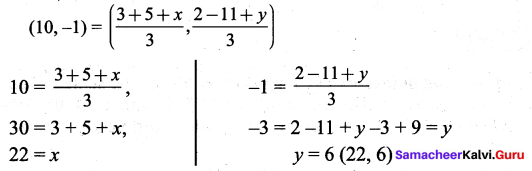You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Civics Solutions Chapter 5 Local Self Government
Local Self Government Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Which committee was appointed by the planning commission in 1985?
(a) Balwant Rai Mehta
(b) Ashok Mehta
(c) G V K Rao
(d) L M Singhvi
Answer:
(c) G V K Rao
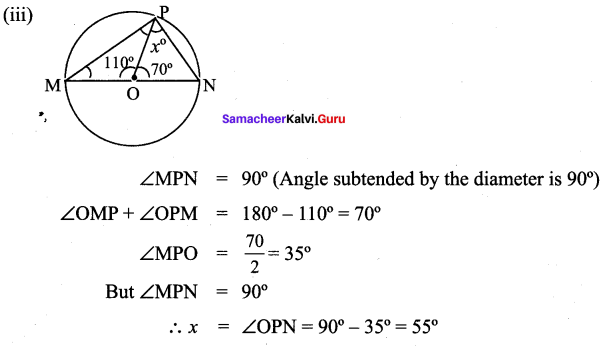
![]()
Question 2.
The Uthiramerur stone inscription show evidences of prevalent local self government during the period in Tamil Nadu.
(a) Chola
(b) Chera
(c) Pandiya
(d) Pallava
Answer:
(a) Chola
Question 3.
The 73rd and 74th constitutional Amendment Acts, were enacted during the year in ………
(a) 1992
(b) 1995
(c) 1997
(d) 1990
Answer:
(a) 1992
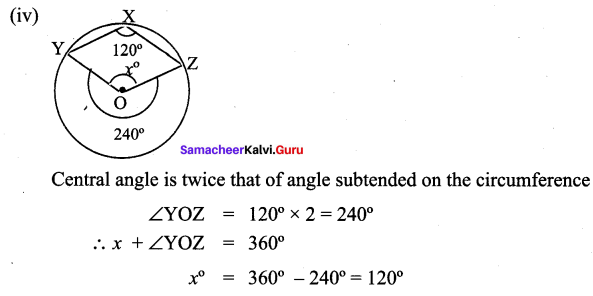
![]()
Question 4.
……. act as the inspector of Village Panchayat.
(a) Commissioner
(b) District Collector
(c) Councilors
(d) Mayor
Answer:
(b) District Collector
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. …….. is known as the “Father of Local Governments”.
2. Restoration of has ……. become an article of faith during our freedom struggle.
3. …… was the name of the secret ballot method exercised to elect members to the village councils during the Chola period.
4. Local Government which are functioning in the Villages are called …….
5. …… will look after the administration of the Town Panchayat.
Answers:
1. LordRipon
2. panchayats
3. Kuda Olai Murai
4. Village Panchayats
5. Executive Officer
III. Match the following:

Answers:
1. (d)
2. (a)
3. (e)
4. (c)
5. (b)
IV. Find out the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) Panchayat Union is formed by grouping of Districts.
(ii) District Panchayat is constituted in each village.
(iii) The Municipal Commissioner will be a person from the Indian Administration Service (IAS).
(iv) In Village Panchayat the President and ward members are nominated by the people.
Answers:
(iii) is correct.
V. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
Name the taxes levied by the Village Panchayat.
Answer:
Taxes
- Property Tax
- Professional Tax
- House Tax
- Taxes for connection of drinking water
- Land Tax
- Taxes levied on shops
Question 2.
List out the salient features of Tamil Nadu Panchayat Raj Apt 1994.
Answer:
The salient features of the new Act are as follows:
(a) A three-tier system
(b) Gram Sabha
(c) Establishment of Election Commission
(d) Constitution of Finance Commission
(e) Reservation of seats for SC/ST’s proportionate to their population One third reservation of seats for women and
(g) Constitution of District Planning Committees.
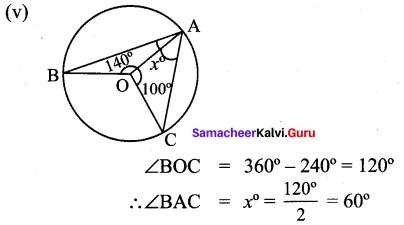
![]()
Question 3.
Mention the important functions of the Village Panchayat.
Answer:
Functions of the Village Panchayat
- Supply of drinking water
- Maintenance of street lights
- Maintenance of roads.
- Maintenance of village libraries
- Maintenance of small bridges
- Granting permission to the housing plots
- Maintenance of drainage
- Construction of group houses
- Cleaning of streets
- Maintenance of burial grounds
- Maintenance of common lavatory facilities
Question 4.
Which are the voluntary functions of the local governments?
Answer:
According to the Tamil Nadu Local Government Act passed in 1994, the following functions to be performed as voluntary functions by the local governments.
- Maintenance of street lights in the villages
- Maintenance of markets and fairs
- Implantation of trees
- Maintenance of play grounds
- Maintenance of parking vehicles, slaughter houses and cattle sheds
- Control over places of exhibition.
Question 5.
Who is the head of the District Panchayat?
Answer:
One district Panchayat is constituted for every 50,000 people and the ward members are directly elected by the people. The Chairman is elected from one among its members and their term is 5 years.
![]()
Question 6.
Name the Urban local governments.
Answer:
Urban Local Government
- Town Panchayat
- Municipality
- Corporation.
VI Answer in paragraph.
Question 1.
Write in details about the salient features of the 73rd & 74th Constitutional Amendment Act (1992).
Answer:
Salient Features of the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts (1992)
- Panchayats and Minicipalities will be ‘institutions of self-government’.
- Basic Units of Democratic System – Grama Sabhas (Villages) and Ward Committees (Municipalities) comprising all the adult members registered as voters.
- Three-tier system of panchayats at village, intermediate block/taluk/mandal and district levels. Two-tier for smaller states with population below 2 million.
- Seats at all levels filled by direct elections.
Seats reserved for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and chairpersons of the Panchayats at all levels also shall be reserved for SCs and STs in proportion to their population. - One-third of the total number of seats reserved for women. One-third of the seats reserved for SCs and STs also reserved for women. One-third offices of chairpersons at all levels reserved for women.
- Uniform five year term and elections to constitute new bodies to be completed before the expiry of the term. In the event of dissolution, elections must be held compulsorily within six months.
Question 2.
Describe the major problems & challenges faced by the local self governments.
Answer:
Local self governments are the crucial basis for our democracy. The Constitutional status of local self governments adds more significance to their functioning. There are, however, a few critical concerns in the working of local self governments in India. Major problems and challenges may be mentioned as below:
- Lack of clear demarcation of powers and functions of local bodies
- Allocation of funds and needs assessment are not matched
- Role of caste, class and religion in decision making at the local self governments
- Poor accountability of elected members and officials at the grassroot levels of democracy
VII. Activity
Question 1.
Meet your President, Panchayat, Municipal Chairman and discuss with him how the local self goverment administered.
Answer:
You can do this activity under the guidance of your teacher.
Local Self Government Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
…… introduced the Local Self Government in 1882.
(a) Ashok Mehta
(b) Lord Rippon
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) E.V.R. Periyar
Answer:
(b) Lord Rippon
Question 2.
Panchayat Raj System was introduced in Rajasthan in
(a) 1952
(b) 1953
(c) 1958
(d) 1959
Answer:
(d) 1959
![]()
Question 3.
Kuda Olai Murai was the name of the secret ballot method exercised by ….. to elect
the village councils.
(a) Chera
(b) Chola
(c) Pandya
(d) Pallava
Answer:
(b) Chola
Question 4.
There are …… corporations in Tamil Nadu.
(a) 12
(b) 13
(c) 14
(d) 15
Answer:
(a) 12
Question 5.
…….. was the chairman of the Erode Municipality for many years since 1917.
(a) C.N. Annadurai
(b) E.V. Ramasamy Periyar
(c) M.G. Ramachandran
(d) Raja Gopalachari
Answer:
(b) E.V. Ramasamy Periyar
II. Find out the correct statement.
Question 1.
(i) Local governments which are functioning in the villages are called Village Panchayat.
(ii) The President and Ward members are indirectly elected.
(iii) Their term office is six years.
(iv) Collector acts as the Inspector of Village Panchayat.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) (iv) is correct
(d) (ii) is incorrect
Answer:
(b) (ii) and (iii) are correct
![]()
Question 2.
(i) The area where less than 10,000 people are living is called as Town Panchayat.
(ii) Members and President of the town Panchayat are directly elected by the people.
(iii) Their term office is 5 years.
(iv) There is one Executive officer to look after the administration of the Town Panchayat.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (ii) and (iii) are incorrect
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii) are incorrect
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
Question 3.
Assertion (A): The Mayor is elected by the people.
Reason (R): He is a link between the members of the corporation and the government.
(a) A is wrong; R is correct
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation of A
(d) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Answers:
(d) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A
III. Match the following:

Answers:
1. (d)
2. (c)
3. (a)
4. (b)
IV. Fill in the blanks.
1. After Independence the Gandhian ideas of ……. greatly influenced the constitution
makers.
2. ……… took some steps towards liberalizing the administration in India.
3. …… are constituted in each and every village wherever population is above 500.
4. …… is formed by grouping of villages.
5. Chennai Minicipality was constituted in …….
6. After which British Lord is Chennai Corporation building named?
7. Corporations, Municipalities’ and Town Panchayats are …… bodies.
Answers:
1. Grama Swaraj
2. Ripon
3. Village Panchayats
4. Panchayat Union
5. 1688
6. Lord Ripon
7. urban
V. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
What do you know about the Local Self Government?
Answer:
Local Self-Governments are institutions that look after the administration of an area or a small community such as a village, a town or a city. Local Self-Government operates at the lowest level of society. It works at the grassroot level, close to the people, touching their everyday life. Local Self-Government is the management of local affairs by such local bodies which have been elected by the local people. These local bodies provide services to the local community as well as act as an instrument of democratic self-government.
Question 2.
Mention any two salient features of the 73rd and 74th constitution Amendment Act 1992.
Answer:
- Panchayats and Minicipalities will be ‘institutions of self-government’.
- Basic Units of Democratic System – Grama Sabhas (Villages) and Ward Committees (Municipalities) comprising all the adult members registered as voters.
Question 3.
What are the functions of the Panchayat Union?
Answer:
Functions of the Panchayat Union are:
- Supply of drinking water
- Maintenance of Village Health Centres
- Maintenance of roads
- Establishment of Maternity Homes
- Establishment of Public fairs
- Establishment of Veterinary hospitals
- Maintenance of Social forests
- Repairing of Primary School buildings
![]()
Question 4.
Comment on District Panchayat.
Answer:
A District Panchayat is constituted in each district. One district Panchayat is constituted for every 50,000 people and the ward members are directly elected by the people. The Chairman is elected from one among its members and their term is 5 years.
Question 5.
What are the functions of the District Panchayat?
Answer:
The functions of the District Panchayat are:
- Advising the government about the developmental schemes of the Village Panchayat and Panchayat Union.
- Supervising the functions of District Planning Commission.
Question 6.
List down the important functions of the Mayor.
Answer:
Important functions of the Mayor
- He acts as a bridge between the members of the corporation and the government.
- He presides over the meetings of the Corporation Council.
- He receives the dignitaries from foreign countries.
VI. Answer in a Paragraph.
Question 1.
Describe the Historical origin and Development of Local Self Government in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
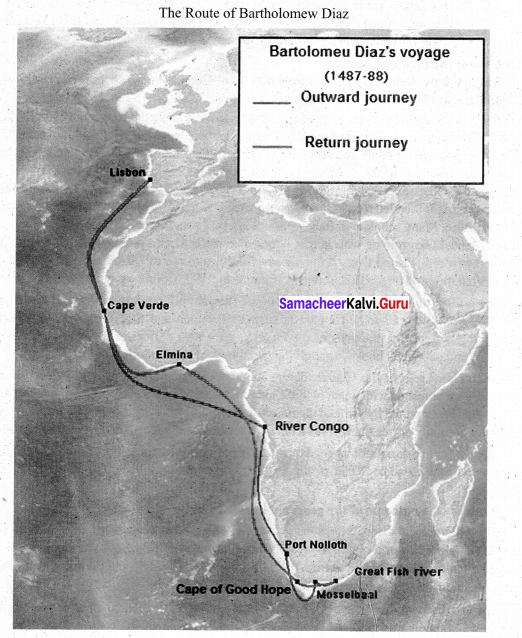
Tamil Nadu has a long history of local self-govemance as is evident Tamil Nadu, in those days was a land of village republics, with community groups undertaking many activities for their area development. This tradition reached its peak during the 10th and 11th centuries under the reign of Cholas when Village Councils used to levy taxes, improve community life and administer justice in their limited area.
These Village Councils had effective links with the Chola rulers. “Kuda Olai Murai” was the name of the secret ballot method exercised to elect members to the Village Councils. With the downfall of Cholas, the state experienced a decline of the village autonomy and rise of the centralized feudal administrative system. This continued till British rules introduced local self-govemance colonial British Government.
In the post independence era, the first enactment in democratic decentralization in the state was the Madras Village Panchayats Act, 1950. Pursuant to the White Paper on the ‘Reform of Local Administration’ in 1957, the Madras Panchayats Act, 1958 and Madras District Development Council Act were enacted with the following salient features.