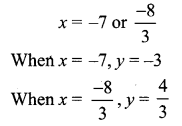You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Complex Numbers Ex 2.4
Question 1.
Write the following in the rectangular form:
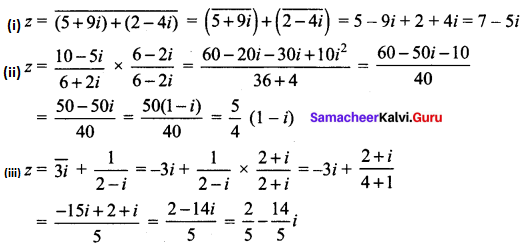
(i) \(\overline{(5+9 i)+(2-4 i)}\)
(ii) \(\frac{10-5 i}{6+2 i}\)
(iii) \(\overline{3 i}+\frac{1}{2-i}\)
Solution:
Question 2.
If z = x + iy, find the following in rectangular form.
(i) Re(\(\frac{1}{z}\))
(ii) Re(i\(\bar{z}\))
(iii) Im(3z + 4\(\bar{z}\) – 4i)
Solution:
(i) Re(\(\frac{1}{z}\)) = Re(\(\frac{1}{x+i y} \times \frac{x-i y}{x-i y}\))
= Re(\(\frac{x-i y}{x^{2}+y^{2}}\))
= \(\frac{x}{x^{2}+y^{2}}\)
(ii) Re(i\(\bar{z}\)) = Re[i(\(\overline{x+i y}\))]
= Re(ix + y)
= y
(iii) Im(3z + 4\(\bar{z}\) – 4i)
= Im (3(x + iy) + 4(x – iy) – 4i)
= Im (3x + 3iy + 4x – 4iy – 4i)
= Im (3x + 4 + i (3y – 4y – 4)
= Im (3x + 4x + i(-y – 4))
= Im [7x + i(-y – 4)]
= -y – 4
= -(y + 4)
![]()
Question 3.
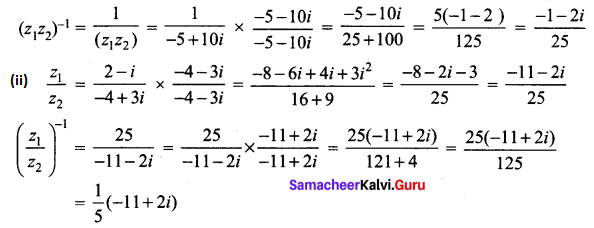
If z1 = 2 – i and z2 = -4 + 3i, find the inverse of z1 z2 and \(\frac{z_{1}}{z_{2}}\)
Solution:
z1 = 2 – i, z2 = -4 + 3i
(i) z1 z2 = (2 – i) (-4 + 3i)
= (-8 + 6i + 4i – 3 i2)
= (-8 + 10i + 3)
= (-5 + 10i)
Question 4.
The complex numbers u, v, and w are related by \(\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{w}\). If v = 3 – 4i and w = 4 + 3i, find u in rectangular form.
Solution:
v = 3 – 4i, w = 4 + 3i = i (3 – 4i)
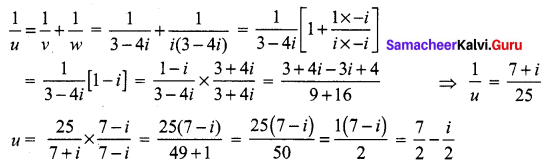
Question 5.
Prove the following properties:
(i) z is real if and only if z = \(\bar{z}\)
(ii) Re(z) = \(\frac{z+\bar{z}}{2}\) and Im(z) = \(\frac{z-\bar{z}}{2 i}\)
Solution:
(i) z is real iff z = \(\bar{z}\)
Let z = x + iy
z = \(\bar{z}\)
⇒ x + iy = x – iy
⇒ 2iy = 0
⇒ y = 0
⇒ z is real.
z is real iff z = \(\bar{z}\)
(ii) \(\frac{z+\bar{z}}{2 i}=\frac{x+i y+x-i y}{2}=\frac{2 x}{2}=x\)
Real part of z = x
(iii) \(\frac{z-\bar{z}}{2 i}=\frac{(x+i y)-(x-i y)}{2 i}=\frac{x+i y-x+i y}{2 i}=\frac{2 i y}{2 i}=y\)
Im part of z = y.
Question 6.
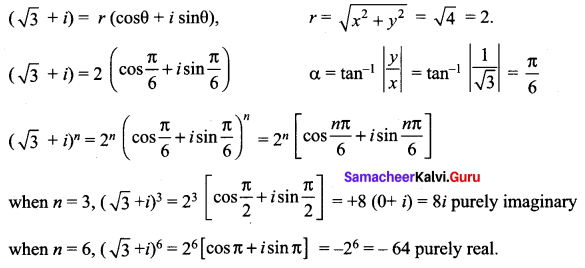
Find the least value of the positive integer n for which (√3 + i)n
(i) real
(ii) purely imaginary
Solution:
(√3 + i)n
(√3 + i)2
= 3 – 1 + 2√3 i
= (2 + 2 √3 i)
(√3 + i)3 = (√3 + i)2 (√3 + i)
= (2 + 2√3 i) (√3 + i)
= 2√3 + 2i + 6i – 2√3
(√3 + i) = 8i ⇒ purely Imaginary when n = 3
(√3 + i)4 = (√3 + i)3 (√3 + i)
= 8i (√3 + i)
= (-8 + 8√3 i)
(√3 + i)5 =(√3 + i)4 (√3 + i)
= (-8 + 8√3 i) (√3 + i)
= -8√3 – 8i + 24i – 8√3
= -16√3 + 16i
(√3 + i)6 = (√3 + i)5 (√3 + i)
= (√3 + i) (-16√3 + 16i)
= 16 (√3 + i) (-√3 + i)
= 16 (-3 + i√3 – i√3 – 1)
= -64 purely real when n = 6
Another Method:
![]()
Question 7.
Show that
(i) (2 + i√3)10 – (2 – i√3)10 is purely imaginary
(ii) \(\left(\frac{19-7 i}{9+i}\right)^{12}+\left(\frac{20-5 i}{7-6 i}\right)^{12}\)
Solution:
(i) (2 + i√3)10 – (2 – i√3)10
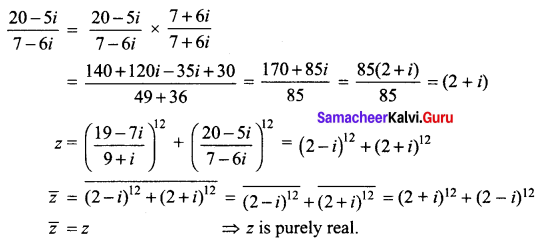
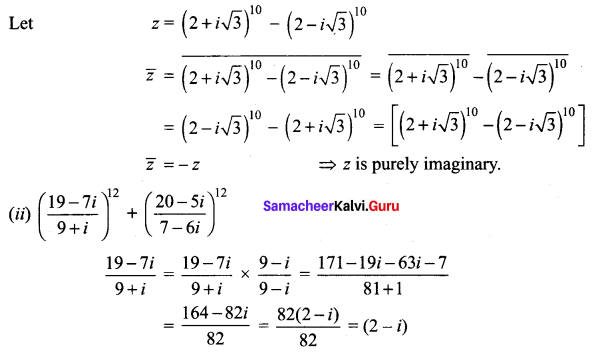
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Complex Numbers Ex 2.4 Additional Problems
Question 1.
Express the following in the standard form a + ib.
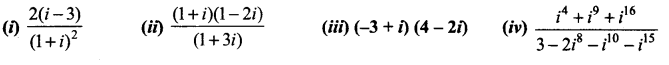
Solution:

Question 2.
Find the least positive integer n such that 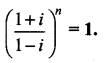
Solution:
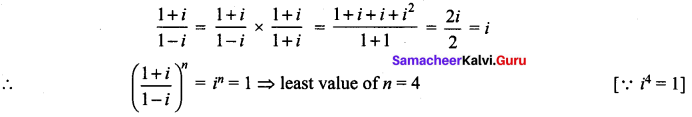
![]()
Question 3.
Find the real values of x and y for which the following equations are satisfied.
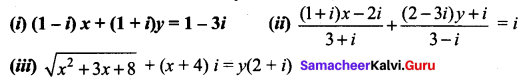
Solution:
(i) (1 – i)x + (1 + i)y = x – ix + y + iy
= (x + y) + i (y – x) = 1 – 3i (given)
So, equating their RP and IP we get,

Take real part, we get
i.e., 3x + (x – 2) + 6y – (1 – 3y) = 0
⇒ 3x + x – 2 + 6y – 1 + 3y = 0
4x + 9y = 3 …….. (1)
Take imaginary part, we get
3(x – 2) – x + 3 (1 – 3y) + 2y = 10
⇒ 3x – 6 – x + 3 – 9y + 2y = 10
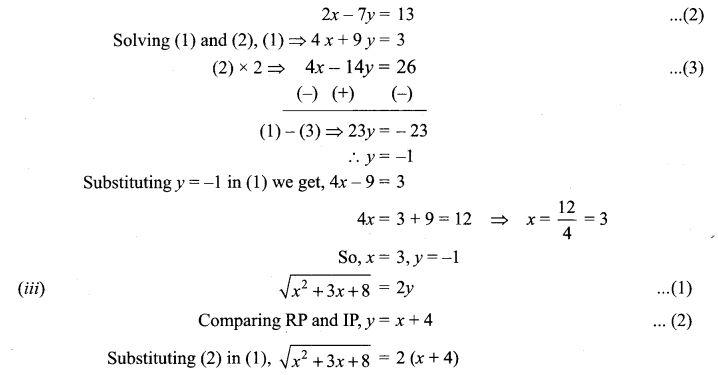
Squaring on both sides, x2 + 3x + 8 = 4 (x + 4)2
i.e., x2 + 3x +8 = 4 (x2 + 8x +16) ⇒ 4x2 + 32x + 64 – x2 – 3x – 8 = 0
3x2 + 29x + 56 = 0
3x2 + 21x + 8x + 56 = 0
(x + 7) (3x + 8) = 0