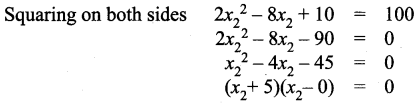You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.16
10th Maths Exercise 3.16 Solution Question 1.
In the matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cccc}{8} & {9} & {4} & {3} \\ {-1} & {\sqrt{7}} & {\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}} & {5} \\ {1} & {4} & {3} & {0} \\ {6} & {8} & {-11} & {1}\end{array}\right]\)
(i) The number of elements
(ii) The order of the matrix
(iii) Write the elements a22, a23, a24, a34, a43, a44
Solution:
(i) 16
(ii) 4 × 4
(iii) \(\sqrt{7}, \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\), 5, 0, -11, 1
10th Maths Exercise 3.16 Solutions Question 2.
If a matrix has 18 elements, what are the possible orders it can have? What if it has 6 elements?
Solution:
1 × 18, 2 × 9, 3 × 6, 6 × 3, 9 × 2, 18 × 1 and 1 × 6, 2 × 3, 3 × 2, 6 × 1
10th Maths Exercise 3.16 Answers Question 3.
Construct a 3 × 3 matrix whose elements are given by then find the transpose of A.
(i) aij = |i – 2j|
(ii) aij = \(\frac{(i+j)^{3}}{3}\)
Solution:
(i) aij = |i – 2j|
a11 = |1 – 2 × 1| = |1 – 2| = |-1| = 1
a12 = |1 – 2 × 2| = |1 – 4| = |-3| = 3
a13 = |1 – 2 × 3| = |1 – 6| = |-5| = 5
a21 = |2 – 2 × 1| = |2 – 2| = 0
a22 = |2 – 2 × 2| = |2 – 4| = |-2| = 2
a23 = |2 – 2 × 3| = |2 – 6| = |-4| = 4
a31 = |3 – 2 × 1| = |3 – 2| = |1| = 1
a32 = |3 – 2 × 2| = |3 – 4| = |-1| = 1
a33 = |3 – 2 × 3| = |3 – 6| = |-3| = 3
∴ \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}{1} & {3} & {5} \\ {0} & {2} & {4} \\ {1} & {1} & {3}\end{array}\right]\) is the required 3 × 3 matrix

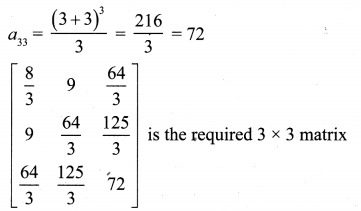
Ex 3.16 Class 10 Samacheer Question 4.

Solution:
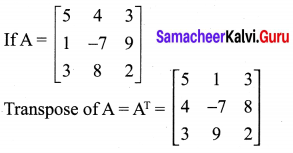
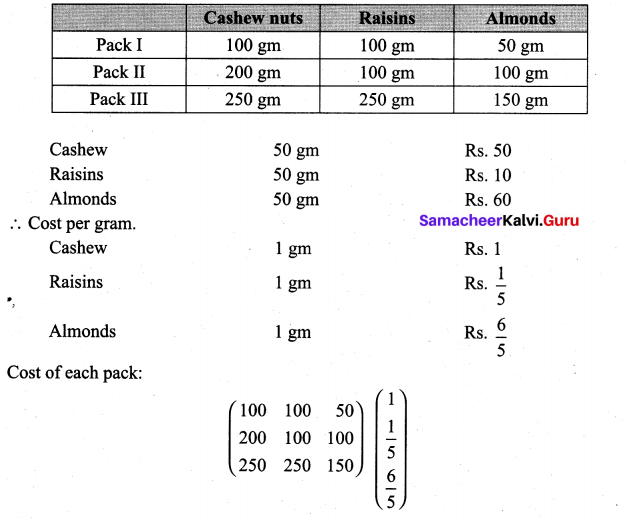
10th Maths Exercise 3.16 Question 5.
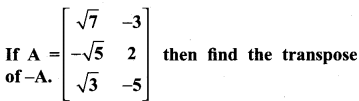
Solution:
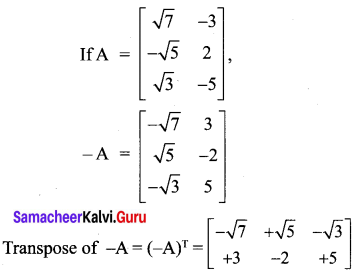
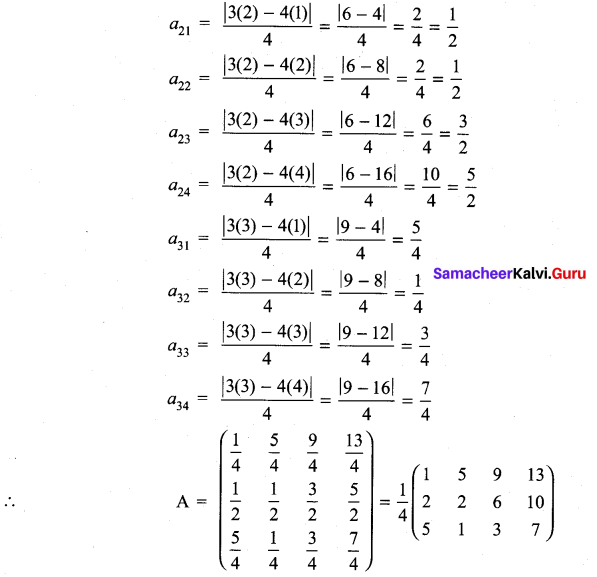
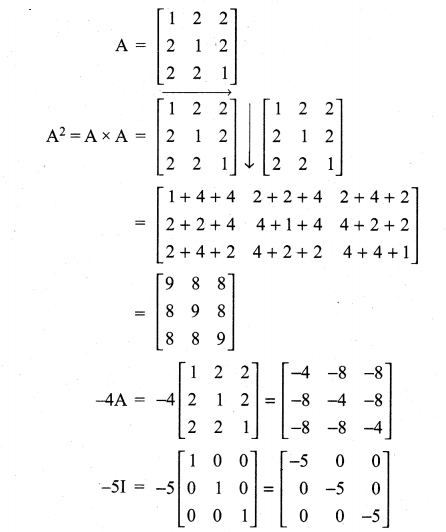
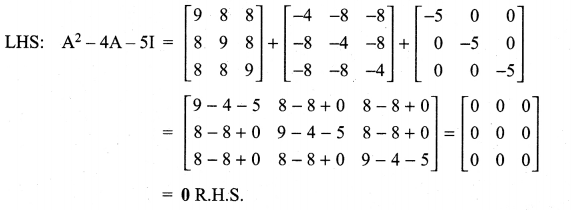
10th Maths 3.16 Question 6.
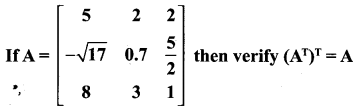
Solution:
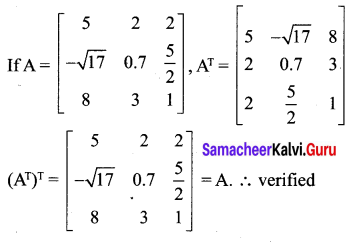
Exercise 3.16 Class 10 Question 7.
Find the values of x,y and z from the following equations
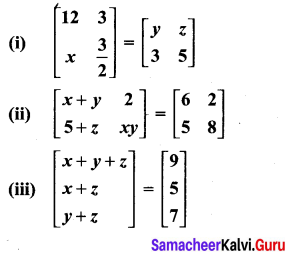
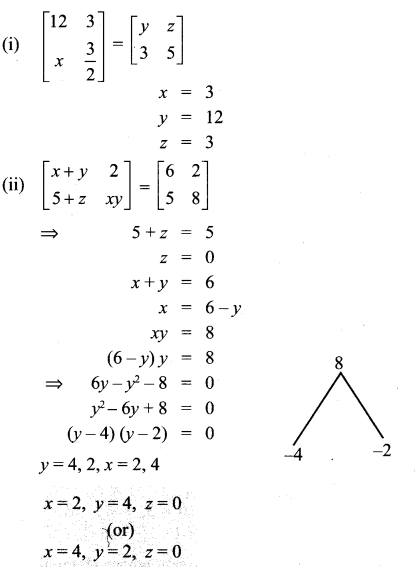
Solution:

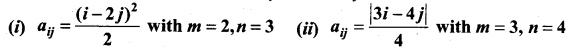
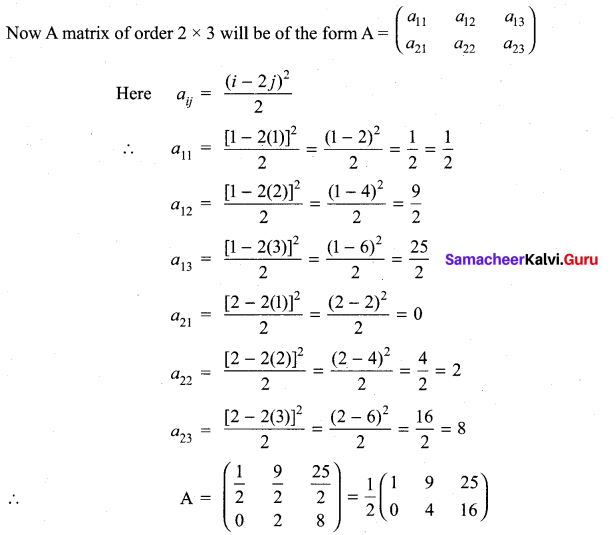
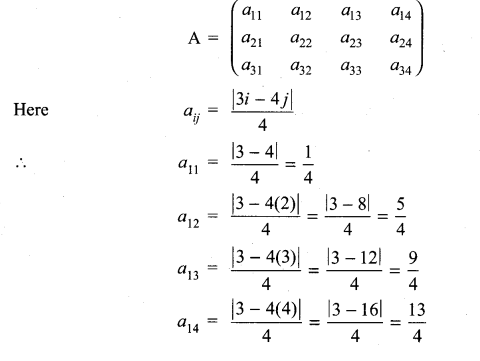
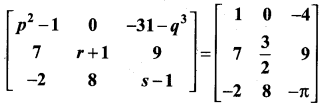
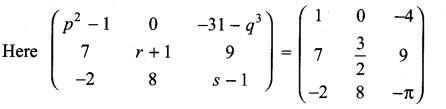
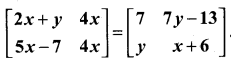
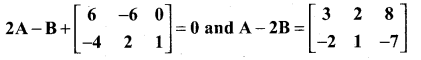
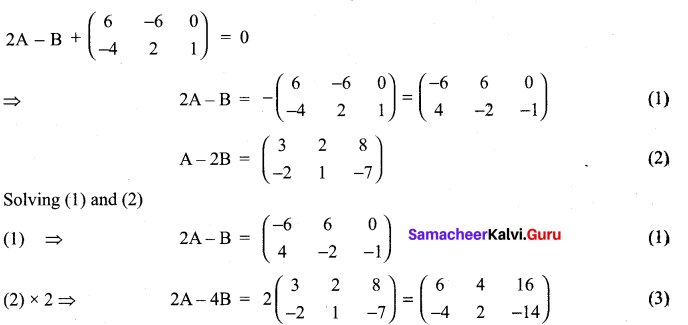

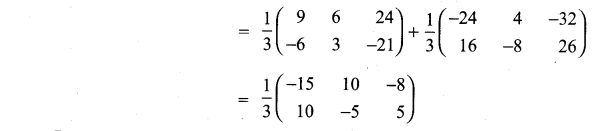
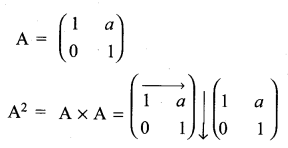
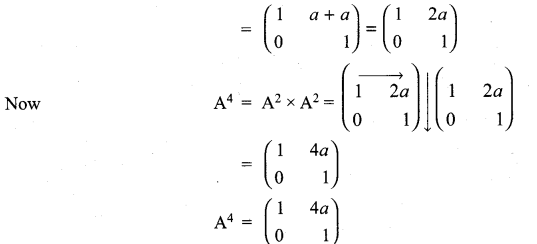
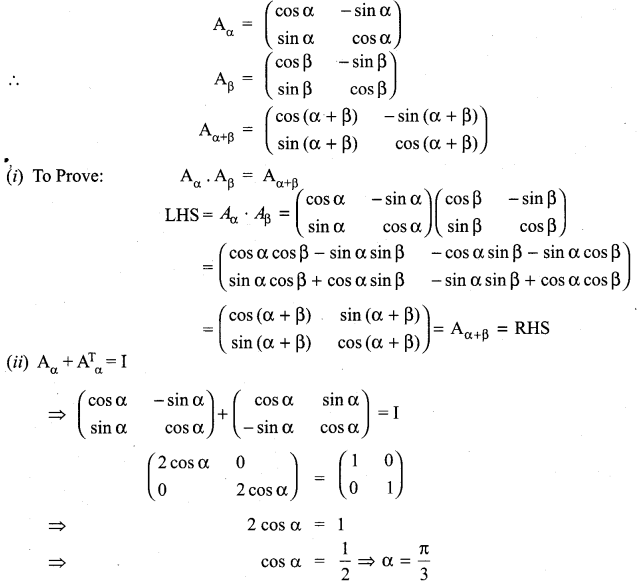
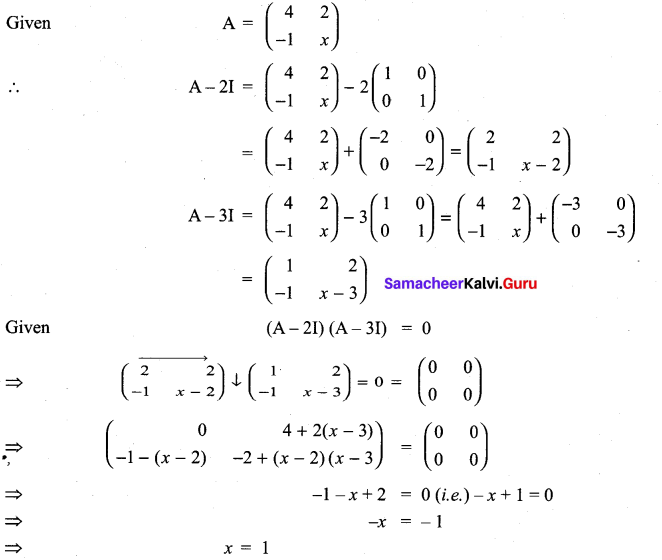
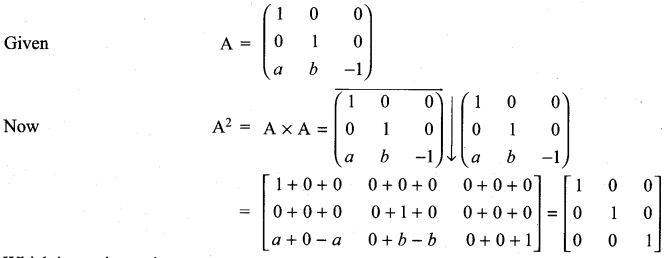
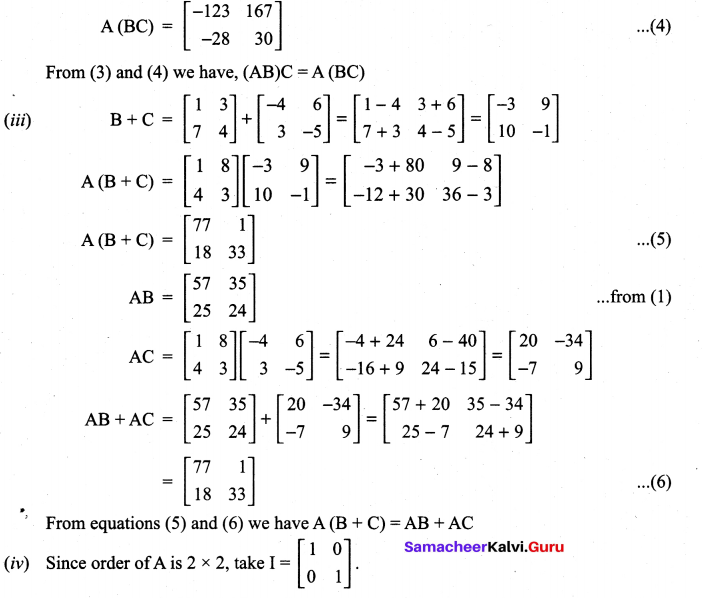
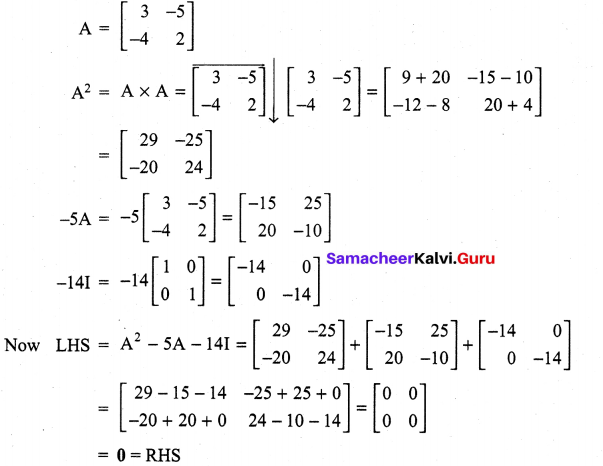
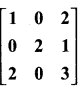 and A3 – 6A2 + 7A + KI = 0, find the value of k.
and A3 – 6A2 + 7A + KI = 0, find the value of k.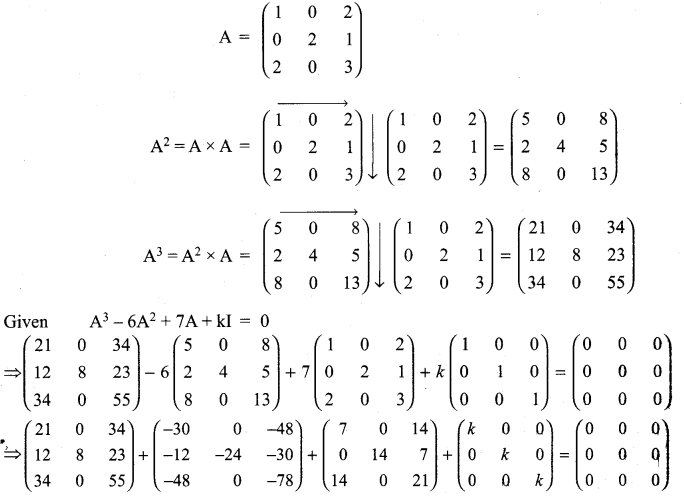
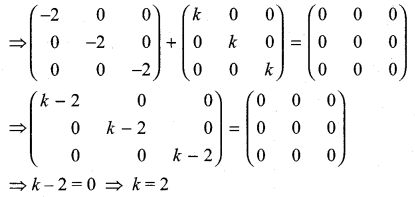
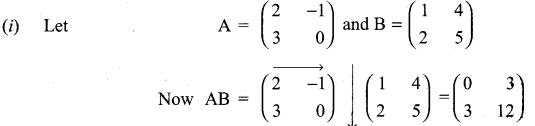
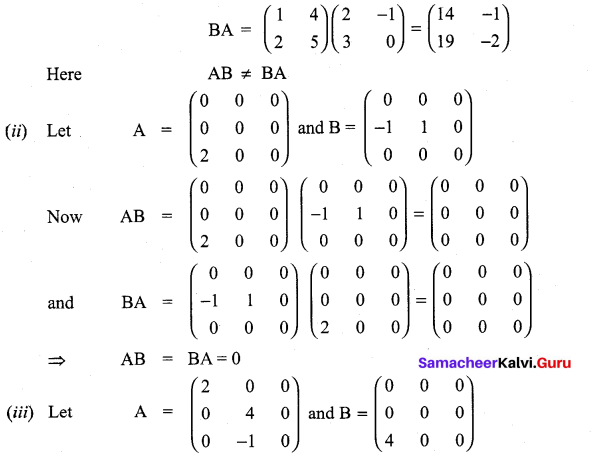
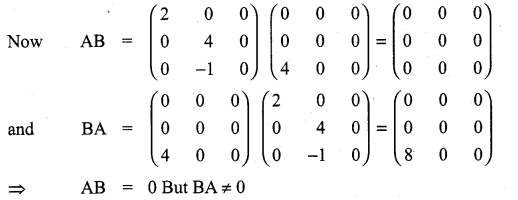
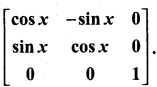
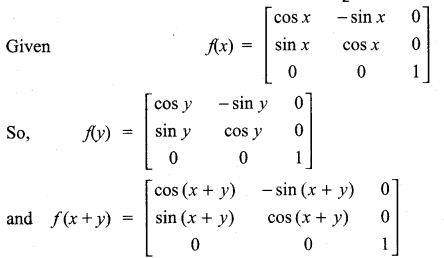
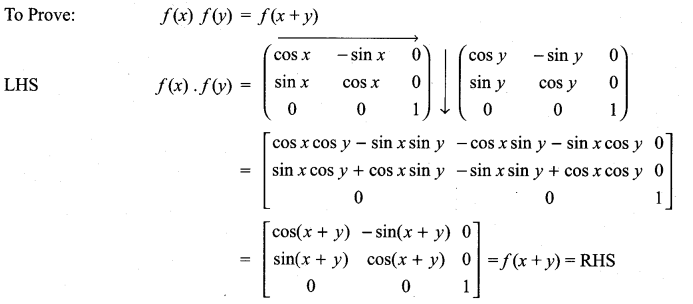
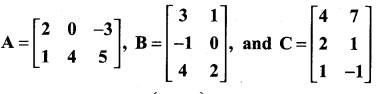
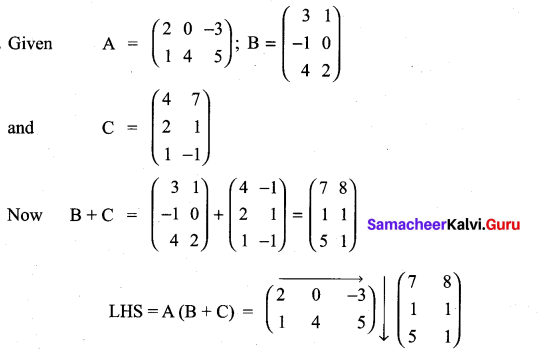
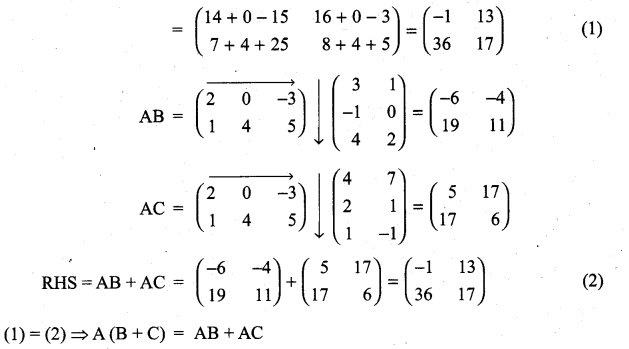
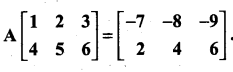
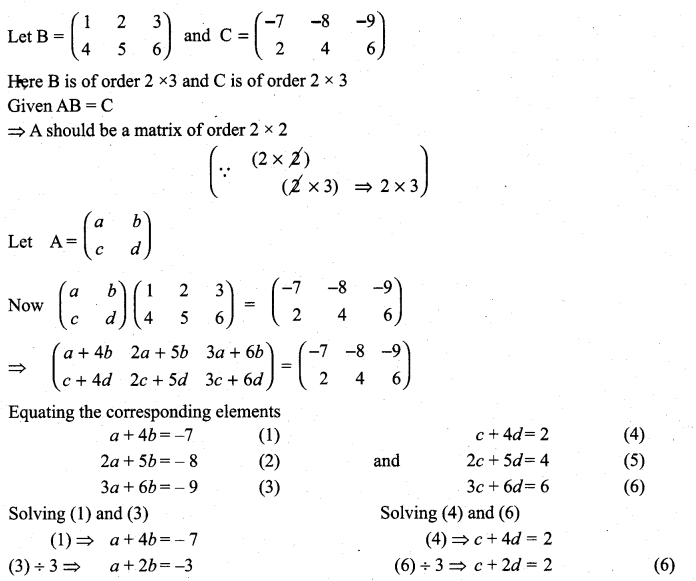

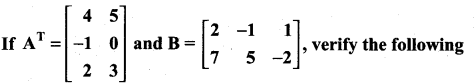
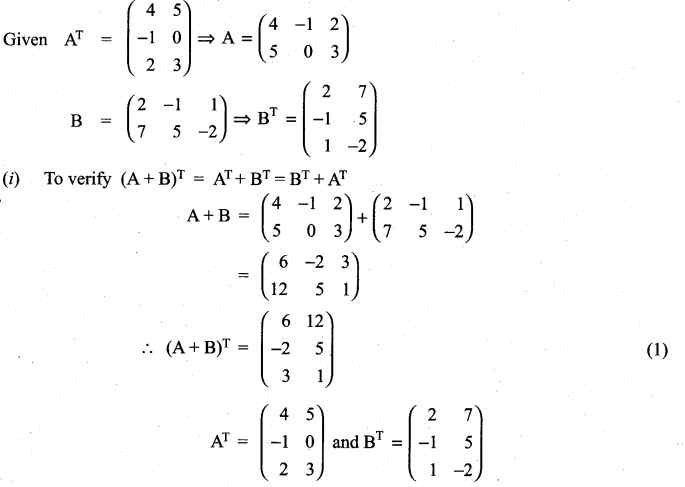
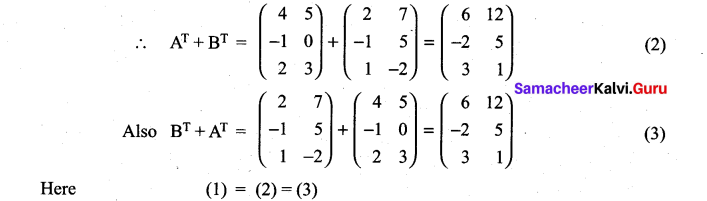
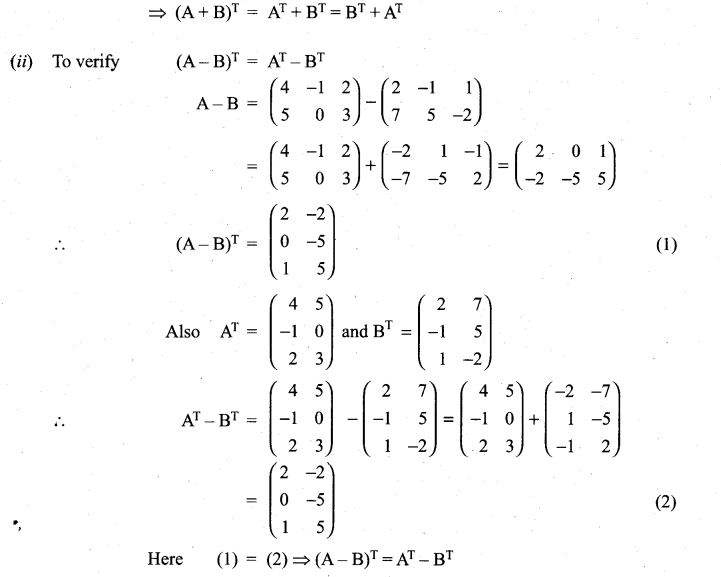
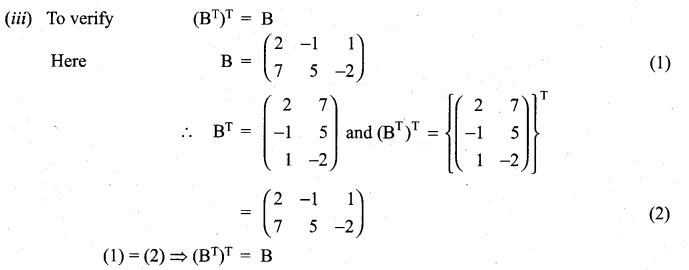

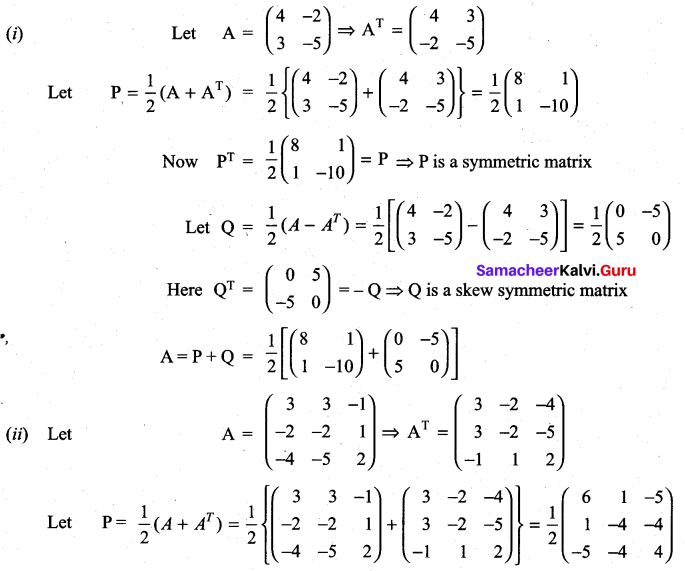
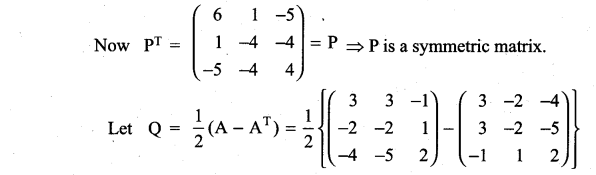
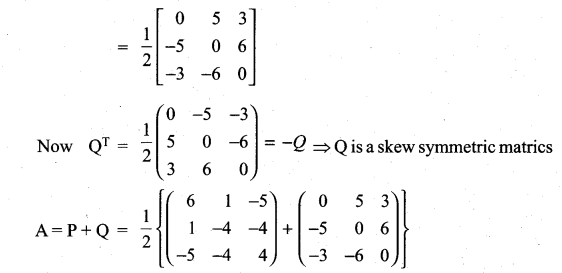
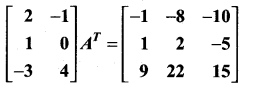
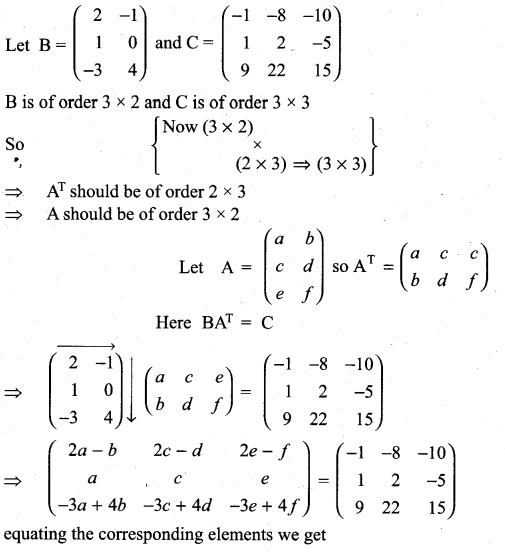
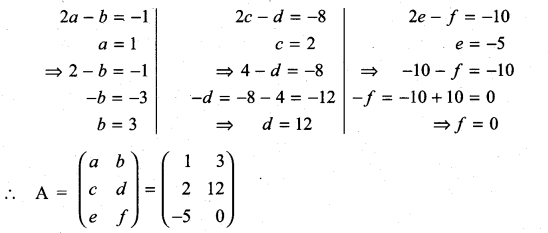
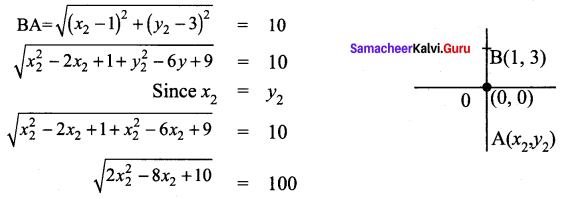
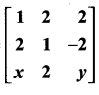 is a matrix such that AAT = 9I, find the values of x and y.
is a matrix such that AAT = 9I, find the values of x and y.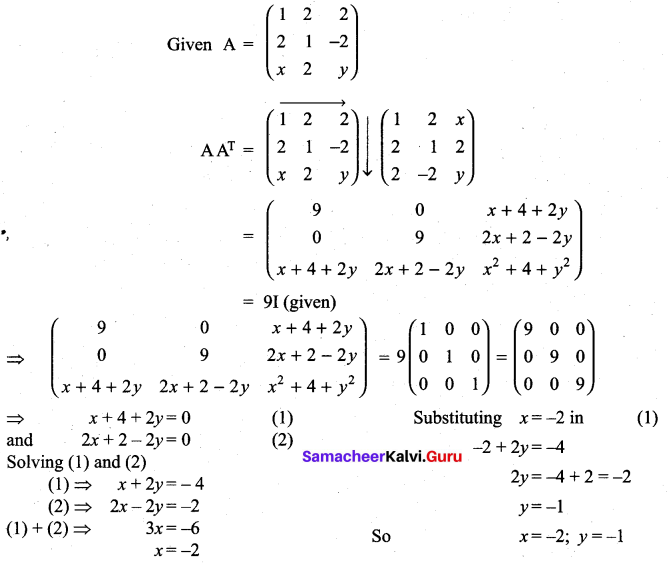

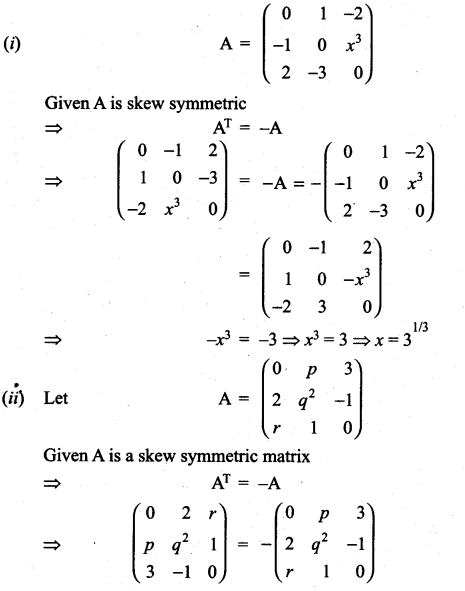
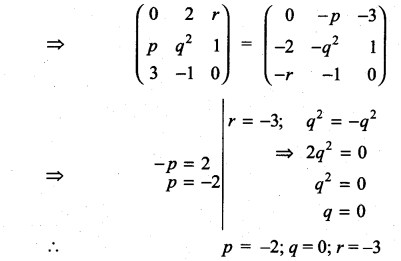
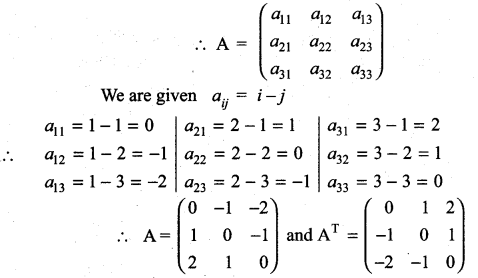

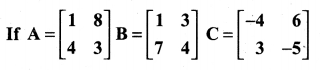

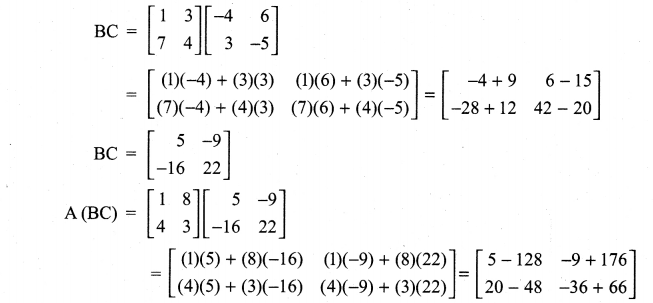
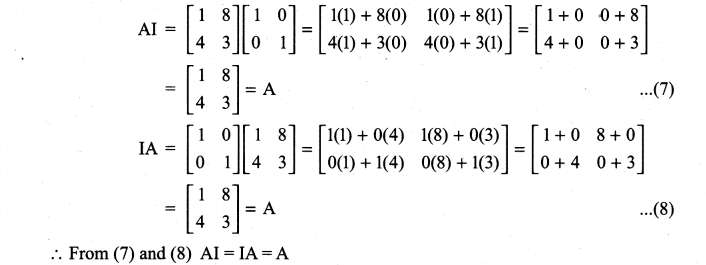
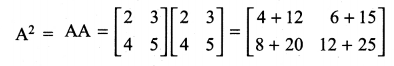
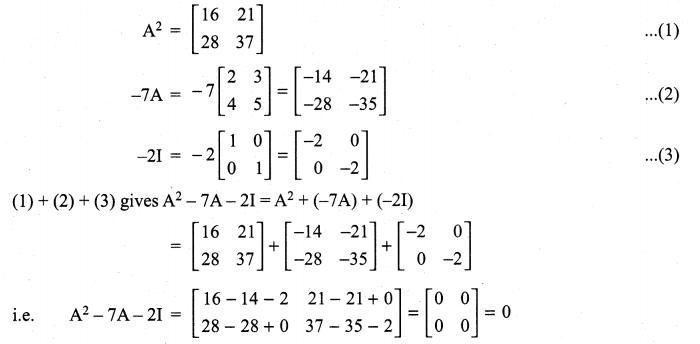
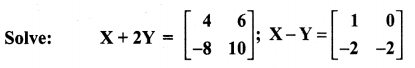

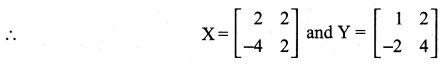
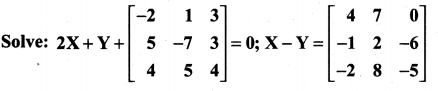
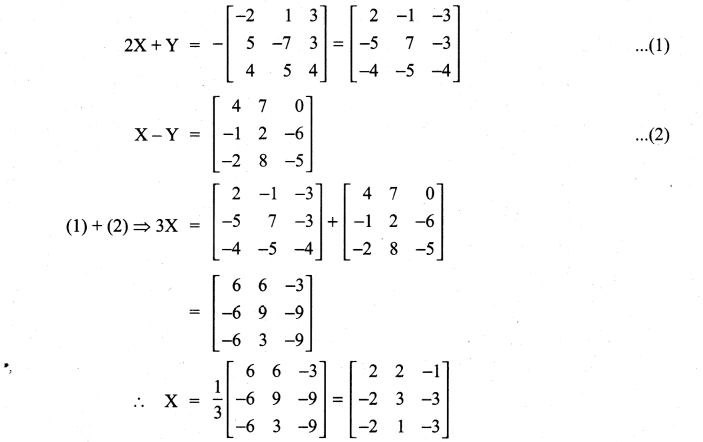
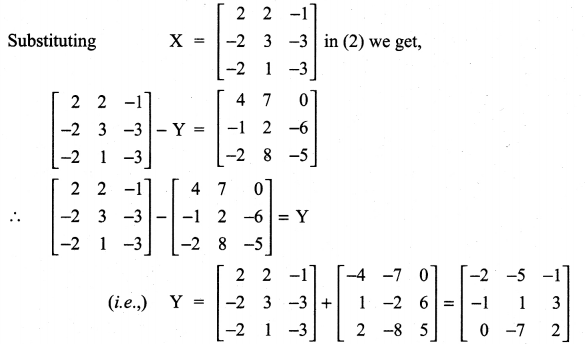
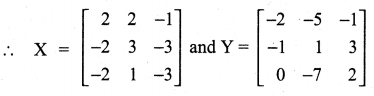
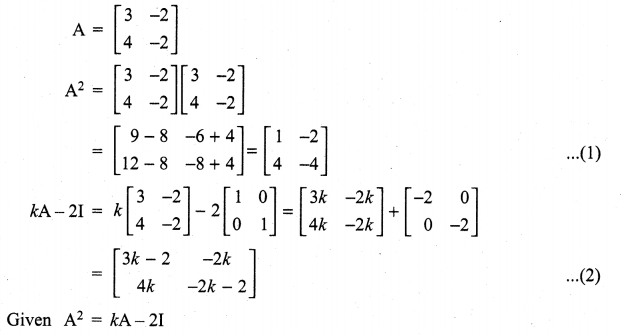
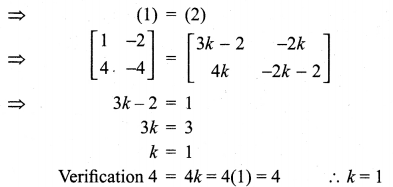
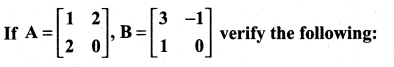
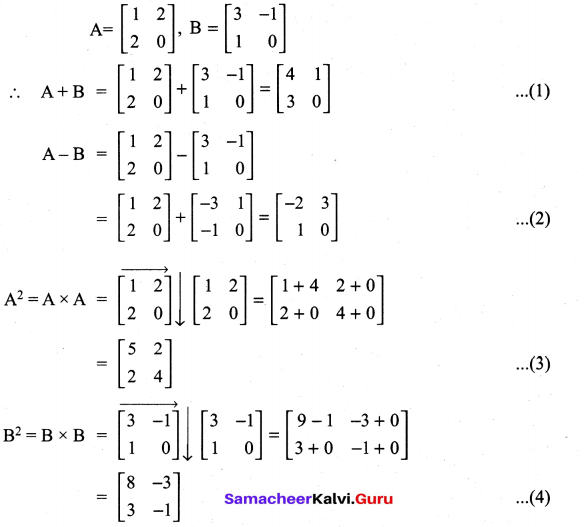
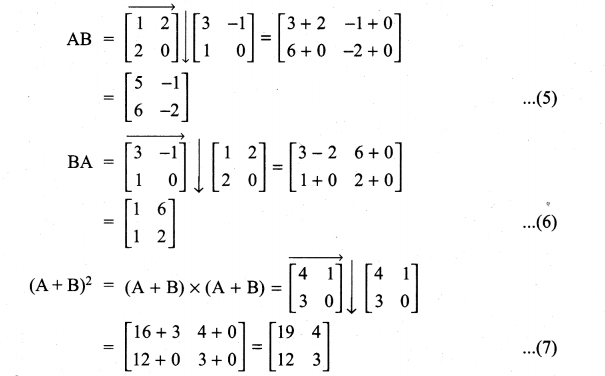
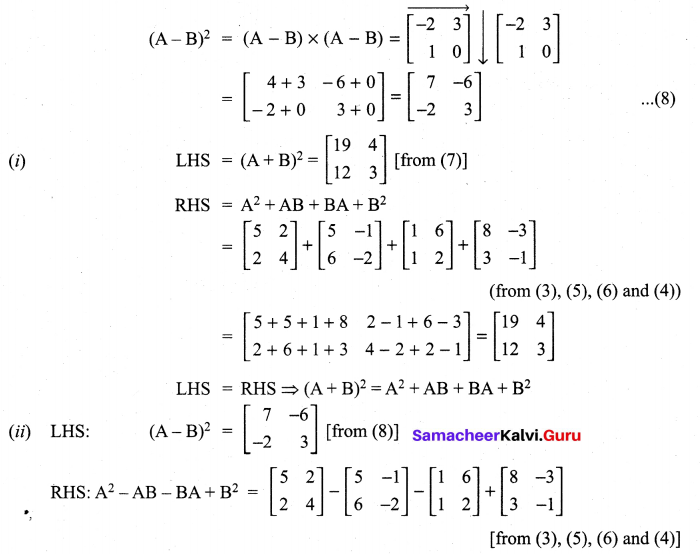
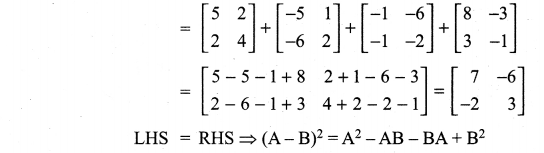
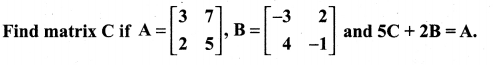
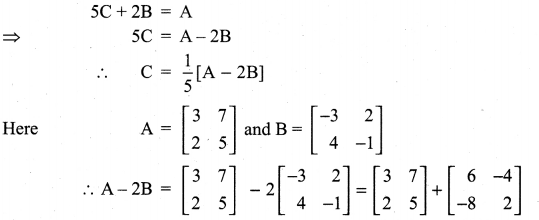
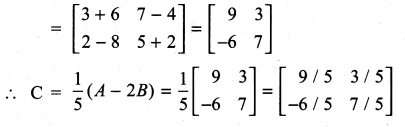
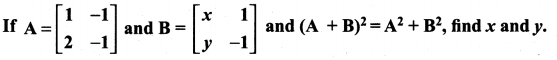
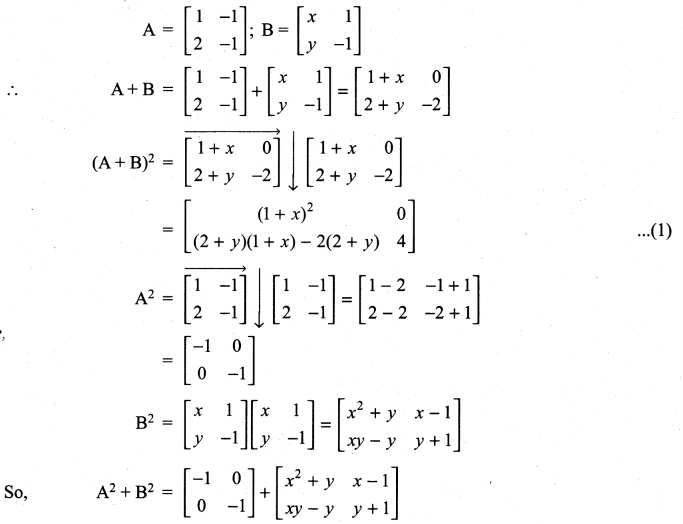


























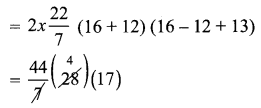
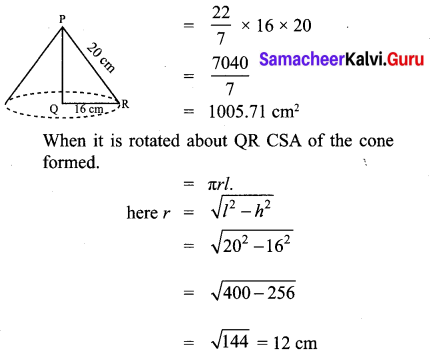
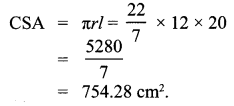
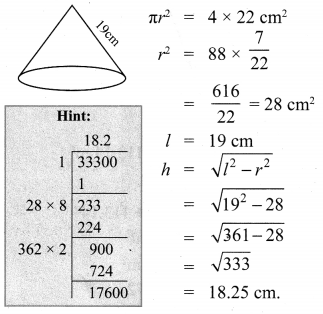











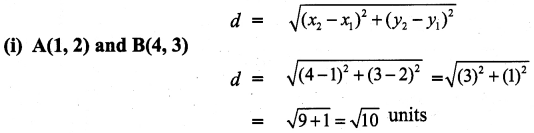
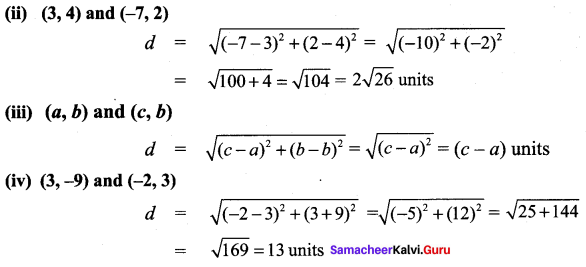
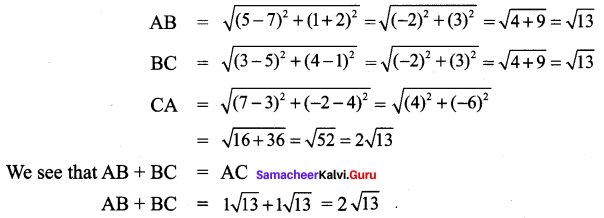
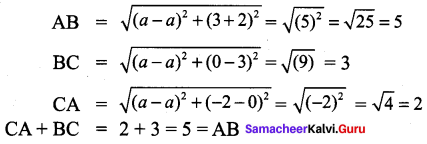
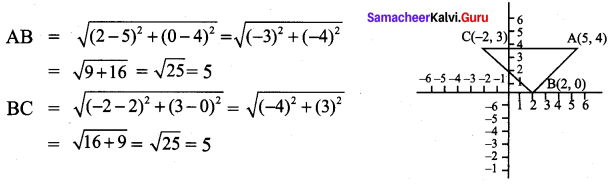
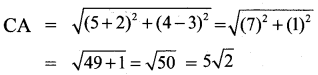
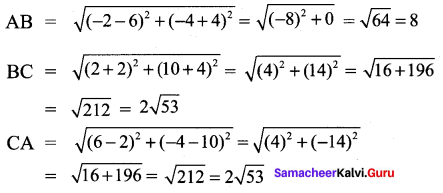
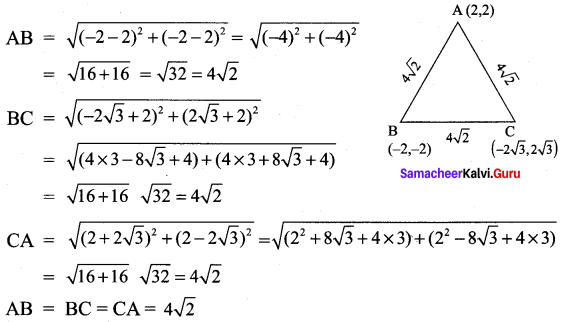
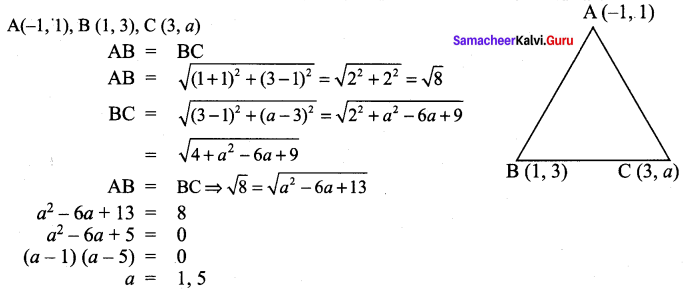
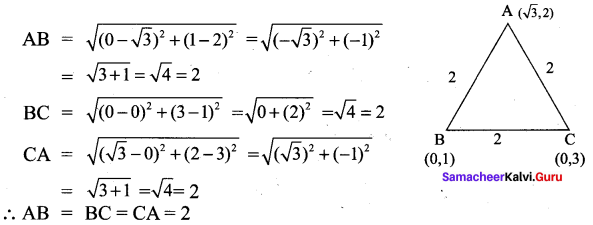 All the 3 sides of ∆ABC are equal. Hence ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle.
All the 3 sides of ∆ABC are equal. Hence ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle.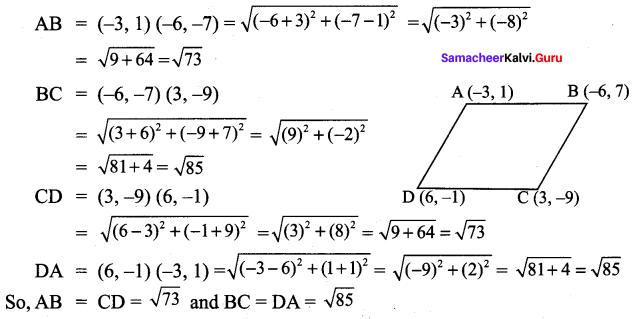
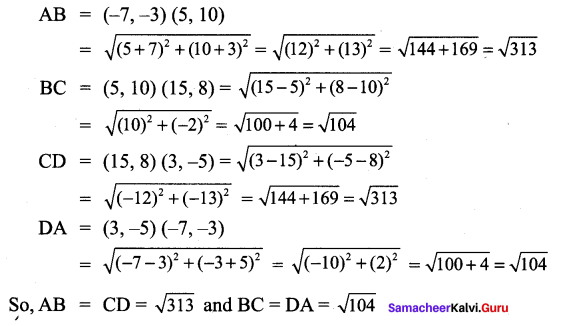
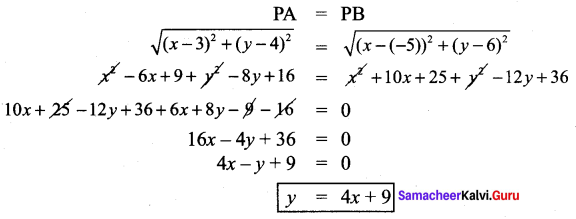
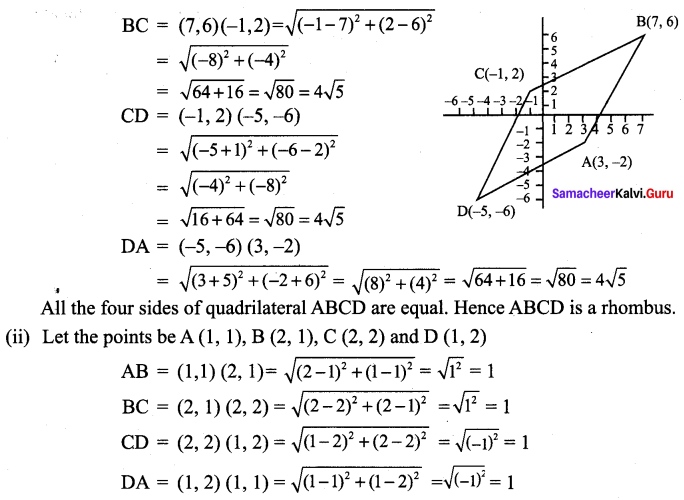 ∴ All the four sides of quadrilateral ABCD are equal. Hence ABCD is a rhombus.
∴ All the four sides of quadrilateral ABCD are equal. Hence ABCD is a rhombus.