Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Biology Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Biology Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts. Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 14 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2.30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio-Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
I. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Inner most layer of anther wall is _________.
(a) Endothecium
(b) Endothelium
(c) Epithelium
(d) Tapetum
Answer:
(d) Tapetum
Question 2.
Test cross involves ______.
(a) Crossing between two genotypes with recessive trait
(b) Crossing between two F1 hybrids
(c) Crossing between F1 hybrid with double recessive genotype
(d) Crossing between two genotypes with dominant trait
Answer:
(c) Crossing between F1 hybrid with double recessive genotype
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Gamma rays are generally used to induce mutation in wheat varieties.
Reason (R): Because they carry lower energy to non-ionize electrons from atom.
(a) A is correct. R is correct explanation of A.
(b) A is correct. R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct. R is wrong explanation of A
(d) A and R are wrong.
Answer:
(c) A is correct. R is wrong explanation of A
Question 4.
Self-ligation is prevented by ________.
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) Helicase
(c) Alkaline phosphate
(d) DNA lipase
Answer:
(c) Alkaline phosphate
Question 5.
Match the following:


Answer:
(a) 1- C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B
Question 6.
A Specific place in an ecosystem, where an organism lives and performs its functions is ______.
(a) habitat
(b) niche
(c) landscape
(d) biome
Answer:
(b) niche
![]()
Question 7.
Find the wrongly matched pair.
(a) Endemism – Species confined to a given region and not found anywhere else.
(b) Hotspots – Western ghats
(c) Ex-situ conservation – Zoological parks
(d) Sacred groves – Saintri hills of Rajasthan
(e) Alien species of India – Water hyacinth
Answer:
(d) Sacred groves – Saintri hills of Rajasthan
Question 8.
The plant source of Marijuana is ______.
(a) Andrographis paniculata
(b) Phyllanthus maderspatesis
(c) Cannabis sativa
(d) Papaver somniferum
Answer:
(c) Cannabis sativa
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
‘Pollination in Gymnosperms in different from Angiosperms’ – Give reasons.
Answer:
In gymnosperms, the ovules are exposed and the pollens are deposited directly on it. Hence the pollination is direct in gymnosperm. Whereas in angiosperms it is said to be indirect, as the pollens are deposited on stigma or the pistil.
![]()
Question 10.
A B C C B D E F G H I
From the above figure identify the type of mutation and explain it.
Answer:
In reverse tandem duplication, the duplicated segment is located immediately after the normal segment but the gene sequence other will be reversed.
Question 11.
Write the various steps involved in cell suspension culture.
Answer:
Step 1: Growing of cells/callus in medium (single or aggregates)
Step 2: Transfer of callus to a liquid medium
Step 3: Agitation of callus using rotary shaker
Step 4: Filtration and separation of cells.
Question 12.
Pyramid of energy is always upright. Give reasons.
Answer:
The energy pyramid represents a successive energy flow at each trophic level in an ecosystem. There is a gradual decrease in energy transfer at successive tropic levels from producers to higher levels, hence the pyramid of energy is always upright.
Question 13.
Write in brief about Atomic Garden.
Answer:
Atomic Garden: Is a form of mutation breeding where plants are exposed to radioactive sources typically cobalt-60 or caesium-137 in order to generate desirable mutation in crop plants.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain the law of dominance in monohybrid cross.
Answer:
Law of dominance states that the offsprings of an individual with contrasting (dissimilar) traits will only express the dominant trait in F1 generation and both the characters are expressed in F1 generation. This law also explains the proportion of 3 : 1 ratio in F2 generation.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Give an account on cytoplasmic inheritance
Answer:
DNA is the universal genetic material. Genes located in nuclear chromosomes follow Mendelian inheritance. But certain traits are governed either by the chloroplast or mitochondrial genes. This phenomenon is known as extra nuclear inheritance. It is a kind of Non-Mendelian inheritance. Since it involves cytoplasmic organelles such as chloroplast and mitochondrion that act as inheritance vectors, it is also called Cytoplasmic inheritance.
![]()
Question 16.
How will you identify a vector?
Answer:
- Vectors are able to replicate autonomously to produce multiple copies of them along with their DNA insert in the host cell.
- It should be small in size and of low molecular weight, less than 10 Kb (kilo base pair) in size so that entry/transfer into host cell is easy.
- Vector must contain an origin of replication so that it can independently replicate within the host.
- It should contain a suitable marker such as antibiotic resistance, to permit its detection in transformed host cell.
- Vector should have unique target sites for integration with DNA insert and should have the ability to integrate with DNA insert it carries into the genome of the host cell. Most of the commonly used cloning vectors have more than one restriction site. These are Multiple Cloning Site (MCS) or polylinker. Presence of MCS facilitates the use of restriction enzyme of choice.
Question 17.
What is Albedo effect? Write its effects.
Answer:
Gases let out to atmosphere causes climatic change. Emission of dust and aerosols from industries, automobiles, forest fire, SO2 and DMS (dimethyl sulphur) play an important role in disturbing the temperature level of any region. Aerosols with small particles is reflecting the solar radiation entering the atmosphere. This is known as Albedo effect.
Question 18.
Ozone acts as a natural sun screen- Justify.
Answer:
Ozone depletion in the stratosphere results in more UV radiations especially UV B radiations (shortwaves). UV B radiation destroys biomolecules (skin ageing) and damages living tissues. UV – C is the most damaging type of UV radiation, but it is completely filtered by the atmosphere (ozone layer). UV – a contribute 95% of UV radiation which causes tanning burning of skin and enhancing skin cancer. Hence the uniform ozone layer is critical for the well being of life on earth.
![]()
Question 19.
Which is called as “The King of Bitters”? Mention their medicinal importance.
Answer:
Andrographis paniculata is called as King of Bitters. Andrographis is a potent hepatoprotective agent and is widely used to treat liver disorders. Concoction of Andrographis paniculata and eight other herbs (Nilavembu Kudineer) is effectively used to treat malaria and dengue.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
(a) With a suitable diagram, explain the structure of an ovule.
Answer:
Structure of ovule(Megasporangium):
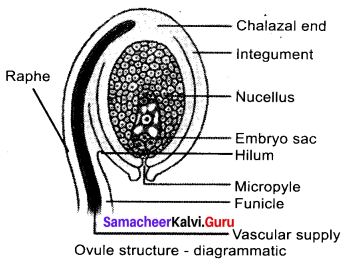
Ovule is also called megasporangium and is protected by one or two covering called integuments. Amature ovule consists of a stalk and a body. The stalk or the funiculus (also called funicle) is present at the base and it attaches the ovule to the placenta. The point of attachment of funicle to the body of the ovule is known as hilum. It represents the junction between ovule and funicle. In an inverted ovule, the funicle is adnate to the body of the ovule forming a ridge called raphe.
The body of the ovule is made up of a central mass of parenchymatous tissue called nucellus which has large reserve food materials. The nucellus is enveloped by one or two protective coverings called integuments. Integument encloses the nucellus completely except at the top where it is free and forms a pore called micropyle. The ovule with one or two integuments are said to be unitegmic or bitegmic ovules respectively.
The basal region of the body of the ovule where the nucellus, the integument and the funicle meet or merge is called as chalaza. There is a large, oval, sac-like structure in the nucellus toward the Raphe micropylar end called embryo sac or female \ gametophyte. It develops from the functional \ megaspore formed within the nucellus. In some species(unitegmic tenuinucellate) the inner layer of the integument may become specialized to perform the nutritive function for the embryo sac and is called as endothelium or integumentary tapetum (Example : Asteraceae).
[OR]
(b) List out the significance of ploidy.
Answer:
- Many polyploids are more vigorous and more adaptable than diploids.
- Many ornamental plants are autotetraploids and have larger flower and longer flowering duration than diploids.
- Autopolyploids usually have increase in fresh weight due to more water content.
- Aneuploids are useful to determine the phenotypic effects of loss or gain of different chromosomes.
- Many angiosperms are allopolyploids and they play a role in an evolution of plants.
![]()
Question 21.
(a) Explain the basic concepts involved in plant tissue culture.
Answer:
Basic concepts of plant tissue culture are totipotency, differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation.
Totipotency: The property of live plant cells that they have the genetic potential when cultured in nutrient medium to give rise to a complete individual plant.
Differentiation: The process of biochemical and structural changes by which cells become specialized in form and function.
Redifferentiation: The further differentiation of already differentiated cell into another type of cell. For example, when the component cells of callus have the ability to form a whole plant in a nutrient medium, the phenomenon is called redifferentiation.
Dedifferentiation: The phenomenon of the reversion of mature cells to the meristematic state leading to the formation of callus is called dedifferentiation. These two phenomena of redifferentiation and dedifferentiation are the inherent capacities of living plant cells or tissue. This is described as totipotency.
[OR]
(b) Write a comparative note on Carbon Foot Print (CFP)
Answer:
Every human activity leaves a mark just like our footprint. This Carbon foot print is the total amount of green house gases produced by human activities such as agriculture, industries, deforestation, waste disposal, buring fossil fuels directly or indirectly. It can be measured for an individual, family, organisation like industries, state level or national level. It is usually estimated and expressed in equivalent tons of CO2 per year.
The burning of fossil fuels releases CO2 and other green house gases. In turn these emissions trap solar energy and thus increase the global temperature resulting in ice melting, submerging of low lying areas and inbalance in nature like cyclones, tsunamis and extreme weather conditions. To reduce the carbon foot print we can follow some practices like
- Eating indigenous fruits and products
- Reduce use of your electronic devices
- Reduce travelling
- Do not buy fast and preserved, processed, packed foods
- Plant a garden
- Less consumption of meat and sea food. Poultry requires little space, nutrients and less pollution comparing cattle farming
- reduce use of Laptops (when used for 8 hours, it releases nearly 2 kg. of CO2 annually)
- Line dry your clothes.
(Example: If you buy imported fruit like kiwi, indirectly it increases CFP. How? The fruit has travelled a long distance in shipping or airliner thus emitting tons of CO2)
Bio-Zoology [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Match the following:


Answer:
(a) 1 – C, 2 – D, 3 – B, 4 – A
Question 2.
The male sex hormone testosterone is secreted from ___________.
(a) Sertoli cells
(b) Leydig cells
(c) Epididymis
(d) Prostate gland
Answer:
(b) Leydig cells
![]()
Question 3.
Select the incorrect action of hormonal contraceptive pills from the following
(a) Inhibition of spermatogenesis
(b) Inhibition of ovulation
(c) Changes in cervical mucus impairing its ability to allow passage and transport of sperm
(d) Alteration in uterine endometrium to make it unsustainable for implantation
Answer:
(a) Inhibition of spermatogenesis
Question 4.
Father of a child is colour blind and mother is carrier for colour blindness, the possibility of the child being colour blind is ________.
(a) 25 %
(b) 50%
(c) 100 %
(d) 75 %
Answer:
(b) 50%
Question 5.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events with reference to the central dogma?
(a) Transcription, Translation, Replication
(b) Transcription, Replication, Translation
(c) Duplication, Translation, Transcription
(d) Replication, Transcription, Translation
Answer:
(d) Replication, Transcription, Translation
Question 6.
Who proposed the Germplasm theory?
(a) August Weismann
(b) Darwin
(c) Lamarck
(d) Alfred Wallace
Answer:
(a) August Weismann
Question 7.
AIDS virus has ________.
(a) Single stranded RNA
(b) Single stranded DNA
(c) Double stranded RNA
(d) Double stranded DNA
Answer:
(c) Double stranded RNA
![]()
Question 8.
Assertion (A): Streptomycin is an antibiotic
Reason (R): Antibiotics are microbial products inhibits the growth of pathogenic microbe.
(a) A is right, R is wrong
(b) R explain A
(c) A and R are wrong
(d) A and R are right. R does not explain A
Answer:
(b) R explain A
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
What is inhibin? State its functions.
Answer:
Inhibin is a hormone secreted by Sertoli cells of testes which is involved in the negative feedback control of sperm production.
![]()
Question 10.
Define criss-cross inheritance.
Answer:
Inheritance of genes from a male parent to female child and then to male grandchild or female parent to male child and then to female grandchild, eg., X-linked gene inheritance.
Question 11.
How does mutation theory of De vries differ from lamarck and Darwins view in the origin of new species.
Answer:
According to de Vries, sudden and large variations were responsible for the origin of new species, whereas Lamarck and Darwin believed in gradual accumulation of all variations as the causative factors in the origin of new species.
Question 12.
What is biological oxygen demand?
Answer:
The BOD (Biochemical oxygen demand or Biological oxygen demand). BOD refers to the amount of the oxygen that would be consumed, if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidized by bacteria. The sewage water is treated till the BOD is reduced. The greater the BOD of the waste water more is its polluting potential.
Question 13.
Differentiate between Eurytherms and Stenotherms.
Answer:
|
Eurytherms |
Stenotherms |
| Organism that can tolerate wide range of temperature. eg: Human beings |
Organism that can tolerate narrow range of temperature. eg: Fish |
![]()
Question 14.
Name the secondary pollutant in photochemical smog. Mention the adverse effect.
Answer:
Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) is a secondary pollutant present in photochemical smog. It is thermally unstable and decomposes into peroxy ethanol radicals and nitrogen dioxide gas causing eye irritation.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
What is amniocentesis? Why a statutory ban is imposed on this technique?
Answer:
Amniocentesis is a prenatal technique used to detect any chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus and it is being often misused to determine the sex of the foetus. Once the sex of the foetus is known, there may be a chance of female foeticide. Hence, a statutory ban on amniocentesis is imposed.
![]()
Question 16.
DNA acts as genetic material for majority of living organisms and not the RNA. Give reasons to support the statement.
Answer:
- RNA was reactive and hence highly unstable.
- Some RNA molecules acts as gene regulators by binding to DNA and affect gene expression.
- Uracil of RNA is less stable than thymine of DNA.
Question 17.
Draw and lable the structure of Immunoglobulin
Answer:
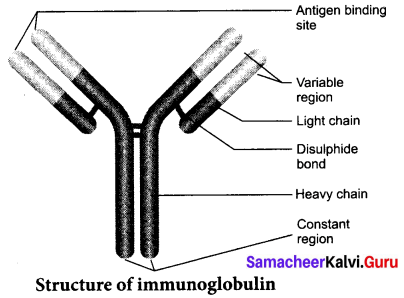
Question 18.
Explain how “Rosie” is different from a normal cow.
Answer:
Rosie was the first transgenic cow. It produced human protein enriched milk, which contained the human alpha lactalbumin (2.4 gm. /litre). This milk was a nutritionally balanced food for infants than the normal milk of cows.
![]()
Question 19.
Extinction of a keystone species led to loss of biodiversity – Justify.
Answer:
A keystone species is an organism that helps define an entire ecosystem. Without the keystone species a particular ecosystem would be dramatically disturbed or even ceased. Keystone species either directly or indirectly affects every species in a particular ecosystem. If a keystone species is lost or removed no other organism would compensate its ecological niche.
eg: Jaguar is a keystone species. As a top predator, it plays a crucial role in ecosystem. Without jaguar there is an exponential increase in herbivoral population that would decimate the plants of the ecosystem. At one point even the herbivore populations also get declined due to the lack of vegetation. Thus jaguar acts a keystone species.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
(a) Define menstrual cycle. Explain its various phase.
Answer:
Menstrual cycle: The menstrual or ovarian cycle occurs approximately once in every 28/29 days during the reproductive life of the female from menarche (puberty) to menopause except during pregnancy. The cycle of events starting from one menstrual period till the next one is called the menstrual cycle during which cyclic changes occurs in the endometrium, every month. Cyclic menstruation is an indicator of normal reproductive phase.
Menstrual cycle comprises of the following phases
- Menstrual phase
- Follicular or proliferative phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Luteal or secretory phase
1. Menstrual phase: The cycle starts with the menstrual phase when menstrual flow occurs and lasts for 3-5 days. Menstrual flow is due to the breakdown of endometrial lining of the uterus, and its blood vessels due to decline in the level of progesterone and oestrogen. Menstruation occurs only if the released ovum is not fertilized. Absence of menstruation may be an indicator of pregnancy. However it could also be due to stress, hormonal disorder and anaemia.
2. Follicular or proliferative phase: The follicular phase extends from the 5th day of the cycle until the time of ovulation. During this phase, the primary follicle in the ovary grows to become a fully mature Graafian follicle and simultaneously, the endometrium regenerates through proliferation.
These changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by the secretion of gonadotropins like FSH and LH, which increase gradually during the follicular phase. It stimulates follicular development and secretion of oestrogen by the follicle cells.
3. Ovulatory phase: Both LH and FSH attain peak level in the middle of the cycle (about the 14th day). Maximum secretion of LH during the mid cycle called LH surge induces the rupture of the Graafian follicle and the release of the ovum (secondary oocyte) from the ovary wall into the peritoneal cavity. This process is called as ovulation.
4. Luteal or secretory phase: During luteal phase, the remaining part of the Graafian follicle is transformed into a transitory endocrine gland called corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone which is essential for the maintenance of the endometrium. If fertilization takes place, it paves way for the implantation of the fertilized ovum. The uterine wall secretes nutritious fluid in the uterus for the foetus. So, this phase is also called as secretory phase.
During pregnancy all events of menstrual cycle stop and there is no menstruation. In the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum degenerates completely and leaves a scar tissue called corpus albicans. It also initiates the disintegration of the endometrium leading to menstruation, marking the next cycle. ,
[OR]
(b) Write the salient features of genetic code.
Answer:
The salient features of genetic code are as follows:
1. The genetic codon is a triplet code and 61 codons code for amino acids and 3 codons do not code for any amino acid and function as stop codon (Termination).
2. The genetic code is universal. It means that all known living systems use nucleic acids and the same three base codons (triplet codon) direct the synthesis of protein from amino acids. For example, the mRNA (UUU) codon codes for phenylalanine in all cells of all organisms. Some exceptions are reported in prokaryotic, mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. However similarities are more common than differences.
3. A non-overlapping codon means that the same letter is not used for two different codons. For instance, the nucleotide sequence GUU and GUC represents only two codons. .
4. It is comma less, which means that the message would be read directly from one end to the other i.e., no punctuation are needed between two codes. .
5. A degenerate code means that more than one triplet codon could code for a specific amino acid. For example, codons GUU, GUC, GUA and GUG code for valine.
6. Non-ambiguous code means that one codon will code for one amino acid.
7. The code is always read in a fixed direction i.e., from 5’ → 3’ direction called polarity.
8. AUG has dual functions. It acts as a initiator codon and also codes for the amino acid methionine.
9. UAA, UAG (tyrosine) and UGA (tryptophan) codons are designated as termination (stop) codons and also are known as “non-sense” codons.
![]()
Question 21.
(a) Suggest some of the ways to prevent drug and alcohol abuse.
Answer:
1. Effectively dealing with peer pressure:
The biggest reason for teens to start on drugs is due to their friends / peer groups imposing pressure on them. Hence, it is important to have a better group of friends to avoid such harmful drugs and alcohol.
2. Seeking help from parents and peers:
Help from parents and peer group should be sought immediately so that they can be guided appropriately. Help may even be sought from close and trusted friends. Getting proper advice to sort out their problems would help the young to vent their feelings of anxiety and guilt.
3. Education and counselling:
Education and counselling create positive attitude to deal with many problems and to accept disappointments in life.
4. Looking for danger signs:
Teachers and parents need to look for sign that indicate tendency to go in for addiction.
5. Seeking professional and medical assistance:
Assistance is available in the form of highly qualified psychologists, psychiatrists and de-addiction and rehabilitation programmes to help individuals to overcome their problems.
[OR]
(b) Mention the advantages and disadvantages of cloning.
Answer:
- Offers benefits for clinical trials and medical research. It can help in the production of
proteins and drugs in the field of medicine. - Aids stem cell research.
- Animal cloning could help to save endangered species.
- Animal and human activists see it as a threat to biodiversity saying that this alters evolution which will have an impact on populations and the ecosystem.
- The process is tedious and very expensive.
- It can cause animals to suffer.
- Reports show that animal surrogates were manifesting adverse outcomes and cloned animals were affected with disease and have high mortality rate.
- It might compromise human health through consumption of cloned animal meat.
- Cloned animals age faster than normal animals and are less healthy than the parent organism as discovered in Dolly
- Cloning can lead to occurrence of genetic disorders in animals.
- More than 90% of cloning attempts fail to produce a viable offspring.