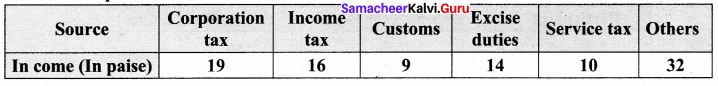
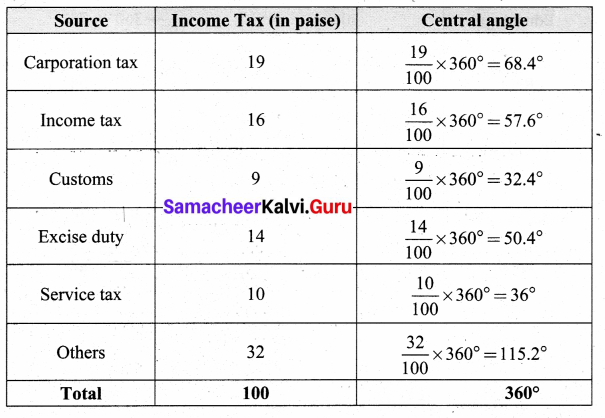
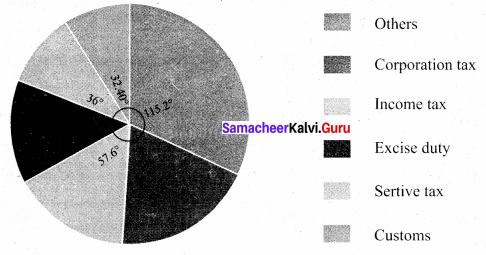
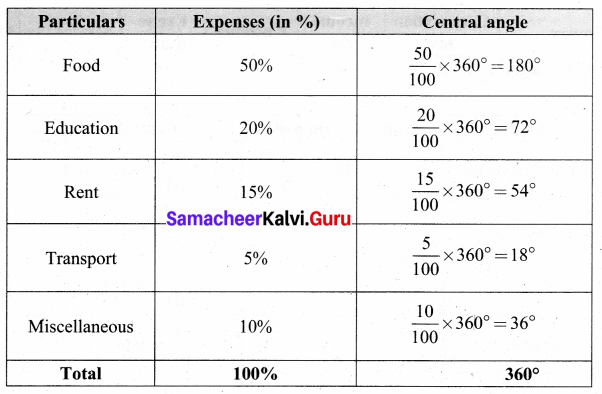
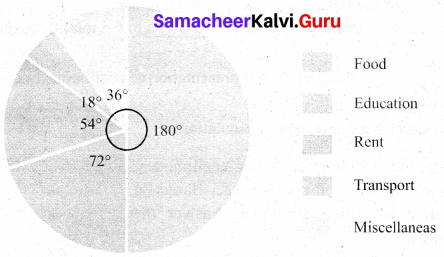
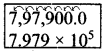Students can Download Maths Chapter 4 Statistics Intext Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 3 Chapter 4 Statistics Intext Questions
Exercise 4.1
Try These (Text book Page no. 77)
Question 1.
Arrange the given data in ascending and descending order:
9, 34, 4, 13, 42, 10, 25, 7, 31, 4, 40
Solution:
Ascending order: 4, 4, 7, 9, 10, 13, 25, 31, 34, 40, 42.
Descending order : 42, 40, 34, 31, 25, 13, 10, 9, 7, 4, 4
Question 2.
Find the range of the given data : 53, 42, 61, 9, 39, 63, 14, 20, 06, 26, 31, 4, 57
Solution:
Ascending order of the given data:
4, 6, 9, 14, 20, 26, 31, 39, 42, 53, 57, 61, 63
Here largest value = 63
Smallest value = 4
∴ Range = Largest value – smallest value = 63 – 4 = 59
![]()
Think (Text book Page no. 79)
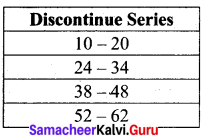
How will you change the given series as continuous series
15 – 25
28 – 38
41 – 51
54 – 64
Solution:
Given series
15 – 25
28 – 38
41 – 51
54 – 64
Difference in the gap = 28 – 25 = 3
Here half of the gap = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(3) = 1.5
∴ 1.5 is the adjustment factor. So we subtract 1.5 from the lower limit and add 1.5 to the upper limit to make it as a continuous series.
|
Discontinuous series |
Continuous series |
| 15-25 |
13.5-26.5 |
|
28-38 |
26.5-39.5 |
| 41-51 |
39.5-52.5 |
|
54 – 64 |
52.5-65.5 |
Think (Text book Page no. 80)
If we want to represent the given data by 5 classes, then how shall we find the interval?
Solution:
We can find the class size by the formula
Number of class intervals = \(\frac{Range}{Class size}\)
Try These (Text book Page no. 82)
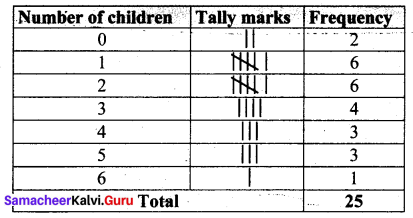
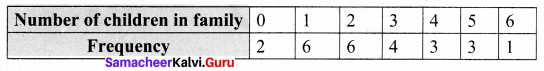
Question 1.
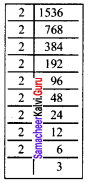
Prepare a frequency table for the data : 3, 4, 2, 4, 5, 6, 1, 3, 2, 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 1, 3, 2, 4
Solution:
Ascending order of the given data.
1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6
The distribution table:
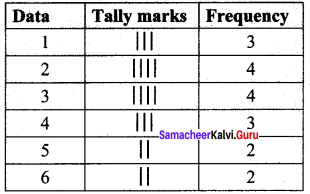
∴ Frequency Table:
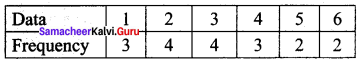
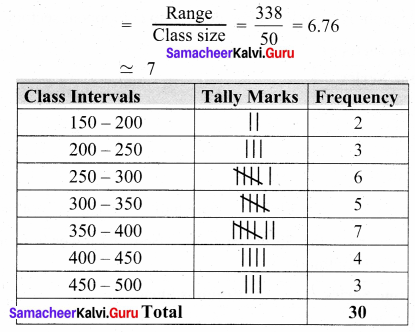
Question 2.
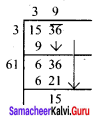
Prepare a grouped frequency table for the data :
10, 9, 3, 29, 17, 34, 23, 20, 39, 42, 5, 12, 19, 47, 18, 19, 27, 7, 13, 40, 38, 24, 34, 15, 40
Largest value = 47
Smallest value = 3
Range = Largest value – Smallest value = 47 – 3 = 44
Suppose we take class size as 10, then Number of class intervals possible
= \(\frac{Range}{Class size}\) = \(\frac{44}{10}\) = 4.4
\(\tilde { – } \) 5
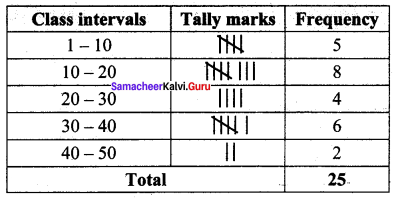
![]()
Exercise 4.2
Think (Text book Page no. 94)
When joining two adjacent midpoints w ithout using a ruler, can you get a polygon?
Solution:
No, because it may be curved lines and they are not considered as polygons.