If you are looking for the best material to read Bio Botany Chapter 9 Plant Breeding Questions and Answers, Notes then Download Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Book Solutions Guide Pdf. You can learn all the topics and subtopics by referring to the Tamilnadu State Board 12th Bio Botany Chapter 9 Plant Breeding Questions and Answers. Samacheer Kalvi12th Bio Botany Subject Material is the notes that you are looking for. Majority of students love to use Samacheer Kalvi Bio Botany Material while preparing for the exam.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 9 Plant Breeding
Every concept of Tamilnadu State Board 12th Bio Botany Subject PDF is explained clearly in an understandable way. Make sure to answer all the Samacheer Kalvi 12th Questions on your own then look for our explanations to make it more easy. We have included all the topics and subtopics to help students for better learning. Best learning comes when you practice with Samacheer Kalvi Board Solutions for 12th Bio Botany Chapter 9 Plant Breeding Questions and Answers.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Plant Breeding Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Assertion: Genetic variation provides the raw material for selection.
Reason: Genetic variations are differences in genotypes of the individuals.
(a) Assertion is right and reason is wrong.
(b) Assertion is wrong and reason is right.
(c) Both reason and assertion is right.
(d) Both reason and assertion is wrong.
Answer:
(c) Both reason and assertion is right.
Question 2.
While studying the history of domestication of various cultivated plants recognized earlier.
(a) Centres of origin
(b) Centres of domestication
(c) Centres of hybrid
(d) Centres of variation
Answer:
(a) Centres of origin
Question 3.
Pick out the odd pair.
(a) Mass selection – Morphological characters
(b) Purline selection – Repeated self pollination
(c) Clonal selection – Sexually propagated
(d) Natural selection – Involves nature
Answer:
(a) Mass selection – Morphological characters
Question 4.
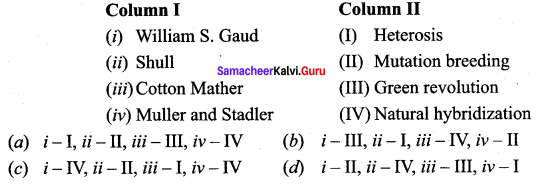
Answer:
(b) i – III, ii – I, iii – IV, iv – II
Question 5.
The quickest method of plant breeding is __________
(a) Introduction
(b) Selection
(c) Hybridization
(d) Mutation breeding
Answer:
(d) Mutation breeding
Question 6.
Desired improved variety of economically useful crops are raised by __________
(a) natural selection
(b) hybridization
(c) mutation
(d) biofertilisers
Answer:
(b) hybridization
Question 7.
Plants having similar genotypes produced by plant breeding are called __________
(a) clone
(b) haploid
(c) autopolyploid
(d) genome
Answer:
(a) clone
Question 8.
Importing better varieties and plants from outside and acclimatising them to local environment is called __________
(a) cloning
(b) heterosis
(c) selection
(d) introduction
Answer:
(d) introduction
Question 9.
Dwarfing gene of wheat is __________
(a) pall
(b) Atomita 1
(c) Norin 10
(d) pelita 2
Answer:
(c) Norin 10
Question 10.
Crosses between the plants of the same variety are called __________
(a) interspecific
(b) intervarietal
(c) intravarietal
(d) intergeneric
Answer:
(c) intravarietal
Question 11.
Progeny obtained as a result of repeat self pollination a cross pollinated crop to called __________
(a) pure line
(b) pedigree line
(c) inbreed line
(d) heterosis
Answer:
(a) pure line
Question 12.
Jaya and Ratna are the semi dwarf varieties of __________
(a) wheat
(b) rice
(c) cowpea
(d) mustard
Answer:
(b) rice
Question 13.
Which one of the following are the species that are crossed to give sugarcane varieties with high sugar, high yield, thick stems and ability to grow in the sugarcane belt of North India?
(a) Saccharum robustum and Saccharum officinarum
(b) Saccharum barberi and Saccharum officinarum
(c) Saccharum sinense and Saccharum officinarum
(d) Saccharum barberi and Saccharum robustum
Answer:
(b) Saccharum barberi and Saccharum officinarum
Question 14.
Match column I (crop) with column II (Corresponding disease resistant variety) and select the correct option from the given codes.
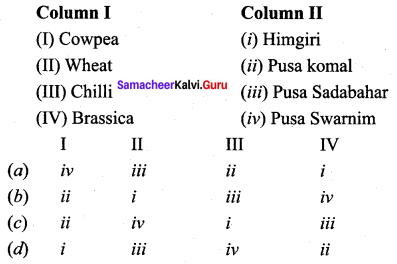
Answer:
(b) ii, i, iii, iv
Question 15.
A wheat variety, Atlas 66 which has been used as a donor for improving cultivated wheat, which is rich in __________
(a) iron
(b) carbohydrates
(c) proteins
(d) vitamins
Answer:
(c) proteins
Question 16.
Which one of the following crop varieties correct matches with its resistance to a disease?

Answer:
(a) Pusa Komal – Bacterial blight
Question 17.
Which of the following is incorrectly paired?
(a) Wheat – Himgiri
(b) Milch breed – Sahiwal
(c) Rice – Ratna
(d) Pusa Komal – Brassica
Answer:
(d) Pusa Komal – Brassica
Question 18.
Match list I with list II:

Answer:
(b) i-d, ii-c, iii-a, iv-b
Question 19.
Differentiate primary introduction from secondary introduction
Answer:
- Primary Introduction: Primary introduction – When the introduced variety is well adapted to the new environment without any alternation to the original genotype.
- Secondary Introduction: Secondary introduction – When the introduced variety is subjected to selection to isolate a superior variety and hybridized with a local variety to transfer one or a few characters to them.
Question 20.
How are microbial innocnlants used to increase the soil fertility?
Answer:
Biofertilizers or microbial innoculants are defined as preparations containing living cells or latent cells of efficient strains of microorganisms that help crop plants uptake of nutrients by their interactions in the rhizosphere when applied through seed or soil.
They are efficient in fixing nitrogen, solubilising phosphate and decomposing cellulose. They are designed to improve the soil fertility, plant growth, and also the number and biological activity of beneficial microorganisms in the soil. They are ecofriendly organic agro inputs and are more efficient and cost effective than chemical fertilizers.
Question 21.
What are the different types of hybridization?
Answer:
Types of Hybridization
According to the relationship between plants, the hybridization is divided into.
- Intravarietal hybridization – The cross between the plants of same variety. Such crosses are useful only in the self-pollinated crops.
- Intervarietal hybridization – The cross between the plants belonging to two different varieties of the same species and is also known as intraspecific hybridization. This technique has been the basis of improving self-pollinated as well as cross pollinated crops.
- Interspecific hybridization – The cross between the plants belonging to different species belonging to the same genus is also called intragenic hybridization. It is commonly used for transferring the genes of disease, insect, pest and drought resistance from one species to another.
Question 22.
Explain the best suited type followed by plant breeders at present?
Answer:
Mutation breeding represents a new method of conventional breeding procedures as they have the advantage of improving the defect without losing agronomic and quality character in agriculture and crop improvement. Mutation means the sudden heritable changes in the genotype or phenotype of an organism. Gene mutations are of considerable importance in plant breeding as they provide essential inputs for evolution as well as for re-combination and selection. It is the only method for improving seedless crops.
Question 23.
Write a note on heterosis.
Answer:
The superiority of the F1 hybrid in performance over its parents is called heterosis or hybrid vigour. Vigour refers to increase in growth, yield, greater adaptability of resistance to diseases, pest and drought. Vegetative propagation is the best suited measure for maintaining hybrid vigour, since the desired characters are not lost and can persist over a period of time. Many breeders believe that its magnitude of heterosis is directly related to the degree of genetic diversity between the two parents. Depending on the nature, origin, adaptability and reproducing ability heterosis can be classified as:
- Euheterosis- This is the true heterosis which is inherited and is further classified as
- Mutational Euheterosis – Simplest type of euheterosis and results from the sheltering or eliminating of the deleterious, unfavourable often lethal, recessive, mutant genes by their adaptively superior dominant alleles in cross pollinated crops.
- Balanced Euheterosis – Well balanced gene combinations which is more adaptive to environmental conditions and agricultural usefulness.
- Pseudoheterosis – Also termed as luxuriance. Progeny possess superiority over parents in vegetative growth but not in yield and adaptation, usually sterile or poorly fertile.
Question 24.
List out the new breeding techniques involved in developing new traits in plant breeding.
Answer:
New Breeding Techniques (NBT) are a collection of methods that could increase and accelerate the development of new traits in plant breeding. These techniques often involve genome editing, to modify DNA at specific locations within the plants to produce new traits in crop plants. The various methods of achieving these changes in traits include the following.
- Cutting and modifying the genome during the repair process by tools like CRISPR /Cas.
- Genome editing to introduce changes in few base pairs using a technique called Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis (ODM).
- Transferring a gene from an identical or closely related species (cisgenesis).
- Organising processes that alter gene activity without altering the DNA itself (epigenetic methods)
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Plant Breeding Additional Questions and Answers
1 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
____________ is the process of bringing a plant species under human control.
(a) Emasculation
(b) Hybridization
(c) Domestication
(d) Acclimatization
Answer:
(c) Domestication
Question 2.
Which of the following scientist developed world’s first cotton hybrid?
(a) Dr. B.P. Pal
(b) C.T. Patel
(c) Dr. K. Ramiah
(d) N.G.P. Rao
Answer:
(b) C.T. Patel
Question 3.
Identify the incorrect statement:
(a) Bio-inoculants are efficient in solubilising phosphate
(A) Bio-inoculants are ecofriendly organic agro outputs
(c) Bio-inoculants are obtained from dead organic matters
(d) Bio-inoculants are designed to improve soil fertility
Answer:
(c) Bio-inoculants are obtained from dead organic matters
Question 4.
Which is not a free-living nitrogen fixing species?
(a) Azotobacter
(b) Clostridium
(c) Nostop
(d) Anabaena
Answer:
(d) Anabaena
Question 5.
Arbuscular mycorrhizae is a symbiotic association between ________
(a) Algae and fungi
(b) Angiosperm roots and fungi
(c) Blue green algae and Azolla fern
(d) Cyanobacteria and corolloid root
Answer:
(b) Angiosperm roots and fungi
Question 6.
Azolla is best suited biofertilizer for ____________
(a) Sugar cane cultivation
(b) Paddy cultivation
(c) Wheat cultivation
(d) Cotton cultivation
Answer:
(A) Paddy cultivation
Question 7.
Assertion (A): SLF promotes vigorous growth and provide resistance against diseases.
Reason (R): SLF is made from kelp containing more than 70 minerals.
(a) Both A and R are true. R explains A.
(A) A is true R is false
(c) A is false R is true
(d) Both A and R are false
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true. R explains A.
Question 8.
Assertion (A): Pure line varieties show homozygosity.
Reason (R): Pure line species are obtained through cross pollination.
(a) Both A and R are true. R explains A.
(b) A is true R is false
(c) A is false R is true
(d) Both A and R are false
Answer:
(b) A is true R is false
Question 9.
Assertion (A): Hybrids show increased growth and elevated yield.
Reason (R): F1 hybrids show Heterosis.
(a) Both A and R are true. R explains A.
(b) A is true R is false
(c) A is false R is true
(d) Both A and R are false
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true. R explains A.
Question 10.
Statement (1): Trichoderma species is a free-living bacteria.
Statement (2): It acts as a potent bio-control agent
(a) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect
(b) Statement 1 is incorrect and Statement 2 is correct
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer:
(b) Statement 1 is incorrect and Statement 2 is correct
Question 11.
Statement (1): Clonal selection is carried out in asexually propagating plants.
Statement (2): Clones show similar genotypes.
(a) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect
(b) Statement 1 is incorrect and Statement 2 is correct
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer:
(c) Both statements are correct
Question 12.
Removal of anthers from a flower to overcome self-pollination and the phenomenon is.
Answer:
Emasculation
Question 13.
Identify the proper sequence of hybridisation technique.
(a) Emasculation → Selection → Bagging → Crossing → Harvesting
(b) Harvesting → Selection → Crossing → Emasculation → Bagging
(c) Selection → Harvesting → Crossing → Emasculation → Bagging
(d) Selection → Emasculation → Bagging → Crossing → Harvesting
Answer:
(d) Selection → Emasculation → Bagging → Crossing → Harvesting
Question 14.
Intra specific hybridization is also termed as
(a) Intravarietal hybridization (b) Intervarietal hybridization
(c) Interspecific hybridization (d) Intergeneric hybridization
Answer:
(b) Intervarietal hybridization
Question 15.
The period of opening of a flower is ________
Answer:
Anthesis
Question 16.
Superiority of hybrids over parents only in vegetative growth not in yield. This phenomenon is termed as ________
(a) Euheterosis
(b) Balanced euheterosis
(c) Luxuriance
(d) Mutational heterosis
Answer:
(c) Luxuriance
Question 17.
The term green revolution was coined by ________
(a) William S Gaud
(b) M.S. Swaminathan
(c) Dr. B.P. Pal
(d) Dr. N.E. Borlaug
Answer:
(a) William S Gaud
Question 18.
Which is the second gamma garden in India?
Answer:
Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI)
Question 19.
Match the following:

Answer:
(a) A – ii, B – i, C – iv, D – iii
Question 20.
Who is popularly called as the “father of green revolution in India”?
(a) Nel Jeyaraman
(b) Dr. M.S. Swaminathan
(c) Dr. Nammalvar
(d) N.G.P. Rao
Answer:
(a) Dr. M. S. Swaminathan
Question 21.
Pusa swamim variety of Brassica species show resistance to ________
(a) White rust
(b) Leaf curl
(c) Black rot
(d) Hill bunt
Answer:
(a) White rust
Question 22.
The first established Atomic Garden in India was ________
(a) Bhabha Atomic Research Institute
(b) Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research
(c) Indian Agricultural Research Institute
(d) Bose Research Institute
Answer:
(d) Bose Research Institute
Question 23.
Triticale is polyploid breed of ________
(a) Triticum cereale x Secale sativus
(b) Triticum durum x Secale cereale
(c) Triticum cereale x Secale sativus
(d) Triticum sativus x Secale cereale
Answer:
(b) Triticum durum x Secale cereale
Question 24.
Raphanobrassica is an example for ________
(a) Autopolyploid
(b) Allopolyploid
(c) Polyploid
(d) Polysomy
Answer:
(b) Allopolyploid
Question 25.
Atlas 66 is a improved variety of ________
(a) Rice
(b) Maize
(c) Wheat
(d) Spinach
Answer:
(c) Wheat
Question 26.
Pusa Sawani variety of okra is resistant against ________
(a) Aphids
(b) Fruit borers
(c) Shoot and fruit borers
(d) Jassids
Answer:
(c) Shoot and fruit borers
Question 27.
________ was the first person to develop world’s first hybrid of sorghum.
Answer:
N.G.P. Rao
Question 28.
Identify the incorrect statement:
(i) SLF is obtained from Kelps – a brown algae
(ii) Azolla is a fern
(iii) Rhizobium is found in association with root nodules
(iv) AM forms symbiotic relation with angiospermic roots
(a) i only
(b) ii, iii and iv only
(c) none of the above
(d) all the above
Answer:
(c) none of the above
Question 29.
Damping off of tomato is controlled by ________
(a) Beauveria species
(b) Trichoderma species
(c) Acacia species
(d) Pseudomonas species
Answer:
(a) Beauveria species
Question 30.
Match the following:

Answer:
(a) A – ii, B – iv, C – i, D – iii
Question 31.
Identify the correct symbiotic association
(a) Rhizobium × Corolloid roots
(b) Arbuscular Mycorrhizae × Angiospermic roots
(c) Azolla × Amantia
(d) Azospirillum × Azolla
(b) Arbuscular Mycorrhizae × Angiospermic roots
Answer:
(b) Arbuscular Mycorrhizae × Angiospermic roots
Question 32.
Atomita 2 – rice is a product by.
(a) Polyploid breeding
(b) Hybridization
(c) Mutation breeding
(d) Clonal selection
Answer:
(c) Mutation breeding
Question 33.
Luxuriance is the term used on par with ________
(a) Heterosis
(b) Anthesis
(c) Hybrids
(d) Mutant breeds
Answer:
(a) Heterosis
Question 34.
The term pureline was coined by.
Answer:
Johannsen
2 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by domestication of plants?
Answer:
Domestication is the process of bringing a plant species under the control of humans and gradually changing it through careful selection,, genetic alteration and handling so that it is more useful to people.
Question 2.
Mention any two free – living nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Answer:
Azotobacter and Clostridium.
Question 3.
What are bio-pesticides? Why they are considered better than synthetic pesticides?
Answer:
Bio-pesticides are biologically based agents used for the control of plant pests. They are in high use due to their non-toxic, cheaper and eco-friendly characteristics as compared to chemical or synthetic pesticides.
Question 4.
Name any four plants used in Green leaf manuring.
Answer:
- Cassia fistula
- Sesbania grandiflora
- Azadirachta indica
- Pongamia pinnata
Question 5.
What is plant breeding?
Answer:
Plant breeding is the science of improvement of crop varieties with higher yield, better quality, resistance to diseases and shorter durations which are suitable to particular environment.
Question 6.
Define acclimatization.
Answer:
The newly introduced plant has to adapt itself to the new environment. This adjustment or adaptation of the introduced plant in the changed environment is called acclimatization.
Question 7.
Who coined the term “pureline”? Define it.
Answer:
Johannsen in 1903 coined the word pureline. It is a collection of plants obtained as a result of repeated self-pollination from a single homozygous individual.
Question 8.
Define the following terms:
Answer:
(a) Emasculation
(b) Bagging
Emasculation: It is a process of removal of anthers to prevent self pollination before anthesis (period of opening of a flower).
Bagging: The stigma of the flower is protected against any undesirable pollen grains, by covering it with a bag.
Question 9.
What is Heterosis?
Answer:
The superiority of the F1 hybrid in performance over its parents is called heterosis or hybrid vigour. Vigour refers to increase in growth, yield, greater adaptability of resistance to diseases, pest and drought.
Question 10.
What does the term ‘luxuriance’ stands for in plant breeding? Explain.
Answer:
Pseudoheterosis – Also termed as luxuriance. Progeny possess superiority over parents in vegetative growth but not in yield and adaptation, usually sterile or poorly fertile.
Question 11.
Mutagens are the substances that induces mutation. Name any two physical and chemical mutagens.
Answer:
- UV short waves, X-rays – Physical mutagens.
- Nitromethyl, Urea – Chemical mutagens.
Question 12.
Write in brief about Atomic Garden.
Answer:
Atomic Garden: Is a form of mutation breeding where plants are exposed to radioactive sources typically cobalt-60 or caesium-137 in order to generate desirable mutation in crop plants.
Question 13.
State any one advantage and one disadvantage of polyploid breeding.
Answer:
- Advantage: Polyploidy often exhibit hybrid vigour and increased tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
- Disadvantage: Polyploidy results in reduced fertility due to meiotic error resulting in seedless varieties.
Question 14.
What are polyploids? Mention its nature.
Answer:
Majority of flowering plants are diploid (2n). The plants which possess more than two sets of chromosome are called polyploids. Polyploidy often exhibit increased hybrid vigour, increased heterozygosity, increase the tolerance to both biotic and abiotic stresses and buffering of deleterious mutations.
Question 15.
Name any two allopolyploid plant species.
Answer:
- Triticale (Triticum durum x Secale cereale).
- Raphanobrassica (Brassica oleraceae x Raphanus sativus).
Question 16.
What is Biofortification?
Answer:
Biofortification is breeding crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals or higher protein and healthier fats. It is the most practical means to improve public health.
Question 17.
Name the insect resistant varieties developed in the following crops.
- Okra
- Rapeseed mustard.
Answer:
- Okra: Pusa Sawani and Pusa A-4 varieties of Okra are resistant to shoot and fruit borers.
- Rapeseed mustard: Pusa gaurav variety of rapeseed mustard shown
Question 18.
In which plant, and by whom the first natural hybridization was performed?
Answer:
The first natural hybridization was done by Cotton Mather in maize.
3 – Mark Questions
Question 19.
In 1926, Vavilov initially proposed eight main geographic centres of crop origin. Mention any six of them.
Answer:
China, India, South America, Mediterranean, Mesoamerica and South East Asia.
Question 20.
Name any three eminent plant breeders of Indian origin.
Answer:
- Dr. M.S. Swaminathan
- C.T. Patel
- Dr. B.P. Pal
Question 21.
How Rhizobium acts as a efficient bio-fertilizer?
Answer:
Bio-fertilizers containing rhizome bacteria are called rhizome bio-fertilizer culture. Symbiotic bacteria that reside inside the root nodules convert the atmospheric nitrogen into a bio available form to the plants. This nitrogen fixing bacterium when applied to the soil undergoes multiplication in billions and fixes the atmospheric nitrogen in the soil. Rhizobium is best suited for the paddy fields which increase the yield by 15 – 40%.
Question 22.
Azolla increases the yield of paddy crop – support your answer.
Answer:
Azolla is a free-floating water fern that fixes the atmospheric nitrogen in association with nitrogen fixing blue green alga Anabaena azolla. It is used as a bio-fertilizer for wetland rice cultivation and is known to contribute 40 – 60 kg/ha/crop. The agronomic potential of Azolla is quite significant particularly for increasing the yield of rice crop, as it quickly decompose in soil.
Question 23.
Mention any three advantages of Arbuscular mycorrhizal association.
Answer:
- Arbuscular mycorrhizae have the ability to dissolve the phosphate found in soil.
- Provides resistance against diseases, germs and unfavourable weather conditions.
- It assures water availability.
Question 24.
What makes the Trichoderma an effective bio-pesticide?
Answer:
Trichoderma species are free-living fungi that are common in soil and root ecosystem. They have been recognized as bio-control agent for
- the control of plant disease
- ability to enhance root growth development
- crop productivity
- resistance to abiotic stress and
- uptake and use of nutrients.
Question 25.
Write a note on Green manuring.
Answer:
Green manuring is defined as the growing of green manure crops and use of these crops directly in the field by ploughing. One of the main objectives of the green manuring is to increase the content of nitrogen in the soil. Also it helps in improving the structure and physical properties of the soil. The most important green manure crops are Crotalaria juncea, Tephrosia purpurea and Indigofera tinctoria.
Question 26.
Point out the objectives of plant breeding.
Answer:
- To increase yield, vigour and fertility of the crop.
- To increase tolerance to environmental condition, salinity, temperature and drought.
- To prevent the premature falling of buds and fruits, etc.
- To improve synchronous maturity.
- To develop resistance to pathogens and pests.
- To develop photosensitive and thermos-sensitive varieties
Question 27.
Give an account on clonal selection.
Answer:
In asexually propagated crop, progenies derived from a plant resemble in genetic constitution with the parent plant as they are mitotically divided. Based on their phenotypic appearance, clonal selection is employed to select improved variety from a mixed population (clones). The selected plants are multiplied through vegetative propagation to give rise to a clone. The genotype of a clone remains unchanged for a long period of time.
Question 28.
Write a short note on autopolyploidy with an example.
Answer:
When chromosome number is doubled by itself in the same plant, is called autopolyploidy.
Example: A triploid condition in sugarbeets, apples and pear has resulted in the increase in vigour and fruit size, large root size, large leaves, flower, more seeds and sugar content in them. It also resulted in seedless tomato, apple, watermelon and orange.
5-Mark Questions
Question 29.
Give a comparative account on Seaweed liquid fertilizer.
Answer:
Seaweed liquid fertilizer (SLF) contains cytokinin, gibberellins and auxin apart from macro and micro nutrients. Most seaweed based fertilizers are made from kelp (brown algae) which grows to length of 150 metres. Liquid seaweed fertilizer is not only organic but also eco-friendly. The alginates in the seaweed that reacts with metals in the soil and form long, cross- linked polymers in the soil. These polymers improve the crumbing in the soil, swell up when they get wet and retain moisture for a long time.
They are especially useful in organic gardening which provides carbohydrates for plants. Seaweed has more than 70 minerals, vitamins and enzymes. It promotes vigorous growth. Improves resistance of plants to frost and disease. Seeds soaked in seaweed extract germinate much rapidly and develop a better root system.
Question 30.
Explain the steps involved in hybridization.
Answer:
Steps involved in hybridization are as follows:
- Selection of Parents: Male and female plants of the desired characters are selected. It should be tested for their homozygosity.
- Emasculation: It is a process of removal of anthers to prevent self pollination before anthesis (period of opening of a flower).
- Bagging: The stigma of the flower is protected against any undesirable pollen grains, by covering it with a bag.
- Crossing: Transfer of pollen grains from selected male flower to the stigma of the female emasculated flower.
- Harvesting seeds and raising plants: The pollination leads to fertilization and finally seed formation takes place.
The seeds are grown into new generation which are called hybrid.
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
Given below are the examples of symbiotic association in which one partner was mentioned. Write the name of the mutual co-partners.
(a) Azollafem + ______________
(b) Root nodules of legume plants + ______________
(c) phycomycetous fungi + ______________
(a) Anabaena azolla (blue green alga)
(b) Rhizobium
Answer:
(c) Angiosperm roots
Question 2.
Provide an example for each of the following agricultural components.
- Bio pesticide
- Green manure crop
- Bio-Fertilzier
Answer:
- Bio pesticide – E.g. Trichoderma species
- Green manure – E.g. Crotalariajuncea
- Bio fertilizer – E.g. Azolla
Question 3.
State the objective of using green manuring.
Answer:
Green manuring helps to increase the content of nitrogen soil and also improves the structure and physical property of soil.
Question 4.
Why plant Breeding is carried out by farmers and scientists?
Answer:
Plant breeding is a proposal manipulation of plant species in order to develop improved crop varieties with higher yield, better quality, resistance to disease and quick maturation.
Question 5.
Yesterday, Ramu visited his friend’s Orchard, where in he noticed few flowers of certain guava trees are covered using thin paper bags.
- Name the process carried out there.
- Why it was done so?
Answer:
- The process is referred as bagging in plant hybridization.
- It is done after emasculation to protect the contact of the stigma of the flower against any other pollen grain.
Question 6.
Who am I?
- Father of Green Revolution.
- Father of Indian Green Revolution.
Answer:
- Dr. Norman E. Borlaug.
- Dr. M.S. Swaminathan.
Question 7.
A plant breeder developed a hybrid sugarcane by grafting two different varieties with desirable characters. The resultant hybrid showed as excellent growth and productivity with increased sucrose content compared to its parental forms.
- What does this phenomenon refers to?
- How this condition can be maintained through further generation?
Answer:
- Heterosis or Hybrid vigour
- Vegetative propogation is the best suited measure to maintain the vigourisity of hybrid.
Hope you love the Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chapter Wise Material. Clearly understand the deep concept of Bio Botany learning with the help of Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chapter 9 Plant Breeding Questions and Answers PDF. Refer your friends to and bookmark our website for instant updates. Also, keep in touch with us using the comment section.