You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.1
Question 1.
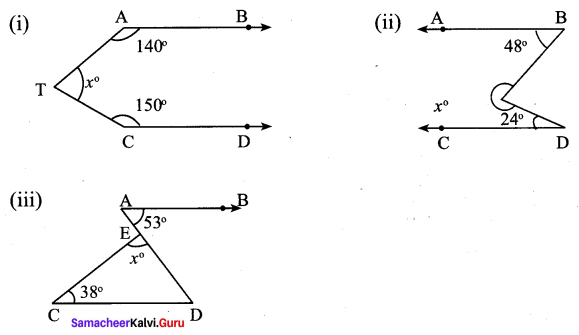
In the figure, AB is parallel to CD, find x
Solution:
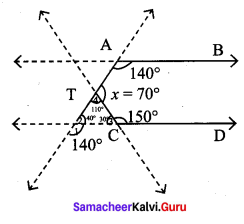
(i) From the figure
∠1 = 140° (∴ corresponding angles are equal)
∠2 = 40° (∴ ∠1 + ∠2= 180°)
∠3 = 30° (∵ ∠3 + 150= 180°)
∠4 = 110° (∵ ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 = 180°)
∴ ∠x = 70° (∵ ∠4 + ∠x = 180°)
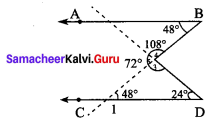
(ii) From the figure
∠1 = 48°
∠3 = 108° (∠1 +24° + ∠3 = 180°)
∠4 = 108° (If two lines are intersect, then the vertically the opposite angles are equal)
∠5 = 72° (∵ ∠3 + ∠5 = 180°)
∴ ∠3 + ∠4 + ∠5 = 108° + 108° + 72°
x = 288°
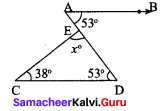
(iii) From the figure
∠D = 53° ( ∵ ∠B and ∠D are alternate interior angles)
Sum of the three angles of a triangle is 180°
∠x° = 180°- (38°+ 53°)
= 180°- 91° = 89°
Question 2.
The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3, find the measure of each angle of the triangle.
Solution:
Let the angles be x, 2x and 3x respectively.
Sum of the three angles of a triangle = 180°
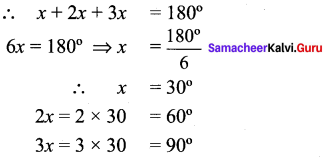
The 3 angles of the triangle are 30°, 60°, 90°.
Question 3.
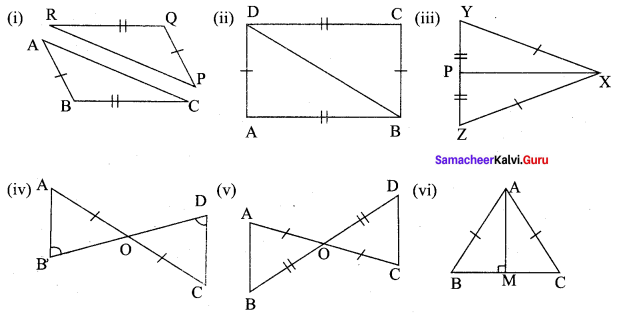
Consider the given pairs of triangles and say whether each pair is that of congruent triangles. If the triangles are congruent, say ‘how’; if they are not congruent say ‘why’ and also say if a small modification would make them congruent:
Solution:
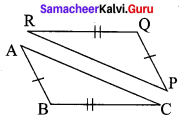
(i) Consider ∆PQR and ∆ABC
Given, RQ = BC
PQ = AB
∆ABC is not congruent to ∆PQR
If PR = AC, then ∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR
(ii) Consider ∆ABD and ∆BCD for the triangles to be congruent.
Given, AB = DC
AD = BC and AB is common side.
∴ By SSS rule ∆ABD ≅ ∆BCD.
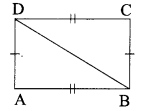
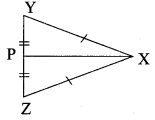
(iii) Consider ∆PXY and ∆PXz,
Given, XY = XZ
PY = PZ and PX is common
∴ By SSS rule ∆PXY ≅ ∆PXZ.
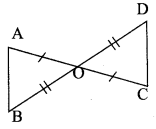
(iv) Consider ∆OAB and ∆ODC,
Given, OA = OC
∠ABO = ∠ODC and ∠AOB = ∠DOC (vertically opposite angles)
∴ By AAS rule, AOAB = AODC.
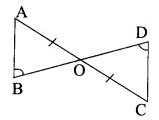
(v) Consider ∆AOB and ∆DOC,
Given, AO = OC
OB = OD
![]()
and ∠AOB = ∠DOC [vertically opposite angles]
∴ By SAS rule, ∆AOB = ∆DOC.
(vi) Consider ∆AMB and ∆AMC,
Given, AB = AC
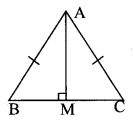
∠AMB = ∠AMC = 90°
∴ AM is common.
∴ By RHS rule
∆AMB ≅ ∆AMC.
Question 4.
∆ABC and ∆DEF are two triangles in which AB = DF, ∠ACB = 70°, ∠ABC = 60°; ∠DEF = 70° and ∠EDF = 60°. Prove that the triangles are congruent.
Solution:
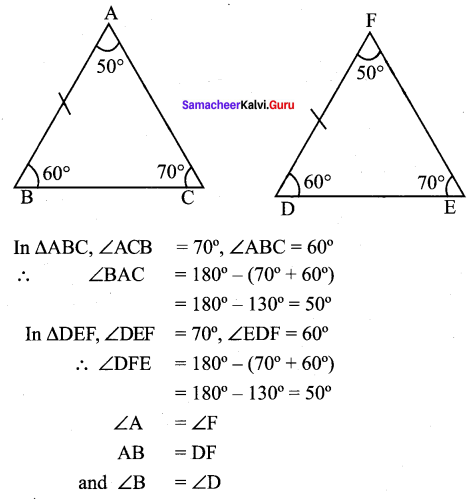
∴ By ASA rule ∆ABC ≅ ∆FDE
Question 5.
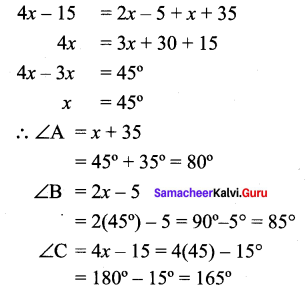
Find all the three angles of the ∆ABC
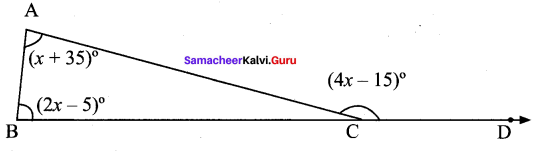
Solution:
Exterior angle = Sum of the two opposite interior angles.