple.
Answer:
Rotating effect of a couple is known as moment of a couple.
Moment of a couple = Force × perpendicular distance between the line of action of forces
M = F × S
Question 6.
State the principle of moments.
Answer:
When a number of like or unlike parallel forces act on a rigid body and the body is in equilibrium, then the algebraic sum of the moments in the clockwise direction is equal to the algebraic sum of the moments in the anticlockwise direction.
Question 7.
State Newton’s second law.
Answer:
“The force acting on a body is directly proportional to the rate of change of linear momentum of the body and the change in momentum takes place in the direction of the force”.
Question 8.
Why a spanner with a long handle is preferred to tighten screws in heavy vehicles?
Answer:
This is because turning effect to tighten the screws depends upon the perpendicular distance of the applied force from the axis of rotation is power arm. Larger the power armless is the force required to turn the screws. So spanner is provided with a long handle.
Question 9.
While catching a cricket ball the fielder lowers his hands backwards. Why?
Answer:
(i) When the fielder lowers his hands backwards, he increases the value of time of collision and so retardation is decreased.
(ii) Hence retarding force becomes lesser than before and the palm of the fielder is not hurt very much.
Question 10.
How does an astronaut float in a space shuttle?
Answer:
An astronaut float in a space shuttle because both are in the state of weightlessness. Both are experiencing equal acceleration towards earth as free fall bodies. Astronauts are not floating but falling freely.
VII. Solve the given problems.
Question 1.
Two bodies have a mass ratio of 3 : 4. The force applied to the bigger mass produces an acceleration of 12 ms-2. What could be the acceleration of the other body, if the same force acts on it?
Solution:
Mass ratio of the bodies = 3 : 4 and same force is (m1 : m2) acting on the body and a2 = 12 ms-2
∴ m1a1 = m2a2
\(\frac{m_{1}}{m_{2}}=\frac{a_{2}}{a_{1}} \Rightarrow \frac{3}{4}=\frac{a_{2}}{a_{1}}\)
\(a_{1}=\frac{4}{3} \times 12=16 \mathrm{ms}^{-2}\)
Question 2.
A ball of mass 1 kg moving with a speed of 10 ms-1 rebounds after a perfectly elastic collision with the floor. Calculate the change in linear momentum of the ball.
Solution:
Mass of a ball = 1 kg
Velocity of the bail before collision,
u = 10 m/s
Velocity of the ball after collision,
v = – u
= -10 m/s
Change in momentum,
P = m(v – u)
P = 1(-10 – 10)
= -20 kg m/s.
Question 3.
A mechanic unscrews a nut by applying a force of 140 N with a spanner of length 40 cm. What should be the length of the spanner if a force of 40 N is applied to unscrew the same nut?
Solution:
Given F1 = 140 N, d1 = 40 cm, F2 = 40 N, d2 = ?
In, both the cases, moment of forces applied are equal
F1d1 = F2d2
\(\begin{array}{l}{d_{2}=\left(\frac{F_{1}}{F_{2}}\right) d_{1}} \\ {d_{2}=40 \times \frac{140}{40}=140 \mathrm{cm}}\end{array}\)
Question 4.
The ratio of masses of two planets is 2 : 3 and the ratio of their radii are 4 : 7 Find the ratio of their accelerations due to gravity.
Solution:
The ratio of masses of two planets m1 : m2 = 2 : 3
The ratio of radii of two planets R1 : R2 = 4 : 7
Formula:
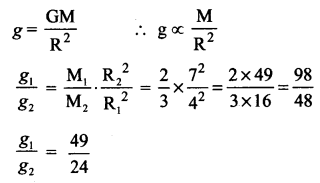
VIII. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
What are the types of inertia? Give an example for each type.
Answer:
Types of Inertia:
(i) Inertia of rest: The resistance of a body to change its state of rest is called inertia of rest. Eg: When you vigorously shake the branches of a tree, some of the leaves and fruits are detached and they fall down.
(ii) Inertia of motion: The resistance of a body to change its state of motion is called inertia of motion. Eg: An athlete runs some distance before jumping. Because, this will help him jump longer and higher.
(iii) Inertia of direction: The resistance of a body to change its direction of motion is called inertia of direction. Eg: When you make a sharp turn while driving a car, you tend to lean sideways.
Question 2.
State Newton’s laws of motion.
Answer:
Newton’s First Law: Everybody continues to be in its state of rest or the state of uniform motion along a straight line unless it is acted upon by some external force.
Newtons Second law: The force acting on a body is directly proportional to the rate of change of linear momentum of the body and the change in momentum takes place in the direction of the force.
Newtons Third Law: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. They always act on two different bodies.
Question 3.
Deduce the equation of a force using Newton’s second law of motion.
Answer:
“The force acting on a body is directly proportional to the rate of change of linear momentum of the body and the change in momentum takes place in the direction of the force”.
Let, ‘m’ be the mass of a moving body, moving along a straight line with an initial speed ‘u’ After a time interval of ‘t’, the velocity of the body changes to ‘v’ due to the impact of an unbalanced external force F.
Initial momentum of the body (Pi) = mu
Final momentum of the body (Pf) = mv
Change in momentum ∆p = Pf – Pi = mv – mu
By Newton’s second law of motion,
Force, F ∝ rate of change of momentum
F ∝ change in momentum / time
\(\begin{array}{l}{\mathrm{F} \propto \frac{m v-m u}{t}} \\ {\mathrm{F}=\frac{k m(v-u)}{t}}\end{array}\)
Here, k is the proportionality constant, k = 1 in all systems of units.
Hence, \(\mathrm{F}=\frac{m(v-u)}{t}\)
Since, acceleration = change in velocity / time,
a = (v – u)/t.
Hence, we have F = m × a
Force = mass × acceleration
- No external force is required to maintain the motion of a body moving with uniform velocity.
- When the net force acting on a body is not equal to zero, then definitely the velocity of the body will change.
- Thus, change in momentum takes place in the direction of the force. The change may take place either in magnitude or in direction or in both.
Question 4.
State and prove the law of conservation of linear momentum.
Answer:
(i) There is no change in the linear momentum of a system of bodies as long as no net external force acts on them.
(ii) Let us prove the law of conservation of linear momentum with the following illustration:
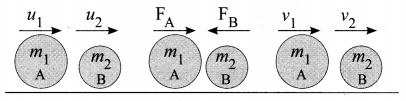
(iii) Let two bodies A and B having masses m1 and m2 move with initial velocity u1 and u2 in a straight line.
(iv) Let the velocity of the first body be higher than that of the second body. i.e., u1 > u2.
(v) During an interval of time t second, they tend to have a collision. After the impact, both of them move along the same straight line with a velocity v1 and v2 respectively.
Force on body B due to A,
\(\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{B}}=\frac{m_{2}\left[v_{2}-u_{2}\right]}{t}\)
Force on body A due to B,
\(\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{A}}=\frac{m_{1}\left[v_{1}-u_{1}\right]}{t}\)
By Newton’s III law of motion, Action force = Reaction force
FA = -FB
\(\begin{aligned} \frac{m_{1}\left[v_{1}-u_{1}\right]}{t} &=\frac{m_{2}\left[v_{2}-u_{2}\right]}{t} \\ m_{1} v_{1}+m_{2} v_{2} &=m_{1} u_{1}+m_{2} u_{2} \end{aligned}\)
The above equation confirms in the absence of an external force, the algebraic sum of the momentum after collision is numerically equal to the algebraic sum of the momentum before collision.
Hence the law of conservation linear momentum is proved.
Question 5.
Describe rocket propulsion.
Answer:
Propulsion of rockets is based on the law of conservation of linear momentum as well as Newton’s III law of motion. Rockets are filled with a fuel (either liquid or solid) in the propellant tank. When the rocket is fired, this fuel is burnt and a hot gas is ejected with a high speed from the nozzle of the rocket, producing a huge momentum. To balance this momentum, an equal and opposite reaction force is produced in the combustion chamber, which makes the rocket project forward.
While in motion, the mass of the rocket gradually decreases, until the fuel is completely burnt out. Since, there is no net external force acting on it, the linear momentum of the system is conserved. The mass of the rocket decreases with altitude, which results in the gradual increase in velocity of the rocket. At one stage, it reaches a velocity, which is sufficient to just escape from the gravitational pull of the Earth. This velocity is called escape velocity.
Question 6.
State the universal law of gravitation and derive its mathematical expression.
Answer:
This law states that every particle of matter in this universe attracts every other particle with a force. This force is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centres of these masses. The direction of the force acts along the line joining the masses.
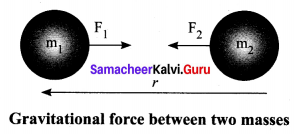
The force between the masses is always attractive and it does not depend on the medium where they are placed.
Let, m1 and m2 be the masses of two bodies A and B placed r metre apart in space.
Force F ∝ m1 × m2
F ∝ \(1 / r^{2}\)
On combining the above two expressions
\(\begin{array}{l}{\mathrm{F} \propto \frac{m_{1} \times m_{2}}{r^{2}}} \\ {\mathrm{F}=\frac{\mathrm{G} m_{1} m_{2}}{r^{2}}}\end{array}\)
Where G is the universal gravitational constant.
Its value in SI unit is 6.674 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2.
Question 7.
Give the applications of the universal law of gravitation.
Answer:
Application of Newton’s law of gravitation are:
(i) Dimensions of the heavenly bodies can be measured using the gravitation law. Mass of the Earth, radius of the Earth, acceleration due to gravity, etc., can be calculated with a higher accuracy.
(ii) Helps in discovering new stars and planets.
(Hi) Helps to explain germination of roots is due to the property of geotropism which is the property of a root responding to the gravity.
(iv) One of the irregularities in the motion of stars is called ‘Wobble’ lead to the disturbance in the motion of a planet nearby. In this condition the mass of the star can be calculated using the law of gravitation.
(v) Helps to predict the path of the astronomical bodies.
IX. HOT Questions.
Question 1.
Two blocks of masses 8 kg and 2 kg respectively, lie on a smooth horizontal surface in contact with one other. They are pushed by a horizontally applied force of 15 N. Calculate the force exerted on the 2 kg mass.
Solution:
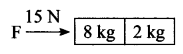
Given: m1 = 8 kg, m2 = 2 kg, F = 15 N
F = mtotal, F = (m1 + m2) a = (8 + 2) a = 10 a
15 = 10 a
⇒ a = \(\frac{15}{10}=\frac{3}{2}\) ms-2
Force exerted by mass of 8 kg
F = m1 a = \(8 \times \frac{3}{2}\) = 12 N.
Question 2.
A heavy truck and bike are moving with the same kinetic energy. If the mass of the truck is four times that of the bike, then calculate the ratio of their momenta. (Ratio of momenta = 1 : 2)
Solution:
Given: Let m1, m2 are the masses of truck and bike.
m1 = 4m2
Here kinetic energies of both truck and bike are same
\(\begin{aligned} m_{1} v_{1}^{2} &=m_{2} v_{2}^{2} \\ 4 m_{2} v_{1}^{2} &=m_{2} v_{2}^{2} \\ \frac{v_{1}}{v_{2}} &=\frac{1}{2} \\ v_{2} &=2 v_{1} \end{aligned}\)
Ratio of momenta: \(\frac{p_{1}}{p_{2}}=\frac{m_{1} v_{1}}{m_{2} v_{2}}=\frac{4 m_{2}}{m_{2}} \cdot \frac{v_{1}}{2 v_{1}}\) = 2
P1 : P2 = 2 : 1.
Question 3.
“Wearing a helmet and fastening the seat belt is highly recommended for the safe journey”.Justify your answer using Newton’s laws of motion.
Answer:
During the motion of car and two wheelers, when the brakes are applied, the vehicles slow down but our body tends to continue in the same state of motion due to inertia. So this may cause injury to passengers. Hence they are advised to wear a helmet and seat belt.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Laws of Motion Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
A cricketer catches a ball of mass 150 gm in 0.1s and which is moving with a speed of 20 ms-1, then he experiences the force of ____ _.
(a) 300 N
(b) 30 N
(c) 3 N
(d) 0.3 N.
Answer:
(b) 30 N
Hint: Impulse = change in momentum
F.∆t = mv – mu
\(\mathrm{F}=\frac{m v-m u}{\Delta t}\)
\(=\frac{150 \times 10^{-3} \times 20}{0.1}=30 \mathrm{N}\)
Question 2.
SI unit of force is:
(a) Dyne
(b) newton
(c) kgms-1
(d) Joule
Answer:
(b) newton
Question 3.
A coin is dropped in a lift. It takes time t1 to reach the floor, when the lift is stationary, it takes time t2, when the lift is moving up with constant acceleration, then ____ _.
(a) t1 > t2
(b) t1 < t2
(c) t1 = t2
(d) None.
Answer:
(a) t1 > t2
Question 4.
An unbalanced force acts on a body, the body:
(a) must remain at rest
(b) must be accelerated
(c) must move with uniform velocity
(d) move with uniform motion
Answer:
(b) must be accelerated
Question 5.
A satellite in its orbit around the earth is weightless on account of its _____.
(a) velocity
(b) momentum
(c) angular momentum
(d) acceleration.
Answer:
(c) angular momentum
Question 6.
When two or more forces acting on a body and the body does not change its position, then the forces are:
(a) imbalanced
(b) mechanical force
(c) balanced forces
(d) none
Answer:
(c) balanced forces
Question 7.
What would be the acceleration due to gravity at another planet, whose mass and radius core twice that of earth?
(a) g
(b) \(\frac{g}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{g}{4}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{g}{2}\)
Hint: We know that \(\mathrm{g}=\frac{\mathrm{GM}}{\mathrm{R}^{2}}\)
\(\frac{g_{1}}{g_{2}}=\frac{\left(\frac{\mathrm{GM}}{\mathrm{R}^{2}}\right)}{\left(\frac{\mathrm{G} .2 \mathrm{M}}{4 \mathrm{R}^{2}}\right)}\)
\(\frac{g_{1}}{g_{2}}=2 \quad \Rightarrow \quad g_{2}=\frac{1}{2} g_{1}\)
Question 8.
At sea level, the value of “g” is maximum at _____.
(a) the poles
(b) the equator
(c) 45° south latitude
(d) 45° north of longitude.
Answer:
(a) the poles
Question 9.
An object cannot change the state of rest or motion, until a force is applied. This inability of the object is called:
(a) inertia
(b) mass
(c) weight
(d) acceleration
Answer:
(a) inertia
Question 10.
The ability of a body to maintain its state of rest or motion is called ______.
(a) mechanics
(b) kinematics
(c) kinetics
(d) Inertia.
Answer:
(d) Inertia.
Question 11.
_____ deals with the bodies, which are at rest under the action of forces.
(a) Statics
(b) Dynamics
(c) Kinematics
(d) Kinetics.
Answer:
(a) Statics
Question 12.
A motor car starts from rest and moves after 5 seconds. If its velocity is 200 m/s then its acceleration is:
(a) 100 m/s²
(b) 40 m/s²
(c) 20 m/s²
(d) 80 m/s²
Answer:
(b) 40 m/s²
Question 13.
_____ deals with the motion of bodies considering the cause of motion.
(a) Force
(b) Dynamics
(c) Statics
(d) Kinetics.
Answer:
(d) Kinetics
Question 14.
Linear momentum = _____
(a) mass × velocity
(b) mass × distance
(c) distance × time
(d) \(\frac{\text { mass }}{\text { velocity }}\).
Answer:
(a) mass × velocity
Question 15.
The inability of the body to change its state is:
(a) force
(b) momentum
(c) acceleration
(d) inertia
Answer:
(d) inertia
Question 16.
Two or more forces of equal or unequal magnitude acting along the same direction, parallel to each other are called _____.
(a) like parallel forces
(b) unlike parallel forces
(c) resultant force
(d) balanced force.
Answer:
(a) like parallel forces
Question 17.
The axis of the fixed edge about which the thing is rotated is called as _____ .
(a) axis of rotation
(b) fixed axis rotation
(c) point of rotation
(d) Fixed point.
Answer:
(a) axis of rotation
Question 18.
When a net force acts on an object, the object will be accelerated in the direction of force with an acceleration proportional to:
(a) force on the object
(b) velocity
(c) mass
(d) inertia
Answer:
(a) force on the object
Question 19.
Rotating effect of a couple is known as ______ .
(a) product of forces
(b) the momentum of a couple
(c) mass
(d) momentum.
Answer:
(b) momentum of a couple
Question 20.
The amount of force required to produce an acceleration of 1 ms-2 in a body of mass _____ is called unit force.
(a) 10 kg
(b) 100 kg
(c) 1 kg
(d) 0 kg.
Answer:
(c) 1 kg
Question 21.
The acceleration of a body is due to:
(a) balance force
(b) electrostatic force
(c) unbalanced force
(d) conservative force
Answer:
(c) unbalanced force
Question 22.
Universal gravitational constant ______ .
(a) G = 6.684 × 10-10 Nm2 kg-1
(b) G = 7.4 × 1010 Nm2
(c) G = 6.623 × 1011 Nm2 kg-1
(d) G = 6.674 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2
Answer:
(d) G = 6.674 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2
Question 23.
Mean value of the acceleration due to gravity is ______ .
(a) 10.1 ms-2
(b) 8.8 ms-2
(c) 9.8 ms-2
(d) 9.8 ms.
Answer:
(c) 9.8 ms-2
Question 24.
The unit of weight is:
(a) kg
(b) g
(c) Newton
(d) ms-1
Answer:
(c) Newton
Question 25.
The value of accelaration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is _____ .
(a) 1.75 ms-1
(b) 3.8 ms-2
(c) 1.625 ms-2
(d) 1.625 ms-1
Answer:
(c) 1.625 ms-2
Question 26.
The unit of weight is _____ .
(a) kg m
(b) kg
(c) newton
(d) kg m-1
Answer:
(c) newton
Question 27.
The weight of a body is _____ poles than at the equatorial region.
(a) more
(b) less
(c) zero
(d) one.
Answer:
(a) more
Question 28.
In a collision between a heavier body and a lighter body, which body experiences greater force?
(a) heavier body
(b) lighter body
(c) both the body experience same force
(d) both body exchange acceleration
Answer:
(c) both the body experience same force
II. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
Turning a tap is an example of ____
Answer:
couple.
Question 2.
Torque is a _______ quantity.
Answer:
vector.
Question 3.
1 gf is equal to _____ dyne.
Answer:
980.
Question 4.
The resultant force acting on a body is equal to zero then the body will be in ______
Answer:
equilibrium.
Question 5.
The force equal to resultant but opposite in direction is ______
Answer:
equilibrate.
Question 6.
The product of force and time is ______
Answer:
impulse.
Question 7.
The force between the masses is always ______
Answer:
attractive.
Question 8.
The quantity of matter contained in the object is known as _____
Answer:
mass.
Question 9.
The magnitude of the universal gravitational constant is _____.
Answer:
6.674 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2
Question 10.
Propulsion of rockets is based on the ____ and ____
Answer:
Law of conservation of linear momentum & Newton’s third law.
Question 11.
Parallel unequal forces are acting in ______ directions.
Answer:
Opposite.
Question 12.
Torque and force are the ____ quantities.
Answer:
vector.
Question 13.
The unit of moment of a couple is _____ .
Answer:
newton metre (Nm).
Question 14.
A _____ enables you to manoeuvre a car easily by transferring a _______ to the wheels with less effort.
Answer:
steering wheel, torque.
Question 15.
_____ is required to produce the acceleration of a body.
Answer:
Force.
Question 16.
The acceleration is produced along the radius is called ______
Answer:
centripetal acceleration.
Question 17.
______ is equal to the magnitude of change in momentum.
Answer:
impulse.
Question 18.
A large force acting for a very short interval of time is called as ______ .
Answer:
impulse Force.
Question 19.
Mass of the earth _____
Answer:
5.972 × 1024 kg.
Question 20.
The relation between acceleration due to gravity (g) and the universal gravitational constant (G) is _____ .
Answer:
\(g=\frac{G M}{R^{2}}\).
III. State whether the following statements are true or false, correct the statement if it is false.
Question 1.
Rest and motion are interrelated terms.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
In the C.G.S. system, the unit of linear momentum is kg ms-1.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: In the C.G.S. system, the unit of linear momentum is g cms-1.
Question 3.
An external force is required to maintain the motion of a body moving with uniform velocity.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: No external force is required to maintain the motion of a body moving with uniform velocity.
Question 4.
The amount of force required for a body of mass 1 gram produces an acceleration of 1 cm s-2
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
By Newton’s III – law of motion, the action force is not equal to the reaction force.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: By Newton’s III – law of motion, the action force is equal to the reaction force.
Question 6.
The value of acceleration due to gravity (g) is not the same at all the points on the surface of the earth.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
The value of acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is 1.625 ms-2.
Answer:
True.
Question 8.
The regularities in the motion of stars are called ‘wobble’.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The irregularities in the motion of stars is called ‘wobble’.
Question 9.
Mechanics is divided into kinematics and kinetics.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Mechanics is divided into statics and dynamics.
Question 10.
Application of Newton’s law of gravitation helps to predict the path of the astronomical bodies.
Answer:
True.
IV. Match the following.
Question 1.
| 1. Linear momentum | (a) Mass and acceleration |
| 2. Force | (b) Change in momentum |
| 3. Moment of force | (c) GM/R2 |
| 4. Impulse | (d) Mass and velocity |
| 5. Acceleration due to gravity | (e) Force and perpendicular distance |
Answer:
1. (d) Mass and velocity
2. (a) Mass and acceleration
3. (e) Force and perpendicular distance
4. (b) Change in momentum
5. (c) GM/R2
Question 2.
| 1. Kinetics | (a) Causes the motion |
| 2. Kinematics | (b) In equilibrium |
| 3. Balanced force | (c) The motion of bodies without cause |
| 4. Unbalanced force | (d) The motion of bodies with cause |
Answer:
1. (d) The Motion of bodies with cause
2. (c) The Motion of bodies without cause
3. (b) In equilibrium
4. (a) Causes the motion
V. Assertion & Reasoning
Mark the correct choice as
(a) If both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion: At poles value of acceleration due to gravity (g) is greater than that of the equator.
Reason: Earth rotates on its axis in addition to revolving around the sun.
Answer:
(a) If both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 2.
Assertion: The force exerted by the earth on an apple is more than that exerted by apple on the earth.
Reason: The force on apple exerts on the earth is determined by the mass of the apple only.
Answer:
(d) The assertion is false but the reason is true
Question 3.
Assertion: A freely falling body is in the state of weightlessness
Reason: A body becomes conscious of its weight only when it is opposed
Answer:
(a) If both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 4.
Assertion: Newton’s third law of motion is applicable only when bodies are in motion.
Reason: Newton’s third law applies to all types of forces, e.g. gravitational, electric or magnetic forces.
Answer:
(d) The assertion is false but the reason is true.
Question 5.
Assertion: The apparent weight of the person is zero, in which condition or state is known as weightless.
Reason: When the person in a lift moves down with an acceleration (a) is equal to the acceleration due to gravity (g)
Answer:
(a) If both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 6.
Assertion: A gear is a circular wheel with teeth around its rim.
Reason: It helps to change the speed of rotation of a wheel by changing the force and helps to transmit power.
Answer:
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
Question 7.
Assertion: Mass of a body is defined as the gravitational force exerted on it due to earth’s gravity alone
Reason: Weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity.
Answer:
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Question 8.
Assertion: Weight is a vector quantity.
Reason: Direction of weight is always towards the centre of the earth.
Answer:
(a) If both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 9.
Assertion: Resultant force is equal to the vector sum of all the forces.
Reason: A system cannot be brought to equilibrium by applying another force.
Answer:
(b) If both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
VI. Answer briefly
Question 1.
Define Linear momentum.
Answer:
The product of mass and velocity of a moving body gives the magnitude of linear momentum. It acts in the direction of the velocity of the object. Linear momentum is a vector quantity.
Linear Momentum = mass × velocity.
Unit of momentum in SI system is Kg ms-1 and in C.G.S system its unit is g cm s-1
Question 2.
What is the resultant force?
Answer:
When several forces act simultaneously on the same body, then the combined effect of the multiple forces can be represented by a single force, which is termed as ‘resultant force’.
Question 3.
What is meant by equilibrant?
Answer:
A system can be brought to equilibrium by applying another force, which is equal to the resultant force in magnitude, but opposite in direction. Such force is called as ‘Equilibrant’.
Question 4.
Explain the Newton third law of motion with examples.
Answer:
‘For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. They always act in two different bodies’.
Example: When you fire a bullet, the gun recoils backwards and the bullet is moving forward (Action) and the gun equalises this forward action by moving backwards (Reaction).
Question 5.
How did the change in momentum achieve?
Answer:
Change in momentum can be achieved in two ways. They are:
- A large force acting for a short period of time and
- A smaller force acting for a longer period of time.
Question 6.
Define impulse.
Answer:
A large force acting for a very short interval of time is called as ‘Impulsive force’.When a force F acts on a body for a period of time t, then the product of force and time is known as ‘impulse’ represented by ‘J’
Impulse, J = F × t …….. (1)
By Newton’s second law
F = ∆p / t (A refers to change)
∆p = F × t ………. (2)
From (1) and (2)
J = ∆p
Impulse is also equal to the magnitude of change in momentum.
Its unit is kg ms-1 or Ns.
Question 7.
What is meant by free fall?
Answer:
- When the person in a lift moves down with an acceleration (a) equal to the acceleration due to gravity (g), i.e., when a = g, this motion is called as ‘free fall’.
- The apparent weight (R = m (g – g) = 0) of the person is zero. This condition or state refers to the state of weightlessness.
Question 8.
Define weightlessness.
Answer:
Whenever a body or a person falls freely under the action of Earth’s gravitational force alone, it appears to have zero weight. This state is referred to as ‘weightlessness’.
Question 9.
Explain the various causes of the apparent weight of a person in a moving lift.
Answer:
| Case 1: Lift is moving upward with an acceleration ‘a’ | Case 2: Lift is moving downward with an acceleration ‘a’ | Case 3: Lift is at rest. | Case 4: Lift is falling down freely |
| R – W = Fnet = ma ⇒ R = W + ma ⇒ R = mg + ma ⇒ R = m(g + a) |
W – R = Fnet = ma ⇒ R = W – ma ⇒ R = mg – ma ⇒ R = m(g – a) |
Here,the acceleration is zero a = 0 R = W R = mg |
Here,the acceleration is equal to g a = g R = m(g – g) = 0 |
| R > W | R < W | R = W | R = 0 |
| Apparent weight is greater than the actual weight. | Apparent weight is lesser than the actual weight. | Apparent weight is equal to the actual weight. | Apparent weight is equal to zero. |
Question 10.
Explain the variation of acceleration due to gravity.
Answer:
Variation of acceleration due to gravity (g):
- Since, g depends on the geometric radius of the Earth, (g ∝ 1 / R2), its value changes from one place to another on the surface of the Earth.
- The geometric radius of the Earth is maximum in the equatorial region and minimum in the polar region, the value of g is maximum in the polar region and minimum at the equatorial region.
- When you move to a higher altitude from the surface of the Earth, the value of g reduces.
- when you move deep below the surface of the Earth, the value of g reduces. Value of g is zero at the centre of the Earth.
Question 11.
Define one newton and one dyne.
Answer:
Definition of 1 newton (N): The amount of force required for a body of mass 1 kg produces an acceleration of 1 ms-2, 1 N = 1 kg ms-2
Definition of 1 dyne: The amount of force required for a body of mass 1 gram produces an acceleration of 1 cms-2, 1 dyne = 1 g cms-2; also 1 N = 105 dyne.
Question 12.
How can you measure the moment of the couple?
Answer:
(i) Rotating effect of a couple is known as the moment of a couple.
(ii) Moment of a couple is measured by the product of any one of the forces and the perpendicular distance between the line of action of two forces. The turning effect of a couple is measured by the magnitude of its moment.
(iii) Moment of a couple = Force × perpendicular distance between the line of action of forces
M = F × S
(iv) The unit of moment of a couple is newton metre (N m) in SI system and dyne cm in the CGS system.
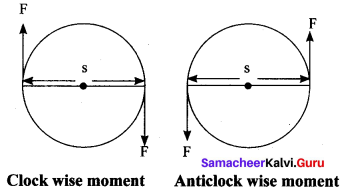
(v) By convention, the direction of moment of a force or couple is taken as positive if the body is rotated in the anti-clockwise direction and negative if it is rotating in the clockwise direction.
They are shown in Figures.
Question 13.
Define Torque.
Answer:
(i) The rotating or turning effect of a force about a fixed point or fixed axis is called the moment of the force about that point or torque (τ).
(ii) τ = F × d
(iii) Torque is a vector quantity.
(iv) Its SI unit is Nm.
VII. Answ er in detail.
Question 1.
Explain any three application of Torque.
Answer:
Application of Torque:
(i) Gears: A gear is a circular wheel with teeth around its rim. It helps to change the speed of rotation of a wheel by changing the torque and helps to transmit power.
(ii) Seasaw: Most of you have played on the seesaw. Since there is a difference in the weight of the persons sitting on it, the heavier person lifts the lighter person. When the heavier person comes closer to the pivot point (fulcrum) the distance of the line of action of the force decreases. It causes less amount of torque to act on it. This enables the lighter person to lift the heavier person.
(iii) Steering Wheel: A small steering wheel enables you to manoeuvre a car easily by transferring torque to the wheels with less effort.
Question 2.
State Newton’s third law. Explain it with three examples.
Answer:
Newton’s third law of motion: Newton’s third law states that ‘for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. They always act in two different bodies’.
If a body A applies a force FA on a body B, then the body B reacts with force FB on the body A, which is equal to FA in magnitude, but opposite in direction.
FB = -FA
Examples:
- When birds fly they push the air downwards with their wings (Action) and the air pushes the bird upwards (Reaction).
- When a person swims he pushes the water using the hands backwards (Action), and the water pushes the swimmer in the forward direction (Reaction).
- When you fire a bullet, the gun recoils backwards and the bullet is moving forward (Action) and the gun equalises this forward action by moving backwards (Reaction).
Question 3.
Derive the relation between ‘g’ and G. Explain how to determine the mass of earth.
Answer:
(i) Let us compute the magnitude of this force in two ways. Let, M be the mass of the Earth and m be the mass of the body.
(ii) The entire mass of the Earth is assumed to be concentrated at its centre.
(iii) The radius of the Earth is R = 6378 km (= 6400 km approximately). By Newton’s law of gravitation, the force acting on the body is given by
\(\mathrm{F}=\frac{\mathrm{GM} m}{\mathrm{R}^{2}}\) ….(1)
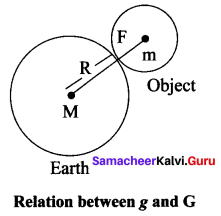
(iv) The radius of the body considered is negligible when compared with the Earth’s radius. Now, the same force can be obtained from Newton’s second law of motion.
(v) According to this law, the force acting on the body is given by the product of its mass and acceleration (called weight). Here, acceleration of the body is under the action of gravity hence a = g
F = ma = mg
F = weight = mg ……. (2)
Comparing equations J = F × t and ΔP = F × t, we get
\(m g=\frac{G M m}{R^{2}}\) …….. (3)
Acceleration due to gravity
\(g=\frac{\mathrm{GMm}}{\mathrm{R}^{2}}\) ……. (4)
Mass of the Earth (M):
Rearranging the equation (4), the mass of the Earth is obtained as follows:
Mass of the Earth M = g R2 / G
Substituting the known values of g, R and G, you can calculate the mass of the Earth as M = 5.972 × 1024 kg.
VIII. Problems.
Question 1.
A cricket ball of mass 0.5 kg strikes a bat normally with a velocity of 30 ms-1 and rebounds with a velocity of 20 ms-1 in the opposite direction, calculate the impulse of the force exerted by the ball on the bat.
Solution:
Impulse = change in momentum = mu – (-mv)
= m (u + v)
= 0.5 (30 + 20)
= 25 Ns
Question 2.
A force exerted on a body of mass 100 g changes its speed by 0.2 ms-1 in each second. Calculate the magnitude of the force.
Given, mass m = 100 g = 0.1 kg and acceleration a = 200 cms-2 = 0.2 ms-2.
Solution:
F = ma = 0.1 × 0.2 = 0.02 N.
Believing that the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 10th Science Chapter 1 Laws of Motion Questions and Answers learning resource will definitely guide you at the time of preparation. For more details about Tamilnadu State Board Class 10th Science Chapter 1 textbook solutions, ask us in the below comments and we’ll revert back to you asap.