You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Ordinary Differential Equations Ex 10.9
Choose the correct or the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives:
Question 1.
The order and degree of the differential equation 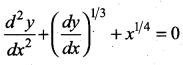 are respectively ………
are respectively ………
(a) 2, 3
(b) 3, 3
(c) 2, 6
(d) 2, 4
Solution:
(a) 2, 3
Hint:
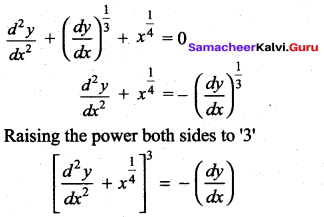
Order = 2,
degree = 3
Question 2.
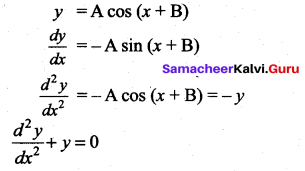
The differential equation representing the family of curves y = A cos (x + B), where A and B
are parameters, is …….
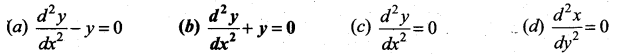
Solution:
(b) \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}+y=0\)
Hint:
![]()
Question 3.
The order and degree of the differential equation ![]() is …..
is …..
(a) 1, 2
(b) 2, 2
(c) 1, 1
(d) 2, 1
Solution:
(c) 1, 1
Hint:
![]()
Since, the first order derivatives are involved, Order = 1 and degree 1.
Question 4.
The order of the differential equation of all circles with centre at (h, k) and radius ‘a’ is …….
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 1
Solution:
(a) 2
Hint:
Equation of circle is (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = a2
Equation is to be differentiated twice as two parameters are given.
∴ Order = 2
Question 5.
The differential equation of the family of curves y = Aex + Be-x, where A and B are arbitrary constants is ……
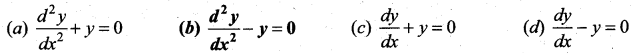
Solution:
\(\frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}-y=0\)
Hint:
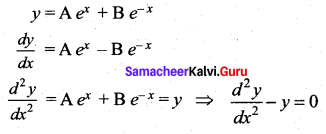
Question 6.
The general solution of the differential equation 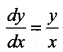 is …..
is …..
(a) xy = k
(b) y = k log x
(c) y = kx
(d) log y = kx
Solution:
(c) y = kx
![]()
Question 7.
The solution of the differential equation 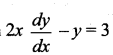 represents ……..
represents ……..
(a) straight lines
(b) circles
(c) parabola
(d) ellipse
Solution:
(c) parabola
Hint:
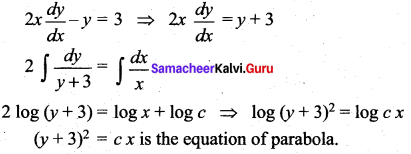
![]()
Question 8.
The solution of ![]() is …….
is …….
![]()
Solution:
(b) \(y=c e^{-\int \mathbf{P} d x}\)
Hint:
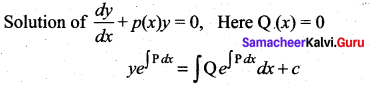
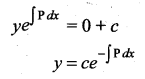
Question 9.
The integrating factor of the differential equation 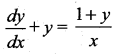 is …….
is …….

Solution:
(b) \(\frac{e^{x}}{x}\)
Hint:
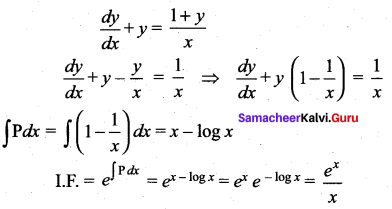
![]()
Question 10.
The integrating factor of the differential equation 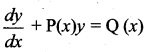 is x, then P(x) …………
is x, then P(x) …………

Hint:
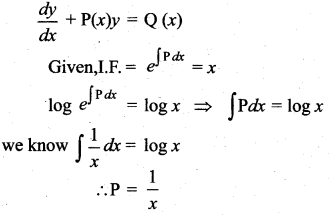
Question 11.
The degree of the dififerential equation 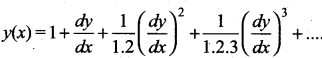 is ……..
is ……..
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 4
Solution:
(c) 1
Hint:
Degree = 1
Question 12.
If p and q are the order and degree of the differential equation 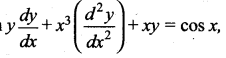 when …..
when …..
(a) p < q
(b) p = q
(c) p > q
(d) p exists and q does not exist
Solution:
(c) p > q
Hint:
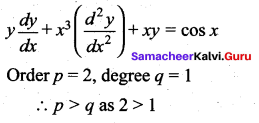
Question 13.
The solution of the differential equation 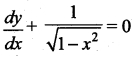 is …….
is …….
![]()
Solution:
(a) \(y+\sin ^{-1} x=c\)
Hint:
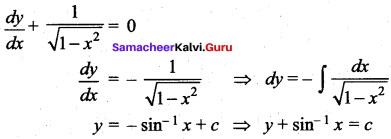
Question 14.
The solution of the differential equation \(\frac{d y}{d x}=2 x y\) is ………
![]()
Solution:
(a) \(y=c e^{x^{2}}\)
Hint:
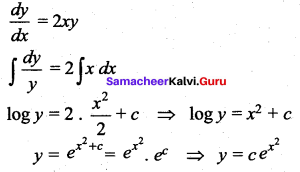
Question 15.
The general solution of the differential equation 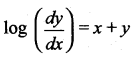 is ……
is ……
![]()
Solution:
(b) \(e^{x}+e^{-y}=c\)
Hint:
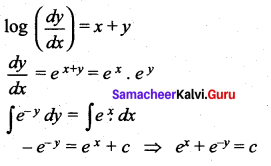
![]()
Question 16.
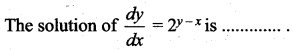
Solution:
(c) \(\frac{1}{2^{x}}-\frac{1}{2^{y}}=c\)
Hint:
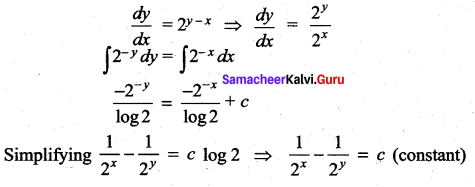
Question 17.
The solution of the differential equation 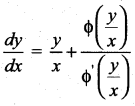 is ……..
is ……..
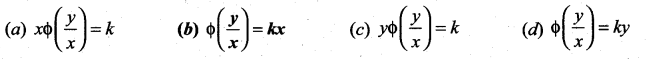
Solution:
(b) \(\phi\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)=k x\)
Hint:
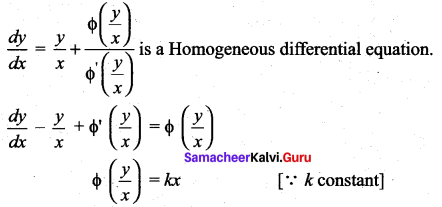
Question 18.
If sin x is the integrating factor of the linear differential equation 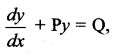 , then P is ……
, then P is ……
(a) log sin x
(b) cos x
(c) tan x
(d) cot x
Solution:
(d) cot x
Hint:
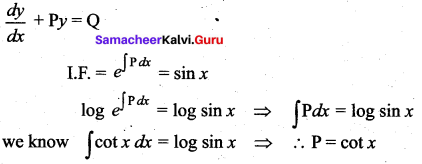
Question 19.
The number of arbitrary constants in the general solutions of order n and n + 1 are respectively ……….
(a) n – 1, n
(b) n, n + 1
(c) n + 1, n + 2
(d) n + 1, n
Solution:
(b) n, n + 1
Question 20.
The number of arbitrary constants in the particular solution of a differential equation of third order is ………….
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 0
Solution:
(d) 0
![]()
Question 21.
Integrating factor of the differential equation 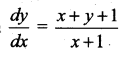 is ……..
is ……..

Solution:
(a) \(\frac{1}{x+1}\)
Hint:
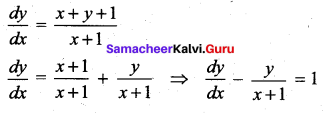
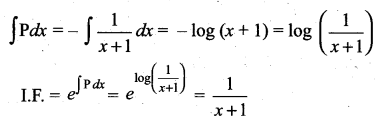
Question 22.
The population P in any year t is such that the rate of increase in the population is proportional to the population. Then ……
![]()
Solution:
(a) \(\mathbf{P}=c e^{k t}\)
Hint:
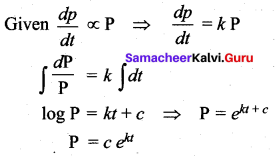
Question 23.
P is the amount of certain substance left in after time t. If the rate of evaporation of the substance is proportional to the amount remaining, then ……
(a) P = cekt
(b) P = ce-kt
(c) P = ckt
(d) Pt = c
Solution:
(b) P = ce-kt
Hint:

Question 24.
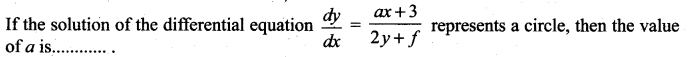
(a) 2
(b) -2
(c )1
(d) -1
Solution:
(b) -2
Hint:

![]()
Question 25.
The slope at any point of a curve y =f (x) is given by 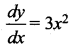 and it passes through (-1, 1). Then the equation of the curve is ……..
and it passes through (-1, 1). Then the equation of the curve is ……..
(a) y = x3 + 2
(b) y = 3x2 + 4
(c) y = 3x3 + 4
(d) y = x3 + 5
Solution:
(a) y = x3 + 2
Hint:
![]()

Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Ordinary Differential Equations Ex 10.9 Additional Problems
Choose the correct or the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives:
Question 1.
The integrating factor of 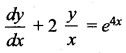 is ………
is ………
(a) log x
(b) x2
(c) ex
(d) x
Solution:
(b) x2
Hint:

Question 2.
If cos x is an integrating factor of the differential equation ![]() then P = ……
then P = ……
(a) – cot x
(b) cot x
(c) tan x
(d) – tan x
Solution:
(d) – tan x
Question 3.
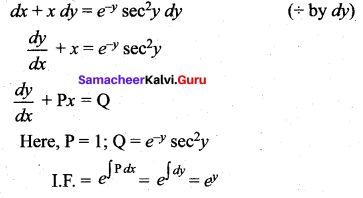
The integrating factor of dx + x dy = e-y sec2y dy is ……….
(a) ex
(b) e-x
(c) ey
(d) e-y
Solution:
(c) ey
Hint:
Question 4.
Integrating factor of 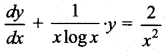
is …..
(a) ex
(b) log x
(c) \(\frac{1}{x}\)
(d) e-x
Solution:
(b) log x
Hint:
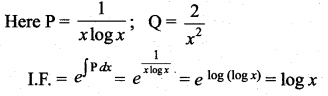
![]()
Question 5.
Solution of ![]() where m < 0 is ……
where m < 0 is ……
![]()
Solution:
\(x=c e^{-m y}\)
Hint:
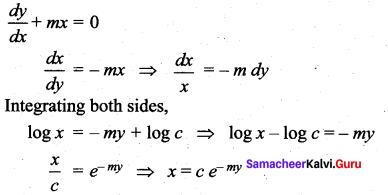
Question 6.
y = cx – c2 is the general solution of the differential equation …….
![]()
Solution:
(a) \(\left(y^{\prime}\right)^{2}-x y^{\prime}+y=0\)
Hint:

Question 7.
The differential equation of all non-vertical lines in a plane is ……

Solution:
\(\frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}=0\)
Hint:
The equation of the straight line is y = mx + c
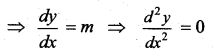
Question 8.
The differential equation of all circles with centre at the origin is
(a) x dy + y dx = 0
(b) x dy – y dx = 0
(c) x dx + y dy = 0
(d) x dx – y dy = 0
Solution:
(c) x dx + y dy = 0
Hint:
The equation of family of circle with the centre at the origin is x2 + y2 = a2
![]()
Question 9.
The differential equation of the family of lines y = mx is ……..
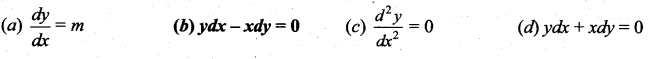
Solution:
(d) 6
Hint:
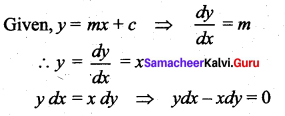
![]()
Question 10.
The degree of the differential equation 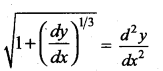
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 6
Solution:
(d) 6
Hint:
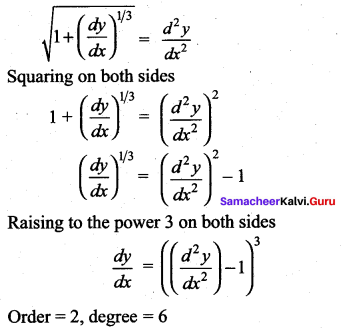
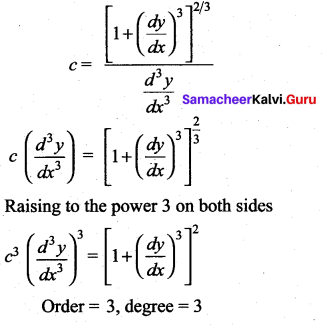
Question 11.
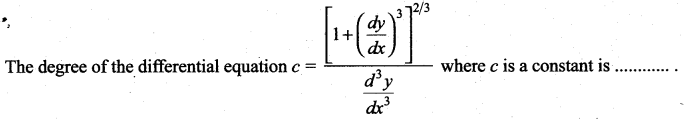
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) -2
(d) 2
Solution:
(b) 3
Hint:
Question 12.
The amount present in a radio active element disintegrates at a rate proportional to its amount. The differential equation corresponding to the above statement is (k is negative)

Solution:
(c) \(\frac{d p}{d t}=k p\)
Hint:
Let p be the amount present in a radio active element

![]()
Question 13.
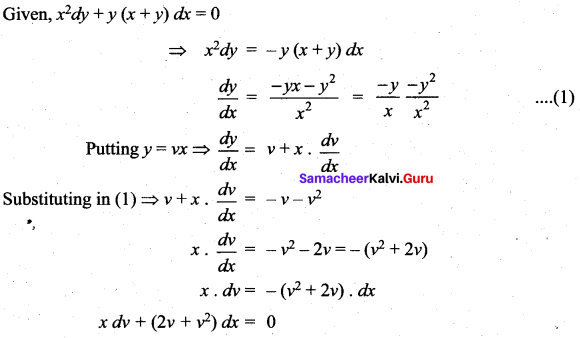
On putting y = vx, the homogeneous differential equation x2dy + y (x + y)dx = 0 becomes …….
(a) xdv + (2v + v2) dx = 0
(b) vdx + (2x + x2)dv = 0
(c) v2dx – (x + x2) dv = 0
(d) vdv + (2x + x2) dx = 0
Solution:
(a) xdv + (2v + v2) dx = 0
Hint: