Students can Download Maths Chapter 1 Rational Numbers Ex 1.1 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 1 Rational Numbers Ex 1.1
8th Maths Exercise 1.1 Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) \(\frac{-19}{5}\) lies between the integers _____ and _____
(ii) The rational number that is represented by 0.44 is ______.
(iii) The standard form of \(\frac{+58}{-78}\) is _____.
(iv) The value of \(\frac{-5}{12}+\frac{7}{15}\) = ______
(v) The value of \(\left(\frac{-15}{23}\right) \div\left(\frac{+30}{-46}\right)\) is ______
Solution:
(i) -4 and -3
(ii) \(\frac{11}{25}\)
(iii) \(\frac{-29}{39}\)
(iv) \(\frac{1}{20}\)
(v) 1
8th Maths Exercise 1.1 In Tamil Question 2.
Say True or False.
(i) 0 is the smallest rational number.
(ii) There are an unlimited rationals between 0 and 1.
(iii) The rational number that does not have a reciprocal is 0.
(iv) The only rational number which is its own reciprocal is -1.
(v) The rational numbers that are equal to their additive inverses are 0 and -1.
Solution:
(i) False
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) False
(v) False
8th Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 3.
List five rational numbers between 2 and 0
(i) -2 and 0
(ii) \(\frac{-1}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{5}\)
(iii) 0.25 and 0.35
(iv) -1.2 and -2.3
Solution:
(i) -2 and 0


Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 1 Pdf Question 4.
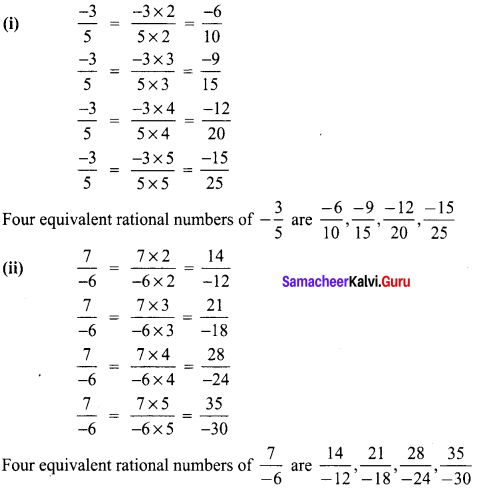
Write four rational numbers equivalent to -3 7
(i) \(\frac{-3}{5}\)
(ii) \(\frac{7}{-6}\)
(iii) \(\frac{8}{9}\)
Solution:
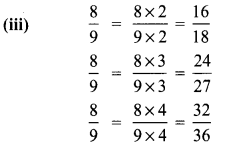

8th Standard Maths Exercise 1.1 Answers Question 5.
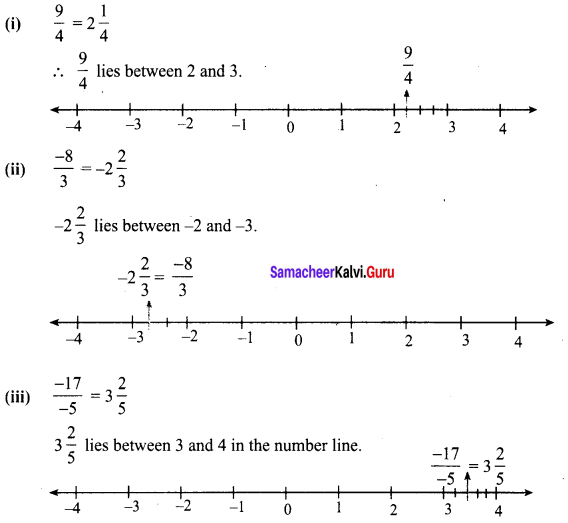
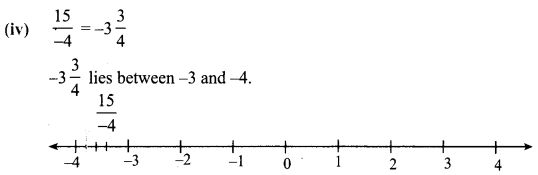
Draw the number line and represent the following rational numbers on it.

Solution:
8th Maths Book Example Sums Question 6.
Find the rational numbers for the points marked on the number line.
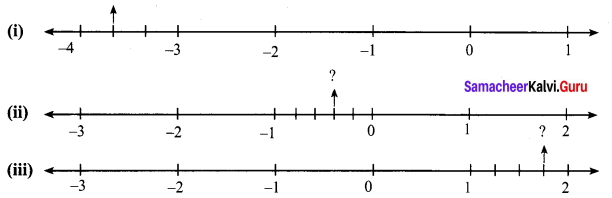
Solution:
(i) The number lies between -3 and -4. The unit part between -3 and -4 is divided into 3 equal parts and the second part is asked.
∴ The required number is \(-3 \frac{2}{3}=-\frac{11}{3}\).
(ii) The required number lies between 0 and -1. The unit part between 0 and -1 is divided into 5 equal parts, and the second part is taken.
∴The required number is \(-\frac{2}{5}\)
(iii) The required number lies between 1 and 2. The unit part between 1 and 2 is divided into 4 equal parts and the third part is taken.
∴ The required number is \(1 \frac{3}{4}=\frac{7}{4}\)
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru 8th Maths Question 7.
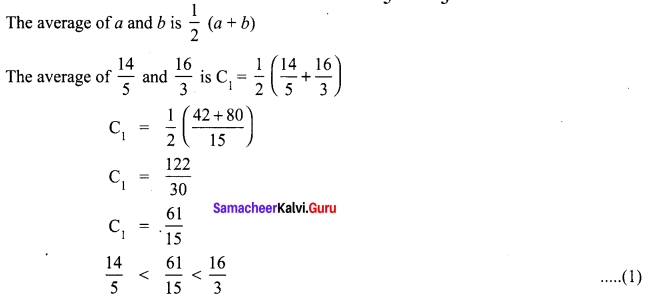
Using average, write 3 rational numbers between \(\frac{14}{5}\) and \(\frac{16}{3}\)
Solution:
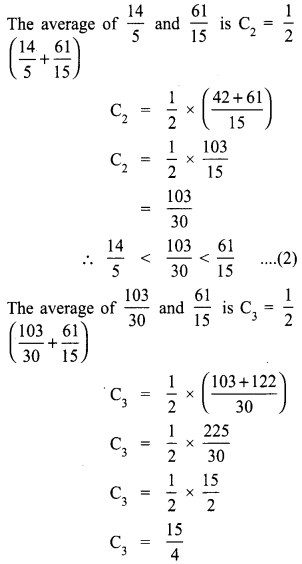
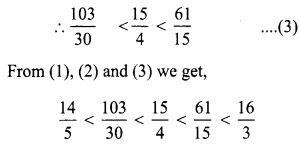
Maths 8th Guide Samacheer Kalvi Question 8.
Verify that -(-x) is the same x for:
(i) x = \(\frac{11}{15}\)
(ii) x = \(\frac{-31}{45}\)
Solution:
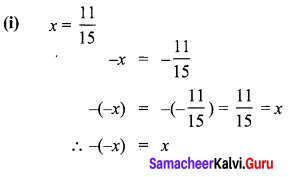
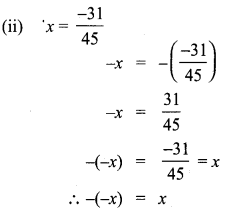
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Question 9.
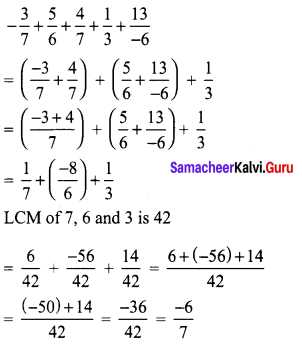
Re-arrange suitable and add :
\(\frac{-3}{7}+\frac{5}{6}+\frac{4}{7}+\frac{1}{3}+\frac{13}{-6}\)
Solution:
8th Maths 1.1 Question 10.
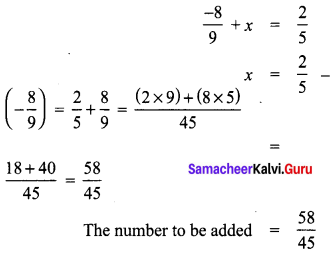
What should be added to \(\frac{-8}{9}\) to get \(\frac{2}{5}\).
Solution:
Let the number to be added = x
8th Std Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 11.
Subtract \(\frac{-8}{44}\) from \(\frac{-17}{11}\)
Solution:
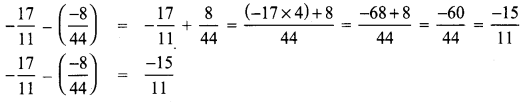
Maths Term 1 Question 12.
Evaluate:
(i) \(\frac{9}{2} \times \frac{-11}{3}\)
(ii) \(\frac{-7}{27} \times \frac{24}{-35}\)
Solution:
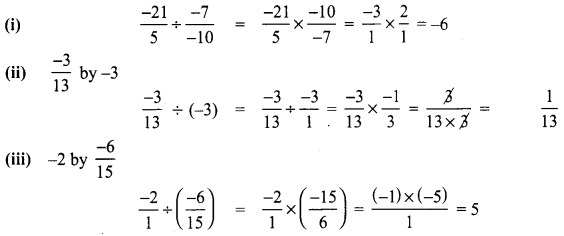
Maths 8th Class Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 13.
Divide
(i) \(\frac{-21}{5}\) by \(\frac{-7}{-10}\)
(ii) \(\frac{-3}{13}\) by -3
(iii) -2 by \(\frac{-6}{15}\)
Solution:

8th Maths In Tamil Question 14.
Simplify \(\left(\frac{2}{5}+\frac{3}{2}\right)+\frac{3}{10}\) as a rational number and show that it is between 6 and 7.
Solution:
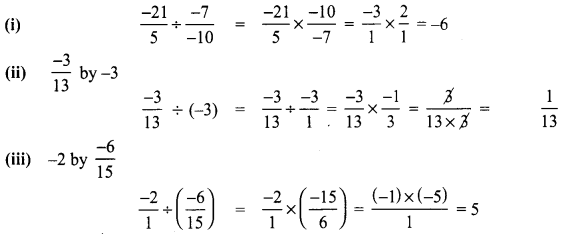
8th Standard Maths Book Exercise 1.1 Question 15.
Write the five rational numbers which are less than -2.
Solution:
All the integers are rational numbers
∴ Rational numbers less than -2 are -10, -15, -20, -25, -30
8th Maths Guide Question 16.
Compare the following pairs of rational numbers

Solution:
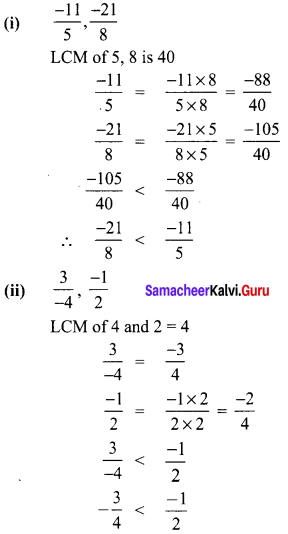
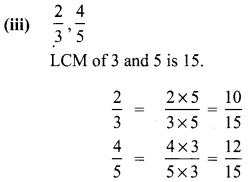
\(\frac{10}{15}<\frac{12}{15}\)
∴ \(\frac{2}{3}<\frac{4}{5}\)
8th Maths Book Answer Question 17.
Arrange the following rational numbers is ascending and descending order.
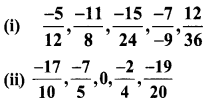
Solution:




Objective Type Questions
8th Std Maths Guide Question 18.
The number which is subtracted from \(\frac{-6}{11}\) to get \(\frac{8}{9}\) is

Solution:
(B) \(\frac{-142}{99}\)
Hint:
Let x be the number be subtracted

Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th Maths Book Solutions Question 19.
Which of the following rational numbers is the greatest?
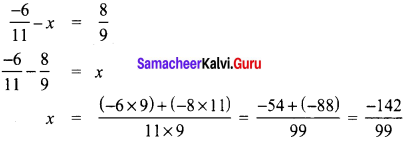
Solution:
(A) \(\frac{-17}{24}\)
Hint:
LCM of 24, 16, 8, 32 = 8 × 2 × 3 × 2 = 96
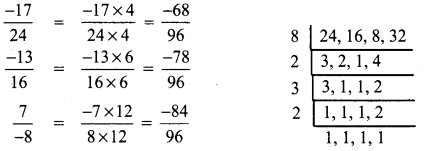
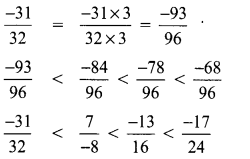
∴ \(\frac{-17}{24}\) is the greatest number.
8th Std Maths Book Answers Question 20.
\(\frac{-5}{4}\) is a rational number which lies between
(A) 0 and \(\frac{-5}{4}\)
(B) -1 and 0
(C) -1 and -2
(D) -4 and -5
Solution:
(C) -1 and -2
Hint:
\(\frac{-5}{4}\) = \(-1 \frac{1}{4}\)
∴ \(\frac{-5}{4}\) lies between -1 and -2.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Question 21.
The standard form of \(\frac{3}{4}+\frac{5}{6}+\left(\frac{-7}{12}\right)\) is
![]()
Solution:
(D) 1
Hint:
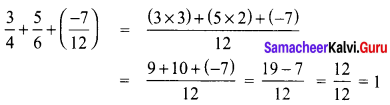
8th Maths Book Samacheer Kalvi Question 22.
The sum of the digits of the denominator in the simplest form of \(\frac{112}{528}\)
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 7
Solution:
(C) 6
Hint:
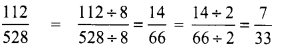
Sum of digits in the denominator = 3 + 3 = 6
Question 23.
The rational number (numbers) which has (have) additive inverses is (are)
(A) 7
(B) \(\frac{-5}{7}\)
(C) 0
(D) all of these
Solution:
(D) all of these
Hint:
Additive inverse of 7 is -7
Additive inverse of \(\frac{-5}{7}\) is \(\frac{-5}{7}\)
Additive inverse of 0 is 0.
Question 24.
Which of the following pairs is equivalent?
![]()
Solution:
(B) \(\frac{16}{-30}, \frac{-8}{15}\)
Hint:
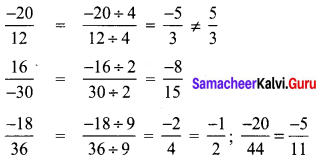
∴ \(\frac{16}{-30}\) and \(\frac{8}{15}\) are equivalent fraction.
Question 25.
\(\frac{3}{4} \div\left(\frac{5}{8}+\frac{1}{2}\right)\) =

Solution:
(C) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Hint:
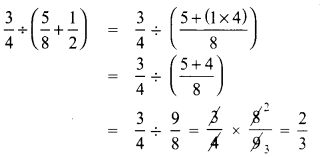


 Answer:
Answer: