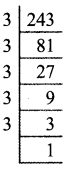
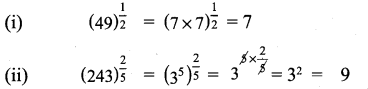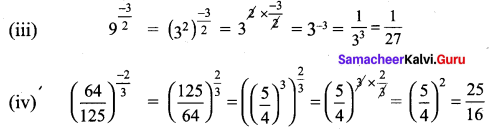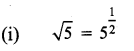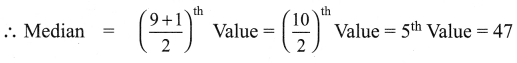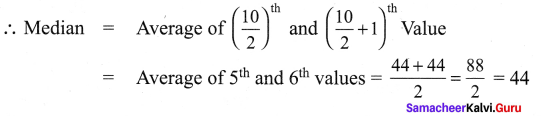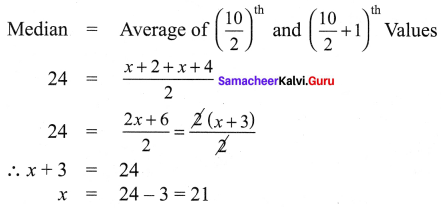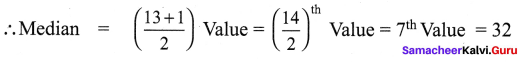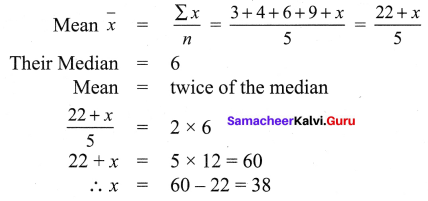You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Statistics Additional Questions
Exercise 8.1
Question 1.
The following data gives the number of residents in an area based on their age. Find the average age of the residents.

Solution:
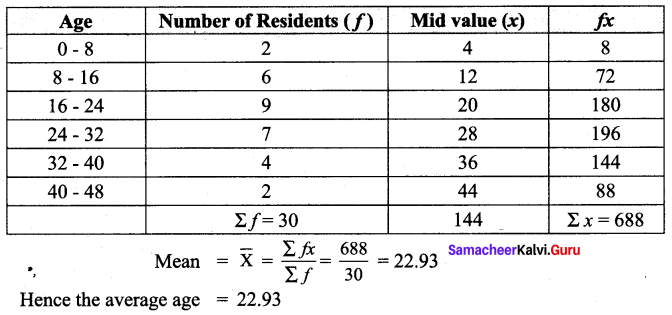
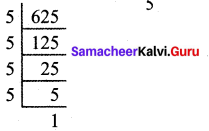
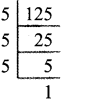
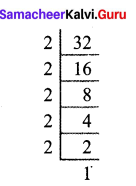
![]()
Question 2.
Find the mean for the following frequency table :

Solution:
Let Assumed mean A = 170
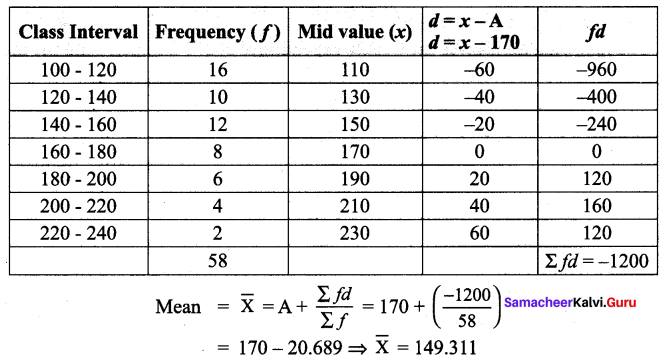
Question 3.
Find the mean for the following distribution using step Deviation Method.

Solution:
Let Assumed mean A = 28, Class width C = 8
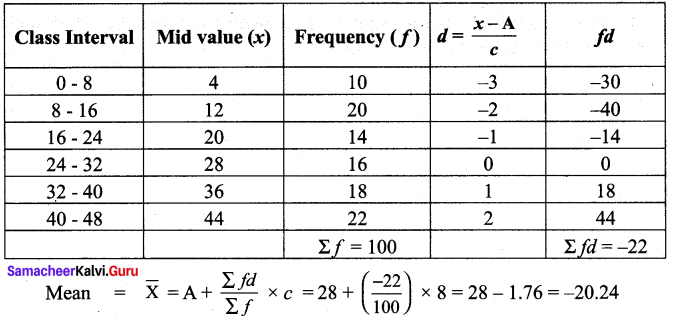
Exercise 8.2
Question 1.
For the following up grouped data 8, 15, 14, 19, 11, 16, 10, 8, 17, 20. Find the median.
Solution:
Arrange the values in ascending order 8, 8, 10, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 20
The number of values = 10
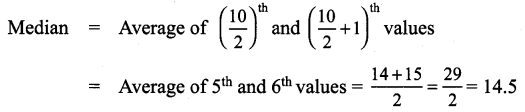
Question 2.
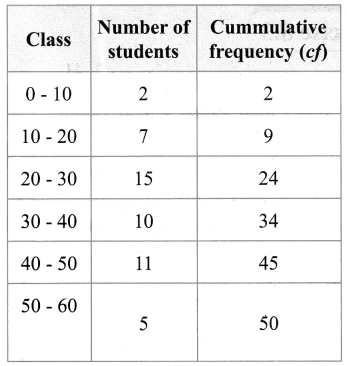
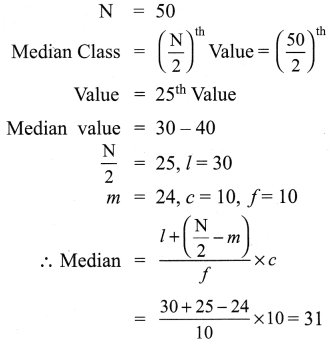
The following table gives the weekly expenditure of 200 families. Find the median of the weekly expenditure.

Solution:

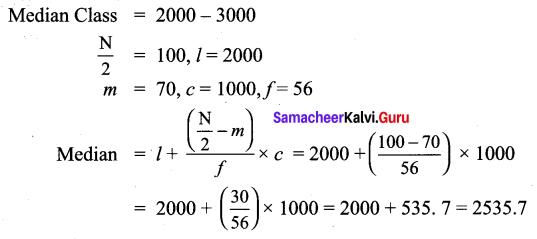
Question 3.
The median of the following data is 24. Find the value of x.
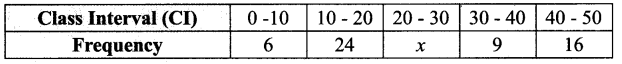
Solution:
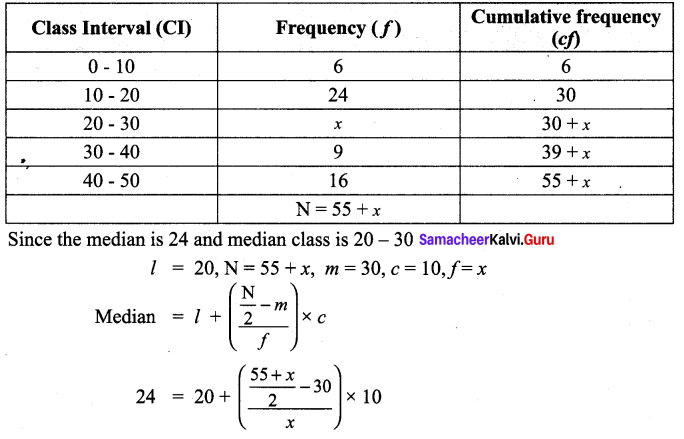
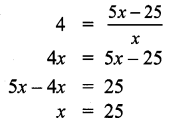
Question 4.
The following are the scores obtained by 11 players in a cricket match 7, 21, 45, 12, 56, 35, 25, 0, 58, 66, 29. Find the median score.
Solution:
Let us arrange the values in ascending order 0, 7, 12, 21, 25, 29, 35, 45, 56, 58, 66
The number of values = 11 which is odd.
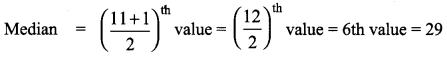
Exercise 8.3
![]()
Question 1.
Find the mode of the given data : 65, 65, 71, 71, 72, 75, 82, 72, 47, 72.
Solution:
In the given data 72 occurs thrice. Hence the mode is 72.
Question 2.
Find the mode:
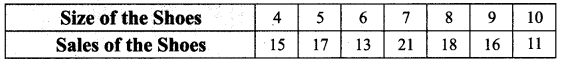
Solution:
7 has the maximum frequency 21. Therefore 7 is the mode.
Question 3.
Find the mode for the following data.

Solution:
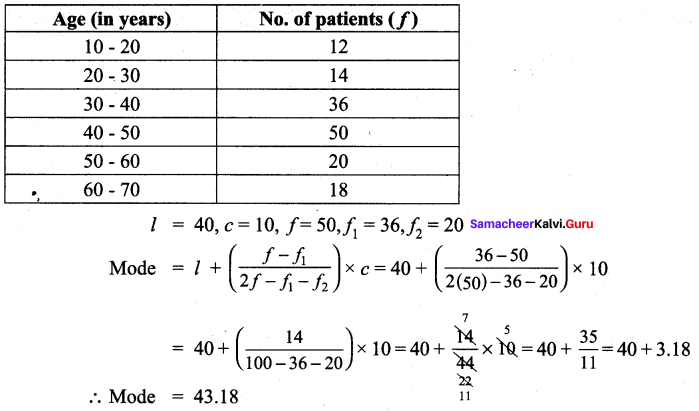
Question 4.
In a distribution, the mean and mode are 46 and 40 respectively. Calculate the median.
Solution:
Given, Mean = 46 and mode = 40
Using mode ≈ 3 median – 2 mean ,
40 ≈ 3 Median – 2 (46)
3 Median ≈ 40 + 92
Therefore, Median ≈ \(\frac{132}{3}\) = 44
Exercise 8.4
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
The mean of first 10 natural numbers.
(1) 25
(2) 55
(3) 5.5
(4) 2.5
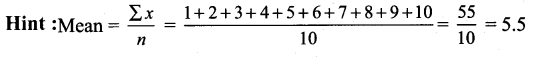
Solution:
(3) 5.5
Question 2.
The mean of a distribution is 23, the median is 24 and the mode is 25.5. It is most likely that this distribution is :
(1) Positively skewed
(2) Symmetrical
(3) Asymptotic
(4) Negatively skewed
Hint: For Negatively skewed means is likely to be less than mode and median
Solution:
(4) Negatively skewed
Question 3.
The middle value of an ordered array of numbers is the
(1) Mode
(2) Mean
(3) Median
(4) Mid point
Solution:
(3) Median
Question 4.
The weights of students in a school is a :
(1) Discrete variable
(2) Continuous variable
(3) Qualitative variable
(4) None of these
Solution:
(2) Continuous variable
![]()
Question 5.
The first hand and unorganized form data is called
(1) Secondary data
(2) Organised data
(3) Primary data
(4) None of these
Solution:
(3) Primary data