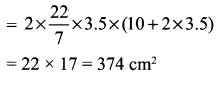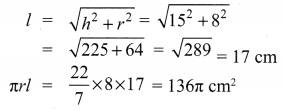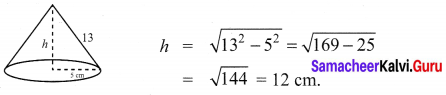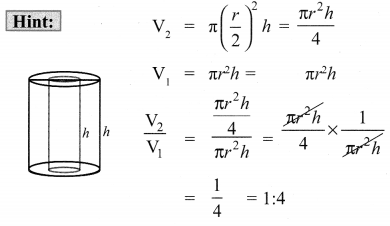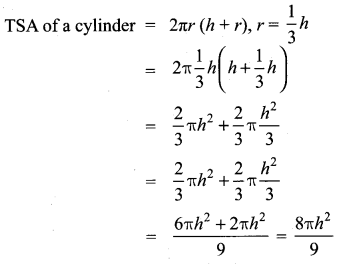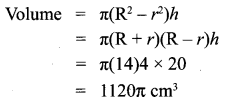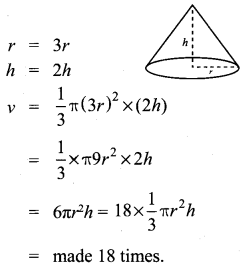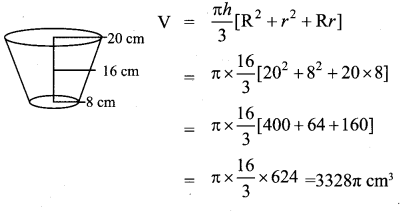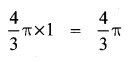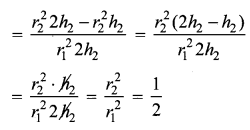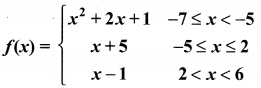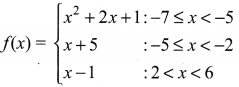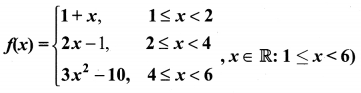You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Mensuration Additional Questions
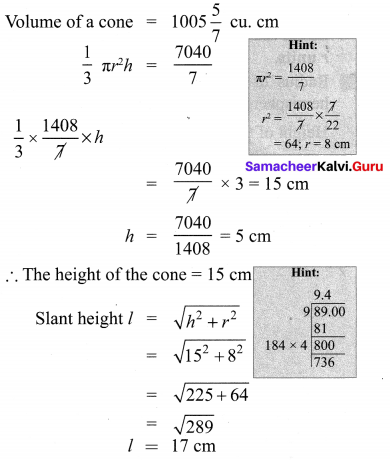
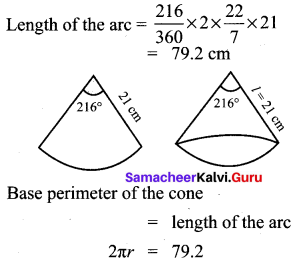
Question 1.
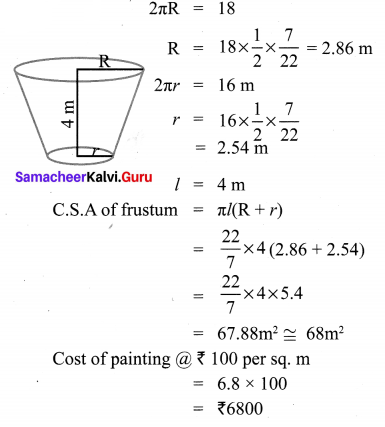
If the radii of the circular ends of a conical bucket which is 45 cm high are 28 cm and 7 cm, find the capacity of the bucket. (Use \(\pi=\frac{22}{7}\))
Solution:
Clearly bucket forms frustum of a cone such that the radii of its circular ends are r1 = 28 cm, r2 = 7 cm, h = 45 cm.
Capacity of the bucket = volume of the frustum
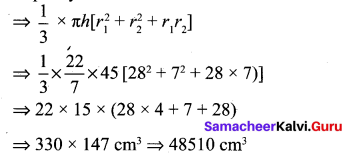
![]()
Question 2.
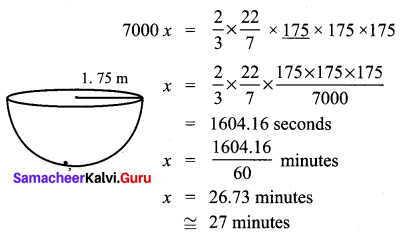
Find the depth of a cylindrical tank of radius 28 m, if its capacity is equal to that of a rectangular tank of size 28 m × 16 m × 11 m.
Solution:
Volume of the cylindrical tank = Volume of the rectangle tank

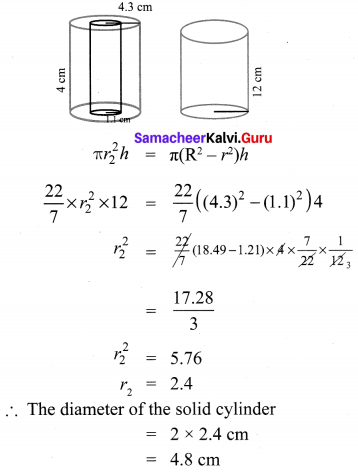
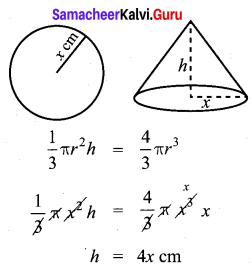
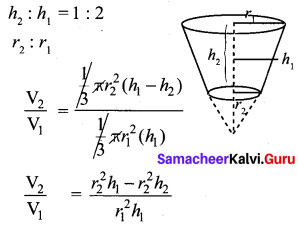
Question 3.
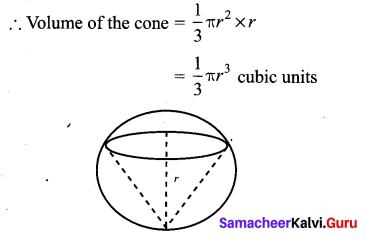
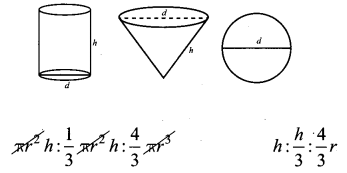
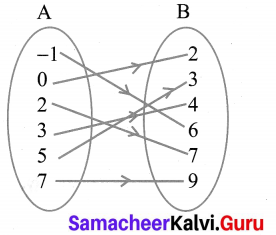
What is the ratio of the volume of a cylinder, a cone, and a sphere. If each has the same diameter and same height?
Solution:
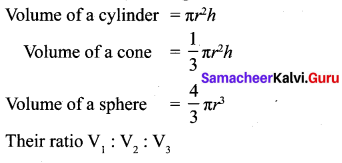
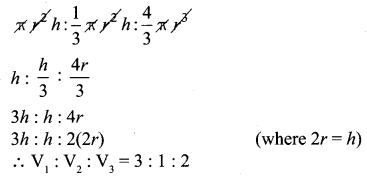
![]()
Question 4.
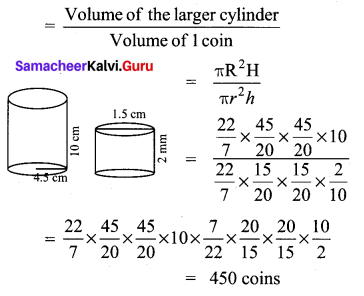
Find the number of coins, 1.5 cm is diameter and 0.2 cm thick, to be melted to form a right circular cylinder of height 10 cm and diameter 4.5 cm.
Solution:
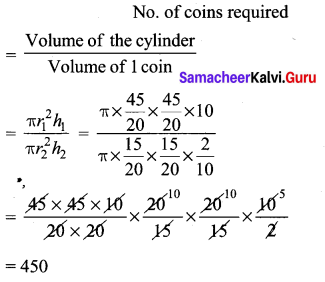
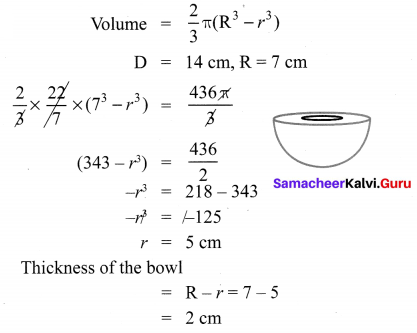
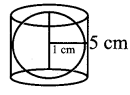
Question 5.
A spherical ball of iron has been melted and made into small balls. If the raidus of each smaller ball is one-fourth of the radius of the original one, how many such balls can be made?
Solution:
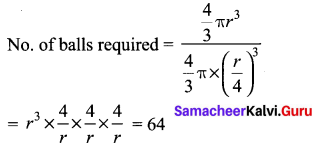
![]()
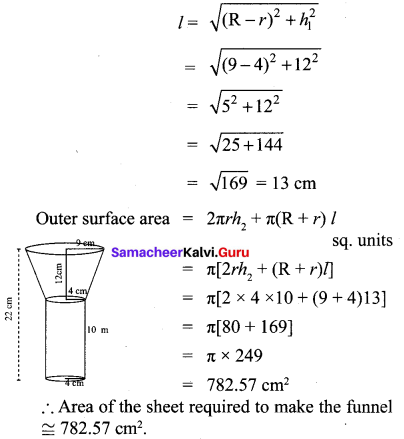
Question 6.
A wooden article was made by scooping out a hemisphere from each end of a cylinder as shown in figure. If the height of the cylinder is 10cm and its base is of radius 3.5 cm find the total surface area of the article.
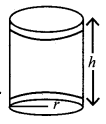
Solution:
Radius of the cylinder be r Height of the cylinder be h Total surface area of the article = CSA of cylinder + CSA of 2 hemispheres = 2πrh + 2πr2 = 2πr (h + 2r)