If you are looking for the best material to read Bio Botany Chapter 5 Plant Tissue Culture Questions and Answers, Notes then Download Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Book Solutions Guide Pdf. You can learn all the topics and subtopics by referring to the Tamilnadu State Board 12th Bio Botany Chapter 5 Plant Tissue Culture Questions and Answers. Samacheer Kalvi12th Bio Botany Subject Material is the notes that you are looking for. Majority of students love to use Samacheer Kalvi Bio Botany Material while preparing for the exam.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 5 Plant Tissue Culture
Every concept of Tamilnadu State Board 12th Bio Botany Subject PDF is explained clearly in an understandable way. Make sure to answer all the Samacheer Kalvi 12th Questions on your own then look for our explanations to make it more easy. We have included all the topics and subtopics to help students for better learning. Best learning comes when you practice with Samacheer Kalvi Board Solutions for 12th Bio Botany Chapter 5 Plant Tissue Culture Questions and Answers.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Plant Tissue Culture Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Choose the correct answer from the given option
Question 1.
Totipotency refers to
(a) capacity to generate genetically identical plants
(b) capacity to generate a whole plant from any plant cell / explant
(c) capacity to generate hybrid protoplasts
(d) recovery of healthy plants from diseased plants
Answer:
(b) capacity to generate a whole plant from any plant cell / explant
Question 2.
Micro propagation involves
(a) vegetative multiplication of plants by using micro-organisms
(b) vegetative multiplication of plants by using small explants
(c) vegetative multiplication of plants by using microspores
(d) Non-vegetative multiplication of plants by using microspores and megaspores
Answer:
(b) vegetative multiplication of plants by using small explants
Question 3.
Match the following:

(a) C A D B
(b) A C B D
(c) B A D C
(d) D B C A
Answer:
(a) C A D B
Question 4.
The time duration for sterilization process by using autoclave is ___________ minutes and the temperature is ___________
(a) 10 to 30 minutes and 125° C
(b) 15 to 30 minutes and 121° C
(c) 15 to 20 minutes and 125° C
(d) 10 to 20 minutes and 121° C
Answer:
(b) 15 to 30 minutes and 121° C
Question 5.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Agar is not extracted from marine algae such as seaweeds
(b) Callus undergoes differentiation and produces somatic embryoids
(c) Surface sterilization of explants is done by using mercuric bromide
(d) PH of the culture medium is 5.0 to 6.0
Answer:
(d) PH of the culture medium is 5.0 to 6.0
Question 6.
Select the incorrect statement from given statements:
(a) A tonic used for cardiac arrest is obtained from Digitalis purpuria
(b) Medicine used to treat Rheumatic pain is extracted from Capsicum annum
(c) An anti-malarial drug is isolated from Cinchona officinalis
(d) Anti-carcinogenic property is not seen in Catharanthus roseus.
(e) All the above are correct
Answer:
(e) All the above are correct
Question 7.
Vims free plants are developed from
(a) Organ culture
(b) Meristem culture
(c) Protoplast culture
(d) Cell suspension culture
Answer:
(b) Meristem culture
Question 8.
The prevention of large scale loss of biological integrity
(a) Biopatent
(b) Bioethics
(c) Biosafety
(d) Biofuel
Answer:
(c) Biosafety
Question 9.
Cryopreservation means it is a process to preserve plant cells, tissues or organs
(a) at very low temperature by using ether
(b) at very high temperature by using liquid nitrogen
(c) at very low temperature of-196 by using liquid nitrogen
(d) at very low temperature by using liquid nitrogen
Answer:
(c) at very low temperature of-196 by using liquid nitrogen
Question 10.
Solidifying agent used in plant tissue culture is
(a) Nicotinic acid
(b) Cobaltous chloride
(c) EDTA
(d) Agar
Answer:
(d) Agar
Question 11.
What is the name of the process given below? Write its 4 types.
Answer:
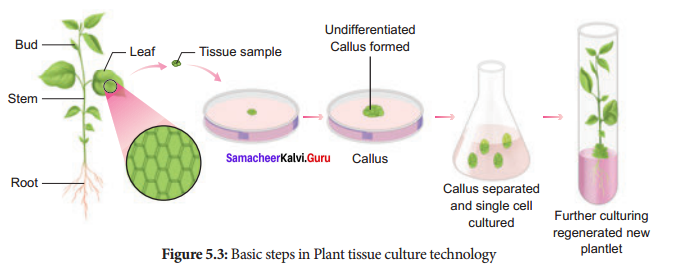
Question 12.
How will you avoid the growing of microbes in nutrient medium during culture process? What are the techniques used to remove the microbes?
Answer:
The microbial growth in culture medium can be overcome by autoclaving the medium at Plant Tissue Culture II 121°C (15 psi) for 15 to 30 minutes.
Chemical sterilization using chemicals, sterilizing using UV radiation. Alcoholic sterilization using ethanol, autoclaving and filtration etc., are the various techniques used to remove microbes.
Question 13.
Write the various steps involved in cell suspension culture.
Answer:
Step 1: Growing of cells/callus in medium (Single or aggregates).
Step 2 : Transfer of callus to a liquid medium.
Step 3: Agitation of callus using rotary shaker.
Step 4: Filtration and separation of cells.
Question 14.
What do you mean by Embryoids? Write its application.
Answer:
Somatic embryogenesis is the formation of embryos from the callus tissue directly and these embryos are called Embryoids or from the in vitro cells directly form pre-embryonic cells which differentiate into embryoids.
Applications:
- Somatic embryogenesis provides potential plantlets which after hardening period can establish into plants.
- Somatic embryoids can be used for the production of synthetic seeds.
- Somatic embryogenesis is now reported in many plants such as Allium sativum, Hordeum vulgare, Oryza sativa, Zea mays and this is possible in any plant.
Question 15.
Give the examples for micro propagation performed plants.
Answer:
Pineapple, banana, strawberry and potato.
Question 16.
Explain the basic concepts involved in plant tissue culture.
Answer:
Basic concepts of plant tissue culture are totipotency, differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation.
1. Totipotency: The property of live plant cells that they have the genetic potential when cultured in nutrient medium to give rise to a complete individual plant.
2.Differentiation: The process of biochemical and structural changes by which cells become specialized in form and function.
3. Redifferentiation: The further differentiation of already differentiated cell into another type of cell. For example, when the component cells of callus have the ability to form a whole plant in a nutrient medium, the phenomenon is called redifferentiation.
4. Dedifferentiation: The phenomenon of the reversion of mature cells to the meristematic state leading to the formation of callus is called dedifferentiation. These two phenomena of redifferentiation and dedifferentiation are the inherent capacities of living plant cells or tissue. This is described as totipotency.
Question 17.
Based on the material used, how will you classify the culture technology? Explain it.
Answer:
Based on explants used culture technology are of following types:
- Organ culture – Embryos, anthers, root and shoot part are used.
- Meristem culture – Meristematic tissues are used.
- Protoplast culture – Protoplasts are used.
- Cell culture – Single cells or aggregate of cells from callus are used.
Question 18.
Give an account on Cryopreservation.
Answer:
Cryopreservation, also known as Cryo-conservation, is a process by which protoplasts, cells, tissues, organelles, organs, extracellular matrix, enzymes or any other biological materials are subjected to preservation by cooling to very low temperature of-196°C using liquid nitrogen. At this extreme low temperature any enzymatic or chemical activity of the biological material will be totally stopped and this leads to preservation of material in dormant status.
Later these materials can be activated by bringing to room temperature slowly for any experimental work. Protective agents like dimethyl sulphoxide, glycerol or sucrose are added before cryopreservation process. These protective agents are called cryoprotectants, since they protect the cells, or tissues frofn the stress of freezing temperature.
Question 19.
What do you know about Germplasm conservation? Describe it.
Answer:
Germplasm conservation refers to the conservation of living genetic resources like pollen, seeds or tissue of plant material maintained for the purpose of selective plant breeding, preservation in live condition and used for many research works.
Germplasm conservation resources is a part of collection of seeds and pollen that are stored in seed or pollen banks, so as to maintain their viability and fertility for any later use such as hybridization and crop improvement. Germplasm conservation may also involve a gene bank, DNAbank of elite breeding lines of plant resources for the maintenance of biological diversity and also for food security.
Question 20.
Write the protocol for artificial seed preparation.
Answer:
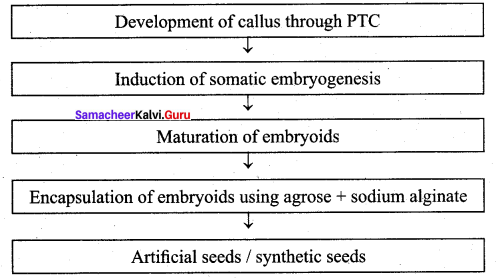
Later these seeds are grown in vitro medium and converted into plantlets. These plantlets require a hardening period (either green house or hardening chamber) and then shifted to normal environment condition.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Plant Tissue Culture Additional Questions and Answers
1 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
_________ is regarded as the Father of tissue culture.
Answer:
Gottlieb Haberland
Question 2.
Identify the group of scientists who developed the intergenic hybrid – the pomato.
(a) Yamada et al.
(b) Horsh et al.
(c) Takebe et al.
(d) Melchers et al.
Answer:
(d) Melchers et al.
Questiom 3.
The production of secondary metabolites require the use of ___________
(a) Protoplast culture
(b) Organ culture
(c) Cell suspension culture
(d) Virus free germ culture
Answer:
(c) Cell suspension culture
Question 4.
Which of the following condition favours callus induction?
(a) Temperature of 25°C ± 5°C with 12 hours of photoperiod
(b) Temperature of 25°C ± 2°C with 18 hours of photoperiod
(c) Temperature of 25°C + 5°C with 14 hours of photoperiod
(d) Temperature of 25°C ± 2°C with 16 hours of photoperiod
Answer:
(d) Temperature of 25°C ± 2°C with 16 hours of photoperiod
Question 5.
Protoplast are the cells devoid of ___________
(a) Cell wall
(b) Cell membrane
(c) Plasma membrane
(d) both A and B
Answer:
(a) Cell wall
Question 6.
A widely used fusogen in protoplast culture is ___________
(a) Polymethyl glycol
(b) Polyethylene glycol
(c) Polyethylene chloride
(d) Polyvinyl chloride
Answer:
(b) Polyethylene glycol
Question 7.
Source of agar is ___________
Answer:
Marine algae (Sea weeds)
Question 8.
Synseeds are developed by encapsulating embryoids with ___________
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Potassium iodide
(c) Sodium alginate
(d) Potassium dichromate
Answer:
(c) Sodium alginate
Question 9.
The optimal pH of culture medium is generally ___________
(a) Acidic
(b) Basic
(c) Neutral
(d) Slightly basic
Answer:
(a) Acidic
Question 10.
Identity the correct sequence regarding steps involved in PTC
(a) Sterilization → Incubation → Inoculation → Embryogenesis → Hardening
(b) Inoculation → Induction →Sterilization → Hardening → Embryogenesis
(c) Induction → Incubation → Inoculation → Hardening → Sterilization
(d) Sterilization → Inoculation → Incubation → Embryogenesis → Hardening
Answer:
(d) Sterilization → Inoculation → Incubation → Embryogenesis → Hardening
Question 11.
Dimethyl sulphoxide is a ___________
(a) Solidifying agent
(b) Cryoprotectant
(c) Fusogenic agent
(d) Stimulant
Answer:
(b) Cryoprotectant
Question 12.
Assertion (A) : Incubation is followed by Inoculation.
Reason (R) : Explant is inoculated to media.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not a correct explanation to A
(b) R explains A
(c) A is correct R is incorrect
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(b) R explains A
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : Sterilization helps to overcome microbes.
Reason (R) : Explants are autoclaved.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not a correct explanation to A
(b) R explains A
(c) A is correct R is incorrect
(d) Both A and R incorrect
Answer:
(c) A is correct R is incorrect
Question 14.
Assertion (A) : Protoplasts are cells devoid of cell wall.
Reason (R) : Secondary metabolites are synthesized by protoplasmic fusion.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not a correct explanation to A
(b) R explains A
(c) A is correct R is incorrect
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(c) A is correct R is incorrect
Question 15.
Assertion (A) : Development of root from callus is called caulogenesis.
Reason (R) : Caulogenesis is the final step of protoplasmic fusion.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not a correct explanation to A
(b) R explains A
(c) A is correct R is incorrect
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Question 16.
Assertion (A) : Liquid nitrogen is used in cryopreservation techniques.
Reason (R) : Gene bank DNA bank are the parts of germplasm conservation.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not a correct explanation to A
(b) R explains A
(c) A is correct R is incorrect
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not a correct explanation to A
Question 17.
Identify the cryoprotectant
(a) Dimethyl formamide
(b) Fructose
(c) Glycerol
(d) Sodium alginate
Answer:
(c) Glycerol
Question 18.
Identify the wrong statement:
(a) Artificial seeds are stored for long time under cryopreservation
(b) Somatic embryos are used for artificial seed production
(c) Period of dormancy of artificial seeds is greatly reduced
(d) Encapsulation of embryoids is done using cryoprotectant
Answer:
(d) Encapsulation of embryoids is done using cryoprotectant
Question 19.
Identify the plant tissue used for virus free germplasm
(a) Apical meristem
(b) Intercalary meristem
(c) Lateral meristem
(d) Plate meristem
Answer:
(a) Apical meristem
Question 20.
Match the following:
(A) Solidifying agent (i) Sucrose
(B) Cryoprotectant (ii) PEG
(C) Growth hormone (iii) Agar
(D) Fusogen (iv) IAA
(1) A – iii B-i C – iv D – ii
(2) A – ii B – iv C – iii D – i
(3) A – iv B – ii C-i D – iii
(4) A – i B – iii C -ii D – iv
Answer:
(1) A – iii B – i C – iv D – ii
Question 21.
Identify the incorrect statement:
(a) Explants are surface sterilized
(b) Nutrient media are autoclaved
(c) Culture rooms are UV radiated for 15 minutes
(d) Glasswares and accessories are autoclaved
(a) a only (b) b and c (c) d only (d) none of the avove
Answer:
(d) none of the above
Question 22.
The enzymatic mixture for chemical isolation of protoplast is
(a) 0.5% macrozyme, 2% onozuka cellulase, 13% mannitol
(b) 1.5% macrozyme, 0.5% onozuka cellulase, 12% sorbitol
(c) 2% macrozyme, 0.5% onozuka cellulase, 13% sorbitol
(d) 0.1% macrozyme, 2% onozuka cellulase, 15% mannitol
Answer:
(a) 0.5% macrozyme, 2% onozuka cellulase, 13% mannitol
Question 23.
The term used to define the ability of a cell to generate entire individual is
(a) Pleuripotent
(b) Totipotent
(c) Multipotent
(d) Unipotent
Answer:
(b) Totipotent
Question 24.
The phenomenon of reversion of mature cells to meristematic state leading to callus ___________
formation is
(a) Redifferentiation
(b) Dedifferentiation
(c) either (a) or (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) Dedifferentiation
Question 25.
Somatic hybridization is achieved through ___________
(a) Protoplast fusion
(b) r-DNA technology
(c) Transformation
(d) Grafting
Answer:
(a) Protoplast fusion
Question 26.
Identify the mismatched pair:
(a) Digoxin – Digitalis purpuria
(b) Codeine – Capsicum annum
(c) Vincristine – Catharanthus roseus
(d) Quinine – Cinchona officinalis
Answer:
(b) Codeine – Capsicum annum
2 – Marks Questions
Question 1.
Define tissue culture.
Answer:
Growing plant protoplasts, cells, tissues or organs away from their natural or normal environment, under artificial condition, is known as Tissue Culture.
Question 2.
Name the four basic concepts of plant tissue culture.
Answer:
Basic concepts of plant tissue culture are totipotency, differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation.
Question 3.
What is the term totipotency refers to?
Answer:
The property of live plant cells that they have the genetic potential when cultured in nutrient medium to give rise to a complete individual plant.
Question 4.
Define sterilization.
Answer:
Sterilization is the technique employed to get rid of microbes such as bacteria and fungi in the culture medium, vessels and explants.
Question 5.
Mention the way by which culture media and explants are sterilized.
Answer:
- Culture media are sterilized by Autoclaving.
- Explants are surface sterilized by chemicals.
Question 6.
Name any four culture media used in plant tissue culture,
Answer:
- Murashige and Skoog medium
- Gamborg medium
- White medium
- Nitsch’s medium
Question 7.
What is Agar? Mention its role in plant tissue culture.
Answer:
Agar is a complex mucilaginous polysaccharide obtained from marine algae (sea weeds), used: as solidifying agent of culture media.
Question 8.
Write the composition of vitamins used in MS medium.
Answer:
Glycine 2.0 mg/1, Nicotinic acid 0.5 mg/1, Pyridoxin HC10.5 mg/1 and Thiamine HC10.1 mg/1.
Question 9.
Define
(a) Callus
(b) Embryoids
Answer:
(a) Callus is a mass of unorganized growth of plant cells or tissues in in vitro culture medium,
(b) The callus cells undergoes differentiation and produces somatic embryos, known as Embryoids.
Question 10.
What do you mean by “Hardening” in plant tissue culture technique?
Answer:
Hardening is the gradual exposure of in vitro developed plantlets in humid chambers in r diffused light for acclimatization so as to enable them to grow under normal field conditions.
Question 11.
Classify plant tissue culture based on types of explants used.
Answer:
Based on the explanin some other plant tissue culture
types are:
- Organ culture
- Meristem culture
- Protoplast culture
- Cell culture
Question 12.
What is cell suspension culture?
Answer:
The growing of cells including the culture of single cells or small aggregates of cells in vitro in liquid medium is known as cell suspension culture.
Question 13.
What is a protoplast? Which chemical stain is used to test its viability?
Answer:
Protoplasts are the cells without a cell wall, bounded by cell membrane. Fluorescein diacetate (FDA) is used to test the viability of protoplast.
Question 14.
What is a cybrid?
Answer:
Cybrid is a cytoplasmic hybrid obtained by the fusion of cytoplasm of cells of different parental sources a term applied to the fusion of cytoplasms of two different protoplasts.
Question 15.
Given below are the secondary metabolites. Mention their plant source.
- Digoxin
- Vincristine.
Answer:
- Digoxin is obtained from Digitalis purpuria.
- Vincristine is obtained from Catharanthus roseus.
Question 16.
Define Organogenesis.
Answer:
The morphological changes occur in the callus leading to the formation of shoot and roots is called organogenesis.
Question 17.
How virus free plants are developed?
Answer:
Shoot meristem tip culture is the method to produce virus-free plants, because the shoot meristem tip is always free from viruses.
Question 18.
State the role of cryoprotectants in conservation of plant resources.
Answer:
Cryoprotectants are the protective agents that are used to protect the cells or tissues from the stress of freezing temperature.
E.g: Sucrose.
Question 19.
Name any two widely used cryoprotectants.
Answer:
- Dimethyl sulphoxide
- Glycerol
Question 20.
Expand and define IPR.
Answer:
Intellectual property right (IPR) is a category of property that includes intangible creation of the human intellect, and primarily consists of copyrights, patents, and trademarks.
Question 21.
Define the patent type – Grant.
Answer:
Grant is a signed document, actually the agreement that grants patent right to the inventor. It is filled at patent office and not published.
Question 22.
Point any four ways by which IPR is protected in India.
Answer:
Patents, Copyrights, trade secrets and geographical indications.
Question 23.
What does ELSI represents to?
Answer:
ELSI which represents ethical, legal and social implications of biotechnology broadly covers the relationship between biotechnology and society with particular reference to ethical and legal aspects.
Question 24.
Mention any two competent national authorities that implement Bio safety guidelines.
Answer:
- Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM)
- Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC)
Question 25.
What does the term ‘Bioethics’ refers to?
Answer:
Bioethics refers to the study of ethical issues emerging from advances in biology and medicine. It is also a moral discernment as it relates to medical policy and practice.
Question 26.
State the mission of ELSI program.
Answer:
The mission of the ELSI program was to identify and address issues raised by genomic research that would affect individuals, families and society.
Question 27.
Name the two inherent capacity responsible for cellular totipotency.
Answer:
Redifferentiation and Dedifferentiation.
3 – Mark Questions
Question 28.
Compare Redifferentiation with Dedifferentiation.
Answer:
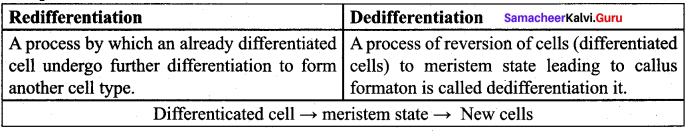
Question 29.
How the autoclaving is done for culture media?
Answer:
Culture media are dispensed in glass containers, plugged with non-absorbent cotton or sealed with plastic closures and then sterilized using autoclave at 15 psi (121°C) for 15 to 30 minutes.
Question 30.
Briefly explain the surface sterilization of explants.
Answer:
The plant materials to be used for tissue culture should be surface sterilized by first exposing the material in running tap water and then treating it in surface sterilization agents like 0.1% mercuric chloride, 70% ethanol under .aseptic condition inside the Laminar Air Flow Chamber.
Question 31.
Point out the factors that determine success rate of tissue culturing.
Answer:
The success of tissue culture lies in the composition of the growth medium, plant growth [ regulators and culture conditions such as temperature, pH, light and humidity.
Question 32.
Mention any three macronutrients and micronutrients used in MS medium.
Answer:
Macronutrients:
- Ammonium nitrate
- Potassium nitrate
- Calcium chloride
Micronutrients:
- Manganese sulphate
- Zinc sulphate
- Potassium iodide
Question 33.
What are the optimal conditions that favours the induction of callus from nutrient medium?
Answer:
After the inoculation of explant in the nutrient medium supplemented with auxins and incubated 1 at 25°C ± 2°C in an alternate light and dark period of 12 hours with light intensity of 1000 lux, induces cell division leading to the development of callus from the surface of explant.
Question 34.
How cell suspension is prepared?
Answer:
The cell suspension is prepared by transferring a portion of callus to the liquid medium and agitated using rotary shaker instrument. The cells are separated from the callus tissue and used for cell suspension culture.
Question 35.
What are Secondary metabolites? Give example.
Answer:
Secondary metabolites are chemical compounds that are not required by the plant for normal growth and development but are produced in the plant as ‘byproducts’ of cell metabolism.
Example: Biosynthesis and isolation of indole alkaloids from Catharanthus roseus plant cell culture.
Question 36.
Name any three secondary metabolites obtained from plants and mention their medicinal aspects.
Answer:
Secondary Metabolites:
- Capsaicin
- Vincristine
- Quinine
Medicinal use:
- Rheumatic pain treatment
- Anti-carcinogenic
- Anti-malarial
Question 37.
What is somatic embryogenesis? Give any two of its applications.
Answer:
Somatic embryogenesis is the formation of embryos from the callus tissue directly and these embryos are called Embryoids.
Applications:
- Somatic embryogenesis provides potential plantlets which after hardening period can establish into plants.
- Somatic embryoids can be used for the production of synthetic seeds.
Question 38.
Differentiate between Somaclonal and Gametoclonal variations.
Answer:
- Somaclonal variations: Somatic variations found in plants regenerated in vitro
(i.e. variations found in leaf, stem, root, tuber or propagule). - Gametoclonal variations: Gametophytic variations found in plants regenerated in vitro gametic origin
(i.e. variations found in gametes and gametophytes)
Question 39.
How synthetic seeds are developed?
Answer:
Artificial seeds or synthetic seeds (synseeds) are produced by using embryoids (somatic embryos) obtained through in vitro culture. They may even be derived from single cells from any part of the plant that later divide to form cell mass containing dense cytoplasm, large nucleus, starch grains, proteins, and oils, etc. To prepare the artificial seeds different inert materials are used for coating the somatic embryoids like agrose and sodium alginate.
Question 40.
Give an account on germplasm conservation.
Answer:
Germplasm conservation refers to the conservation of living genetic resources like pollen, seeds or tissue of plant material maintained for the purpose of selective plant breeding, preservation in live condition and used for many research works.
Germplasm conservation resources is a part of collection of seeds and pollen that are stored in seed or pollen banks, so as to maintain their viability and fertility for any later use such as hybridization and crop improvement. Germplasm conservation may also involve a gene bank and DNA bank of elite breeding lines of plant resources for the maintenance of biological diversity and also for food security.
Question 41.
How cryopreservation works?
Answer:
Cryopreservation, also known as Cryo-conservation, is a process by which protoplasts, cells, tissues, organelles, organs, extracellular matrix, enzymes or any other biological materials are subjected to preservation by cooling to very low temperature of-196°C using liquid nitrogen. At this extreme low temperature any enzymatic or chemical activity of the biological material will be totally stopped and this leads to preservation of material in dormant status. Later these materials can be activated by bringing to room temperature slowly for any experimental work.
Question 42.
What does the terms specification and claim refers with respect to patents?
Answer:
- The specification part is narrative in which the subject matter of invention is described as how the invention was carried out.
- The claim specifically defines the scope of the invention to be protected by the patent which the others may not practice.
Question 43.
Comment on Biosafety.
Answer:
Biosafety is the prevention of large-scale loss of biological integrity, focusing both on ecology and human health. These prevention mechanisms include conduction of regular reviews of the biosafety in laboratory settings, as well as strict guidelines to follow. Biosafety is used to protect from harmful incidents.
Many laboratories handling biohazards employ an ongoing risk management assessment and enforcement process for biosafety. Failures to follow such protocols can lead to increased risk of exposure to biohazards or pathogens. Human error and poor techniques contribute to unnecessary exposure to hazards and compromise the best safeguards set into place for protection.
Question 44.
Write any three points that you know about Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
Answer:
GEAC is an apex body under Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate change for regulating manufacturing, use, import, export and storage of hazardous microbes or genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and cells in the country. It was established as an apex body to accord approval of activities involving large scale use of hazardous microorganisms and recombinants in research and industrial production.
The GEAC is also responsible for approval of proposals relating to release of genetically engineered organisms and products into the environment including experimental field trials (Biosafety Research Level trial-I and II known as BRL-I and BRL-II).
Question 45.
What is cybrid?
Answer:
The fusion product of protoplasts without nucleus of different cells is called a cybrid.
5 – Mark Questions
Question 46.
Explain the steps involved in protoplast culture.
Answer:
Protoplasts are cells without a cell wall, but bounded by a cell membrane or plasma membrane. Using protoplasts, it is possible to regenerate whole plants from single cells and also develop somatic hybrids.
The steps involved in protoplast culture are:
(i) Isolation of protoplast: Small bits of plant tissue like leaf tissue are used for isolation of protoplast. The leaf tissue is immersed in 0.5% Macrozyme and 2% Onozuka cellulase enzymes dissolved in 13% sorbitol or mannitol at pH 5.4. It is then incubated over night at 25°C. After a gentle teasing of cells, protoplasts are obtained, and these are then transferred to 20% sucrose solution to retain their viability. They are then centrifuged to get pure protoplasts as different from debris of cell walls.
(ii) Fusion of protoplast: It is done through the use of a suitable fusogen. This is normally PEG (Polyethylene Glycol). The isolated protoplast are incubated in 25 to 30% concentration of PEG with Ca++ ions and the protoplast shows agglutination (the formation of clumps , of cells) and fusion.
(iii) Culture of protoplast: MS liquid medium is used with some modification in droplet, plating or micro-drop array techniques. Protoplast viability is tested with fluorescein diacetate before the culture. The cultures are incubated in continuous light 1000-2000 lux at 25°C. The cell wall formation occurs within 24-48 hours and the first division of new cells occurs between 2-7 days of culture.
(iv) Selection of somatic hybrid cells: The fusion product of protoplasts without nucleus of different cells is called a cybrid. Following this nuclear fusion happen. This process is called somatic hybridization.
Question 47.
Point out the applications of plant tissue culture.
Answer:
Plant tissue culture techniques have several applications such as:
- Improved hybrids production through somatic hybridization.
- Somatic embryoids canbe encapsulated into synthetic seeds (synseeds). These encapsulated seeds or synthetic seeds help in conservation of plant biodiversity.
- Production of disease resistant plants through meristem and shoot tip culture.
- Production of stress resistant plants like herbicide tolerant, heat tolerant plants.
- Micropropagation technique to obtain large numbers of plantlets of both crop and tree species useful in forestry within a short span of time and all through the year.
- Production of secondary metabolites from cell culture utilized in pharmaceutical,
Question 48.
Discuss the protocol for micropropagation of banana.
Answer:
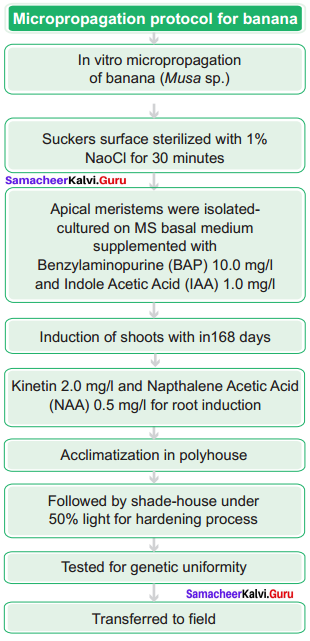
Question 49.
Enumerate the advantages of Artificial seeds.
Answer:
Advantages of Artificial seeds:
Artificial seeds have many advantages over the true seeds as follows:
- Millions of artificial seeds can be produced at any time at low cost.
- They provide an easy method to produce genetically engineered plants with desirable traits.
- It is easy to test the genotype of plants.
- They can potentially stored for long time under cryopreservation method.
- Artificial seeds produce identical plants.
- The period of dormancy of artificial seeds is greatly reduced, hence growth is faster with a shortened life cycle.
Question 50.
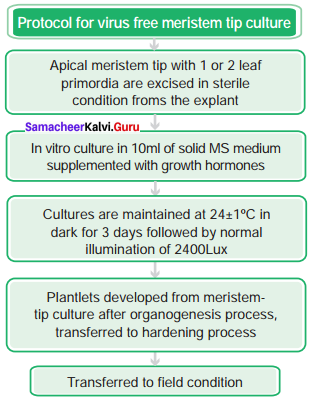
Prepare a protocol for virus free meristem tip culture.
Answer:
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
Transferred to field condition
Study the process given below and mention the phenomena A and B
- Meristematic tissue → Permanent tissue
- Callus → Embryoid
Answer:
- A – Differentiation
- B – Redifferentiation
Question 2.
Given below are the list of components and accessories used in PTC technique. Sort them out according to their mode of sterilization.
- Glass wares
- Laminar air flow chamber
- Nutrient medium
- Explain
Answer:
- Glass wares are sterilized by auto claving.
- Nutrient medium is sterilized by auto claving.
- Laminar air flow chamber is sterilized by UV radiation.
- Explant is surface sterilized using chemicals.
Question 3.
Name the explant through which virus free plantlets can be generated using tissue culturing technique.
Answer:
Shoot – tip meristem
Question 4.
Geographical Indication refers to the products confined to a specific geographical origin. Name any three Tamil Nadu products of your knowledge that hold GI tag.
Answer:
Kanchipuram Silk, Tanjavore dancing doll, Madurai malli.
Hope you love the Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chapter Wise Material. Clearly understand the deep concept of Bio Botany learning with the help of Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chapter 5 Plant Tissue Culture Questions and Answers PDF. Refer your friends to and bookmark our website for instant updates. Also, keep in touch with us using the comment section.