Get Tamilnadu Board Class 12 Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter wise Study Material to score good marks in the exam. Various chapters with subtopics are explained clearly in Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology Solutions Material. All the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology Book Solutions Chapter 6 Evolution Questions, answers, Notes, Guide, Pdf along with the explanations are provided by the subject experts. Students can easily learn Tamilnadu Board Class 12 Chapter wise Bio Zoology with the help of the step by step guide provided on our site. Learn all the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology concepts to attempt the exam with more confidence. Read all the concepts of Tamilnadu Board Solutions for Class 12 Bio Zoology Chapter 6 Evolution.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 6 Evolution
Whether you want to become an expert in Bio Zoology or to get good marks in the exam, you have one and only solution is practicing with Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter wise Solutions. Strengthen your weakness by learning the Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter 6 Evolution Questions and Answers on our site. You can learn directly online on our website or learn offline by downloading Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter wise material. Save your time and read Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Subject at your comfort level.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Evolution Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The first life on Earth originated __________
(a) in air
(b) on land
(c) in water
(d) on mountain
Answer:
(c) in water
Question 2.
Who published the book “Origin of species by Natural Selection” in 1859?
(a) Charles Darwin
(b) Lamarck
(c) Weismann
(d) Hugo de Vries
Answer:
(a) Charles Darwin
Question 3.
Which of the following was the contribution of Hugo de Vries?
(a) Theory of mutation
(b) Theory of natural Selection
(c) Theory of inheritance of acquired characters
(d) Germplasm theory
Answer:
(a) Theory of mutation
Question 4.
The wings of birds and butterflies is an example of __________
(a) Adaptive radiation
(b) convergent evolution
(c) divergent evolution
(d) variation
Answer:
(b) convergent evolution
Question 5.
The phenomenon of “ Industrial Melanism” demonstrates __________
(a) Natural selection
(b) induced mutation
(c) reproductive isolation
(d) geographical isolation
Answer:
(a) Natural selection
Question 6.
Darwin’s finches are an excellent example of __________
(a) connecting links
(b) seasonal migration
(c) adaptive radiation
(d) parasitism
Answer:
(c) adaptive radiation
Question 7.
Who proposed the Germplasm theory?
(a) Darwin
(b) August Weismann
(c) Lamarck
(d) analysis of bones
Answer:
(b) August Weismann
Question 8.
The age of fossils can be determined by __________
(a) electron microscope
(b) weighing the fossils
(c) carbon dating
(d) analysis of bones
Answer:
(c) carbon dating
Question 9.
Fossils are generally found in __________
(a) igneous rocks
(b) metamorphics
(c) volcanic rocks
(d) sedimentary rocks
Answer:
(d) sedimentary rocks
Question 10.
Evolutionary history of an organism is called __________
(a) ancestry
(b) ontogeny
(c) phylogeny
(d) paleontology
Answer:
(c) phylogeny
Question 11.
The golden age of reptiles was __________
(a) Mesozoic era
(b) Cenozoic era
(c) Paleozoic era
(d) Proteroic era
Answer:
(a) Mesozoic era
Question 12.
Which period was called “Age of fishes”?
(a) Permian
(b) Triassic
(c) Devonian
(d) Ordovician
Answer:
(c) Devonian
Question 13.
Modem man belongs to which period?
(a) Quaternary
(b) Cretaceous
(c) Silurian
(d) Cambrian
Answer:
(a) Quaternary
Question 14.
The Neanderthal man had the brain capacity of __________
(a) 650 – 800cc
(b) 1200cc
(c) 900cc
(d) 1400c
Answer:
(d) 1400c
Question 15.
List out the major gases seems to fie found in the primitive Earth.
Answer:
C02, NH3, UV and Water vapour
Question 16.
Explain the three major categories in which fossilization occur.
Answer:
(i) Actual remains is the most common method of fossilization. When marine animals die, their hard parts such as bones and shells, etc. are covered with sediments and are protected from further deterioration. They get preserved as such as they are preserved in vast ocean
the salinity in them prevents decay. The sediments become hardened to form definite layers or strata. For example, Woolly Mammoth that lived 22 thousand years ago were preserved in the frozen coast of Siberia as such. Several human beings and animals living in die ancient city of Pompeii were preserved intact by volcanic ash which gushed out from Mount Vesuvius.
(ii) Petrifaction – When animals die the original portion of their body may be replaced molecule for molecule by minerals and the original substance being lost through disintegration. This method of fossilization is called petrifaction. The principle minerals involved in this type fossilization are iron pyrites, silica, calcium carbonate and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium.
(iii) Natural moulds and casts – Even after disintegration, the body of an animal might leave indelible impression on the soft mud which later becomes hardened into stones. Such impressions are called moulds. The cavities of the moulds may get filled up by hard minerals and get fossilized, which are called casts. Hardened faecal matter termed as coprolites, occur as tiny pellets. Analysis of the coprolites enables us to understand the nature of diet, the prehistoric animals thrived.
Question 17.
Differentiate between divergent evolution and convergent evolution with one example for each.
Answer:
Divergent Evolution:
- Divergent evolution is a result of homology.
- Eg: The wings of bird and the forelimbs of human both are homologous structures modified according to functions. In birds, it is used for flight and in humans used for writing and other purposes.
Convergent Evolution:
- Convergent evolution is a result of analogy,
- E.g: Root modification in sweet potato, and stem modification in potato are analogous structures both performing same function i.e., storage,
Question 18.
How does Hardy-Weinberg’s expression (p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1) explain that genetic equilibrium is maintained in a population? List any four factors that can disturb the genetic equilibrium.
Answer:
The allele frequencies in a population are stable and are constant from generation to generation in the absence of gene flow, genetic drift, mutation, recombination and natural selection. If a population is in a state of Hardy Weinberg equilibrium, the frequencies of alleles and genotypes or sets of alleles in that population will remain same over generations. Evolution is a change in the allele frequencies in a population over time. Hence population in Hardy Weinberg is not evolving.
Suppose we have a large population of beetles, (infinitely large) and appear in two colours ’ dark grey (black) and light grey, and their colour is determined by ‘A’ gene. ‘AA’ and ‘Aa’ beetles are dark grey and ‘aa’ beetles are light grey. In a population let’s say that ‘ A’ allele has frequency (p) of 0.3 and ‘a’ allele has a frequency (q ) of 0.7. Then p+q= 1.
If a population is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium the genotype frequencycan be estimated by Hardy Weinberg equation.
(p + q)2 = p2 + 2pq + q2
p2 = frequency of AA
2pq = frequency of Aa
q2 = frequency of aa
p = 0.3, q = 0.7 then,
p2 = (0.3)2 = 0.09 = 9 %AA
2pq = 2(0.3) (0.7) = 0.42 = 42 % Aa
q2 = (0.7)2 0.49 = 49 % aa
Hence the beetle population appears to be in Hardy- Weinberg equilibrium. When the beetles in Hardy- Weinberg equilibrium reproduce the allele and genotype frequency in the next generation would be: Let’s assume that the frequency of ‘A’ and ‘a’ allele in the pool of gametes that make the next generation would be the same, then there would be no variation in the progeny. The genotype frequencies of the parent appears in the next generation.
(i.e. 9% AA, 42% Aa and 49% aa).
If we assume that the beetles mate randomly (selection of male gamete and female gamete in the pool of gametes), the probability of getting the offspring genotype depends on the genotype of the combining parental gametes.
Question 19.
Explain how mutations, naturalxelection and genetic drift affect Hardy Weinberg equilibrium.
Answer:
Natural selection occurs when one allele (or combination of alleles of differences) makes an organism more or less fit to survive and reproduce in a given environment. If an allele reduces fitness, its frequencies tend to drop from one generation to the next.
The evolutionary path of a given gene (i.e) how its allele’s change in frequency in the population across generation, may result from several evolutionary mechanisms acting at once. For example, one gene’s allele frequencies might be modified by both gene flow and genetic drift, for another gene, mutation may produce a new allele, that is favoured by natural selection.
Genetic drift / Sewall Wright Effect is a mechanism of evolution in which allele frequencies of a population change over generation due to chance (sampling error). Genetic drift occurs in all population sizes, but its effects are strong in a small population. It may result in a loss of some alleles (including beneficial ones) and fixation of other alleles. Genetic drift can have major effects, when the population is reduced in size by natural disaster due to bottle neck effect or when a small group of population splits from the main population to form a new colony due to founder’s effect.
Although mutation is the original source of all genetic variation, mutation rate for most organisms is low. Hence new mutations on an allele frequencies from one generation to the next is usually not large.
Question 20.
How did Darwin explain fitness of organisms?
Answer:
Organisms struggle for food, space and mate. As these become a limiting factor, competition exists among the members of the population. Darwin denoted struggle for existence in three ways
Intra specific struggle between the same species for food, space and mate Inter specific struggle with different species for food and space.
Struggle with the environment to cope with the climatic variations, flood, earthquakes and drought, etc.
According to Darwin, nature is the most powerful selective force. He compared origin of species by natural selection to a small isolated group. Darwin believed that the struggle for existence resulted in the survival of the fittest. Such organisms become better adapted to the changed environment.
Question 21.
Mention the main objections to Darwinism.
Answer:
Some objections raised against Darwinism were Darwin failed to explain the mechanism of variation.
- Darwinism explains the survival of the fittest but not the arrival of the fittest.
- He focused on small fluctuating variations that are mostly non-heritable.
- He did not distinguish between somatic and germinal variations.
- He could not explain the occurrence of vestigial organs, over specialization of some organs like large tusks in extinct mammoths and over sized antlers in the extinct Irish deer, etc.
Question 22.
Taking the example of Peppered moth, explain the action of natural selection. What do you call the above phenomenon?
Answer:
Natural selection can be explained clearly through industrial melanism. Industrial melanism is a classical case of Natural selection exhibited by the peppered moth, Bistort betularia. These were available in two colours, white and black. Before industrialization peppered moth both white and black coloured were common in England. Pre-industrialization witnessed white colpured background of the wall of the buildings hence the white coloured moths escaped from their predators. Post industrialization, the tree trunks became dark due to smoke and soot let out from the industries.
The black moths camouflaged on the dark bark of the trees and the white moths were easily identified by their predators. Hence the dark coloured moth population was selected and their number increased when compared to the white moths. Nature offered positive selection pressure to the black coloured moths. The above proof shows that in a population, organisms that can adapt will survive and produce more progenies resulting in increase in population through natural selection.
Question 23.
Darwin’s finches and Australian marsupials are suitable examples of adaptive radiation – Justify the statement.
Answer:
Darwin’s finches are the birds whose common ancestor arrived on the Galapagos about 2 million years ago. During that time, Darwin’s finches have evolved into 14 recognized species differing in body size, beak shape and feeding behavior. Changes in the size and form of the beak have enabled different species to utilize different food resources such as insects, seeds, nectar from cactus flowers and blood from iguanas, all driven by Natural selection. Genetic variation in the ALX1 gene in the DNA of Darwin finches is associated with variation in the beak shape. Mild mutation in the ALX1 gene leads to phenotypic change in the shape of the beak of the Darwin finches.
Marsupials in Australia and placental mammals in North America are two subclasses of mammals they have adapted in similar way to a particular food resource, locomotory skill or climate. They were separated from the common ancestor more than 100 million years ago and each lineage continued to evolve independently.
Despite temporal and geographical separation, marsupials in Australia and placental mammals in North America have produced varieties of species living in similar habitats with similar ways of life. Their overall resemblance in shape, locomotory mode, feeding and foraging are superimposed upon different modes of reproduction. This feature reflects their distinctive evolutionary relationships.
Over 200 species of marsupials live in Australia along with many fewer species of placental mammals. The marsupials have undergone adaptive radiation to occupy the diverse habitats in Australia, just as the placental mammals have radiated across North America.
Question 24.
Who disproved Lamarck’s Theory of acquired characters? How?
Answer:
Lamarck’s “Theory of Acquired characters” was disproved by August Weismann who conducted experiments on mice for twenty generations by cutting their tails and breeding them. All mice bom were with tail. Weismann proved that change in the somatoplasm will not be transferred to the next generation but changes in the germplasm will be inherited.
Question 25.
How does Mutation theory of De Vries differ from Lamarck and Darwin’s view in the origin of new species.
Answer:
According to de Vries, sudden and large variations were responsible for the origin of new species, whereas Lamarck and Darwin believed in gradual accumulation of all variations as the causative factors in the origin of new species.
Question 26.
Explain stabilizing, directional and disruptive selection with examples.
Answer:
i. Stabilising selection (centipetal selection): This type of selection operates in a stable environment as shown in fig. The organisms with average phenotypes survive whereas the extreme individuals from both the ends are eliminated. There is no speciation but the phenotypic stability is maintained within the population over generation. For example, measurements of sparrows that survived the storm clustered around the mean, and the sparrows that failed to survive the storm clustered around the extremes of the variation showing stabilizing selection.
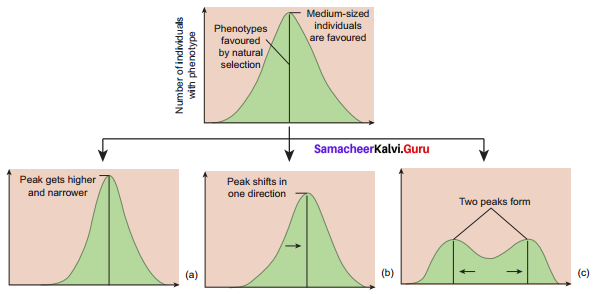
ii. Directional Selection: The environment” which undergoes gradual change is subjected to directional selection, as shown in fig. This type of selection removes the individuals from one end towards the other end of phenotypic distribution. For example, size differences between male and female sparrows. Both male and female look alike externally but differ in body weight. Females show directional selection in relation to body weight.
iii. Disruptive selection: (centrifugal selection) When homogenous environment changes into heterogenous environment this type of selection is operational as shown in fig. The organisms of both the extreme phenotypes are selected, whereas individuals with average phenotype are eliminated. This results in splitting of the population into sub population/species. This is a rare form of selection but leads to formation of two or more different species. It is also (called adaptive radiation. (E.g:) Darwin’s finches beak size in relation to seed size inhabiting Galapagos islands. Group selection and sexual selection are other types of selection. The two major group selections are Altrusim and Kin selection.
Question 27.
Rearrange the descent in human evolution.
Answer:
Australopithecus → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens → Ramapithecus → Homo habilis
Ramapithecus → Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
Question 28.
Differentiate between the eating habit and brain size of Australopithecus and Ramapithecus.
Answer:
| Australopithecus | Ramapithecus | |
| Eating Habit | Herbivores | Omnivores |
| Brain Size | 350- 450 cc | 200 – 300 cc |
Question 29.
How does Neanderthal man differ from the modern man in appearance?
Answer:
Neanderthal man differ from the modem human in having semierect posture, flat cranium, sloping forehead, thin large orbits, heavy brow ridges, protruding jaws and no chin.
Question 30.
Mention any three similarities found common in Neanderthal man and Homo sapiens. Common characters showed by Neanderthal man and Homo sapiens are:
Answer:
- Usage of Fire
- Burying of deadbodies
- Protecting themselves from predators
Question 31.
According to Darwin, the organic evolution is due to
(а) Intraspecific competition
(b) Interspecific competition
(c) Competition within closely related species.
(d) Reduced feeding efficiency in one species due to the presence of interfering species.
Answer:
(d) Reduced feeding efficiency in one species due to the presence of interfering species.
Question 32.
A population will not exist in Hardy – Weinberg equilibrium if
(a) Individuals mate selectively
(b) There are no mutations
(c) There is no migration
(d) The population is large
Answer:
(a) Individuals mate selectively
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Evolution Additional Questions and Answers
1 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
Identify the incorrect statement in concern with Neanderthals.
(a) Neanderthal human were found in Germany.
(b) They possessed flat cranium.
(c) They used to bury their dead.
(d) Their brain size is of 650 – 800 cc
Answer:
(d) Their brain size is of 650 – 800 cc
Question 2.
Which of the following statement does not satisfy Hardy Weinberg principle?
(a) A population undergoing random mating
(b) Small sized population
(c) Population where there is no mutation or gene flow
(d) Absence of natural selection
Answer:
(b) Small sized population
Question 3.
Match column I with column II

Answer:
(a) a – iii b – ii c – iv d – i
Question 4.
Placental mammals develop during _______
(a) Eocene
(b) Oligocene
(c) Pliocene
(d) Paleocene
Answer:
(d) Paleocene
Question 5.
Identify the correct sequence from oldest to youngest
(а) Cambrian → Permian → Devonian → Silurian → Ordovician
(b) Permian → Silurian → Devonian → Ordovician → Cambrian
(c) Permian → Devonian → Silurian → Cambrian → Ordovician
(d) Cambrian → Ordovician → Silurian → Devonian → Permian
Answer:
(d) Cambrian → Ordovician → Silurian Devonian → Permian
Question 6.
Match the scientists with their terminologies used
(a) Biogenesis (i) Oparin
(b) Prebiotic soup (ii) Henry Bastin
(c) Coacervates (iii) Thomas Huxley
(d) Abiogenesis (iv) Haldane
(a) a – iii b – iv c – ii d – i
(b) a – ii b – iv c – i d – iii
(c) a – iii b – i c – iv d – ii
(d) a – i b – iv c – iii d – ii
Answer:
(b) a – ii b – iv c – i d – iii
Question 7.
Anatomical structures that have similar functions but not similar structures are called
(a) Homologous structures
(b) Vestigial structures
(c) Analogus structures
(d) Generalized structures
Answer:
(c) Analogous structures
Question 8.
Who propounded the theory of recapitulation?
(a) Ernst Von Haeckel
(b) Charles Darwin
(c) Thomas Huxley
(d) Oparin
Answer:
(c) Ernst Von Haeckel
Question 9.
Mammal in human male is
(a) Atavistic organ
(b) Rudimentary Organ
(c) Vestigial organ
(d) Homologous structure
Answer:
(c) Vestigial organ
Question 10.
Which of the following is/are not examples of analogous structure
(a) Wings of Birds and Bats
(b) Wings of Birds and Insects
(c) Thom of Bougainvillea and Tendril of cururbita
(d) Flippers of Penguins and Dolphins
(i) a, b, c
(ii) a and c
(iii) b andd
(iv) All the above
Answer:
(ii) a and c
Question 11.
identify the mismatched pairs
(a) Thom of Bougainvillea and Tenrdril of – Analogy
(b) Forelimbs of whale and cat – Analogy
(c) Octopus eye & Mammalian eye – Homology
(d) Root of sweet potato & stem of potato – Homology
Answer:
(a) Thorn of Bougainvillea & Terdril of crucurbita – Analogy
Question 12.
Witnesses for evolution are found in
(a) Rocks
(b) Ocean beds
(c) Fossils
(d) Desert
Answer:
(c) Fossils
Question 13.
Assertion (A): Oparin used the term coacervases
Reason (R): Coacervates are colloidal particles in aqueous environment
(a) Both A and Rare incorrect
(b) Both A and R are correct
(c) Both A and R are correct. R explains A.
(d) A is correct R is incorrect
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are correct. R explains A.
Question 14.
According to the theory of spontaneous generation, life originated from
(a) Cosmic particles
(b) Non-living materials
(c) Coacervates
(d) Sea
Answer:
(b) Non-living materials
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Hardy – Weinberg principle states that allelic frequency of a population remain constant
Reason (R) : Constancy is maintained through natural selection and mutation
(a) A is true R is false
(b) A is false R is true
(c) Both A and R are true
(d) R explains
Answer:
(a) A is true R is false
Question 16.
Calculate the allelic frequency of Aa. frequency of 0.7
(a) 0.67
(b) 0.42
(c) 0.36
Answer:
(b) 0.42
Question 17.
Match the following

Answer:
(a) a – iv b – i c – ii d – iii
Question 18.
Genetic drift leads to
(a) Mutation
(b) Bottle neck effect
(c) Immigration
(d) Isolation
Answer:
(b) Bottle neck effect
Question 19.
Atavism refers to
(a) Inheritance of triat by mother
(b) Inheritance of triat by father
(c) Criss-cross inheritance
(d) Inheritance of characters not shown by parents
Answer:
(d) Inheritance of characters not shown by parents
2 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
State the theory of spontaneous generation.
Answer:
According to the theory of spontaneous generation or Abiogenesis, living organisms originated from non-living materials and occurred through stepwise chemical and molecular evolution over millions of years. Thomas Huxley coined the term abiogeneis.
Question 2.
List the four eras of geological time scale.
Answer:
- Precambrian era
- Paleozoic era
- Mesozoic era
- Cenozoic era
Question 3.
Which periods of paleozoic era are referred as
- Age of fishes
- Invertebrates
Answer:
- Age of fishes – Devonian period
- Age of invertebrates – Cambrian period
Question 4.
Point out the epochs of carboniferous period.
Answer:
- Pennsylvanian
- Mississippian
Question 5.
Compare relative dating with absolute dating.
Answer:
Relative dating is used to determine a fossil by comparing it to similar rocks and fossils of known age. Absolute dating is used to determine the precise age of a fossil by using radiometric dating to measure the decay of isotopes
Question 6.
Wing of a cockroach and the wing of parrot. What do you infer from this statement with reference to evolution?
Answer:
Both the wings of cockroach and bird are different in structure but similar in their function. Thus, they are analogous structure that brings about convergent evolution.
Question 7.
Name the scientists who propounded the following theories.
- Mutation theory
- Chemical theory of evolution
Answer:
- Mutuation theory was propounded by Hugo de Vries.
- Chemical theory of evolution was propounded by Oparin and Haldane
Question 8.
Define fossilization and mention its types.
Answer:
Fossilization is the process by which plant and animal remains are preserved in sedimentary rocks. It is of three major types,
- Actual remains
- Petrifaction
- Natural moulds and casts.
Question 9.
Name the principle minerals involved in petrifaction.
Answer:
Iron pyrites, silica, calcium carbonate and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium.
Question 10.
What is meant by petrifaction?
Answer:
When animals die the original portion of their body may be replaced molecule for molecule by minerals and the original substance being lost through disintegration. This method of fossilization is called petrifaction. The principle minerals involved in this type fossilization are iron pyrites, silica, calcium carbonate and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium.
Question 11.
Define analogous organ with an example.
Answer:
Organisms having different structural patterns but similar function are termed as analogous structures. For example, the wings of birds and insects are different structurally but perform the same function of flight that brings about convergent evolution.
Question 12.
Mention any four organs homologous to human hand.
Answer:
Flippers of whale, wings of bat, wings of bird and forelimb of horse.
Question 13.
Thorn of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Pisum sativum represent homology. How?
Answer:
The thorn of Bougainvillea and the tendrils of Curcurbita and Pisum sativum represent homology. The thorn in former is used as a defence mechanism from grazing animals and the tendrils of latter is used as a support for climbing.
Question 14.
Which type of evolution is brought out by homologous structures and analogous structures?
Answer:
Homologous structures brings about divergent evolution. Analogous structures brings about convergent evolution.
Question 15.
What are vestigial organs? Give example.
Answer:
Structures that are of no use to the possessor, and are not necessary for their existence are called vestigial organs. Vestigial organs may be considered as remnants of structures which were well developed and functional in the ancestors, but disappeared in course of evolution due to their non-utilization.
E.g: Human appendix.
Question 16.
Human appendix is a vestige. Give reason.
Answer:
Human appendix is the remnant of caecum which is functional in the digestive tract of herbivorous animals like rabbit. Cellulose digestion takes place in the caecum of these animals. Due to change in the diet containing less cellulose, caecum in human became functionless and is reduced to a vermiform appendix, which is vestigial.
Question 17.
What are connecting link? Give example.
Answer:
The organisms which possess the characters of two different groups (transitional stage) are called connecting links. Example Peripatus (connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda) Archaeopteryx (connecting link between Reptiles and Aves).
Question 18.
Name one fossilised connecting link between reptiles and Aves also one living connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda.
Answer:
Archaeopteryx – connecting link between Reptiles and Aves.
Peripatus – Connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda.
Question 19.
Why it is considered as a connecting link?
Answer:
Peripatus is a worm that shown the characters of both Annelidia and Arthropoda. Hence it is a connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda.
Question 20.
Atavistic organs – comment.
Answer:
Sudden appearance of vestigial organs in highly evolved organisms is called atavistic organs. Example, presence of tail in human baby is an atavistic organ.
Question 21.
Define Ontogeny and Phytogeny.
Answer:
- Ontogeny refers to the life history of an individual.
- Phytogeny refers to the evolutionary history of a race.
Question 22.
Who proposed the theory of recapitulation? State the theory.
Answer:
Ernst Von Haeckel proposed the theory of recapitulation, which states that life history of an individual briefly repeats the evolutionary history of the race.
Question 23.
Name few Neo – Lamarckists.
Answer:
Cope, Osborn, Packard and Spencer.
Question 24.
Who proposed the theory of acquired characters? Also mention the scientist who disproved it.
Answer:
The theory of acquired characters was proposed by Jean Baptise de Lamarck and it was disproved by August Weismann.
Question 25.
Point out the basic principles of Darwin’s theory of evolution.
Answer:
Over production, struggle for existence, Universal occurence of variation, Survival of fittest and Natural selection.
Question 26.
Name any four Neo – Darwinists.
Answer:
Gregor Mendel, August Weismann, Russel Wallace and Heinrich.
Question 27.
Enumerate the salient features of mutation theory.
Answer:
- Mutations or discontinuous variation are transmitted to other generations.
- In naturally breeding populations, mutations occur from time to time.
- There are no intermediate forms, as they are fully fledged.
- They are strictly subjected to natural selection.
Question 28.
Who proposed Mutation theory? Name the organism on which the experiment was carried out.
Answer:
Mutation theory was put forth by Hugo de Vries. Based on the experiments in Oenothera lamarckiana (The evening primrose plant).
Question 29.
What are the basic factors of modern synthetic theory that leads to evolution?
Answer:
Gene mutation, Chromosomal mutation, Genetic recombination, Natural selection and Reproductive isolation.
Question 30.
Name the scientists who supported modern synthetic theory.
Answer:
Sewell Wright, Dobzhansky, Huxley and Simpson.
Question 31.
Define point mutation.
Answer:
Gene mutation refers to the changes in the structure of the gene. It is also called gene / point mutation. It alters the phenotype of an organism and produces variations in their offsprings.
Question 32.
Point out the factors that alters allelic frequency of a population.
Answer:
Natural selection, Genetic drift, Mutation and Geneflow
Question 33.
Mention any two differences between Homo habilis and Homo erectus
Answer:
- Homo habilis: The brain capacity was between 650-800 cc. They were probably vegetarians.
- Homo erectus: The brain capacity was around 900 cc. They probably ate meat.
Question 34.
Write a brief note on Homo sapiens with respect to evolution.
Answer:
Homo sapiens or modem human arose in Africa some 25,000 years ago and moved to other continents and developed into distinct races. They had a brain capacity of 1300 – 1600 cc. “They started cultivating crops and domesticating animals.
Question 35.
Define evolution.
Answer:
The term evolution describes heritable changes in one or more characteristics of a population of species from one generation to the other.
3 – Mark Question
Question 36.
Write a short note on Big Bang theory.
Answer:
Big bang theory explains the origin of universe as a singular huge explosion in physical terms. The primitive Earth had no proper atmosphere, but consisted of ammonia, methane, hydrogen and water vapour. The climate of the Earth was extremely high. UV rays from the Sun split up water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Gradually the temperature cooled and the water vapour condensed to form rain. Rain water filled all the depressions to form water bodies. Ammonia and methane in the atmosphere combined with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and other gases.
Question 37.
Theory of chemical evolution states that organisms have evolved from inorganic substances. If so, what was the atmospheric condition that favoured evolution?
Answer:
The atmosphere was devoid of O2, and with high level of CO2, NH3 and UV radiations.
Question 38.
Name the periods of Mesozoic era. Also mention the flora and fauna dominates during that periods.
Answer:
- Mesozoic era is divided into three periods namely Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous.
- Dominating Fauna : Reptiles and Dinosaurs Dominating
- Flora : Conifers, Ferns and Ginkgon.
Question 39.
Which era is referred as Age of Mammals? What are the periods of that era? And also mention the fauna during the periods.
Answer:
Cenozoic era is called as Age of Mammals. Tertiary and Quaternary are the two periods of Cenozoic era. Tertiary periods marks the abundance of mammalian fauna. Quaternary period marks the beginning of human social life.
Question 40.
Write a short note on Cenozoic era.
Answer:
Cenozoic era (Age of mammals) is subdivided into two periods namely Tertiary and Quaternary. Tertiary period is characterized by abundant mammalian fauna. This period is subdivided into five epochs namely, Paleocene (placental mammals, Eocene (Monotremes except duck billed Platypus and Echidna, hoofed mammals and carnivores), Oligocene (higher placental mammals appeared), Miocene (origin of first man like apes) and Pliocene (origin of man from man like apes). Quaternary period witnesses decline of mammals and beginning of human social life.
Question 41.
Name the gaseous mixture used in Urey – Miller’s experiment. Which type of physical force is applied to generate amino acids?
Answer:
Ammonia, Methane, Hydrogen, Water vapour are the gaseous mixture allowed to circulate over electric discharge from a tungsten electrode.
Question 42.
Which is the most common methods of fossilization? Explain how it occurs.
Answer:
Actual remains – The original hard parts such as bones, teeth or shells are preserved as such in the Earth’s atmosphere. This is the most commpn method of fossilization. When marine animals die, their hard parts such as bones and shells, etc., are covered with sediments and are protected from further deterioration.
They get preserved as such as they are preserved in vast ocean; the salinity in them prevents decay. The sediments become hardened to form definite layers or strata. For example, Woolly Mammoth that lived 22 thousand years ago were preserved in the frozen coast of Siberia as such. Several human beings and animals living in the ancient city of Pompeii were preserved intact by volcanic ash which gushed out from Mount Vesuvius.
Question 43.
What are coprolites? Mention its role in phytogeny.
Answer:
Coprolites are the hardened faecal matters occurs as small pieces. Analysing the coprolites helps to understand the nature of diet of pre-historic animals.
Question 44.
What are moulds and casts?
Answer:
Even after disintegration, the body of an animal might leave indelible impression on the soft mud which later becomes hardened into stones. Such impressions are called moulds. The cavities of the moulds may get filled up by hard minerals and get fossilized, which are called casts.
Question 45.
How will you compute the age of fossil?
Answer:
The age of fossils can be determined using two methods namely, relative dating and absolute dating. Relative dating is used to determine a fossil by comparing it to similar rocks and fossils of known age. Absolute dating is used to determine the precise age of a fossil by using radiometric dating to measure the decay of isotopes.
Question 46.
“Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny” – comment on the statement with example.
Answer:
The embryonic stages of a higher animal resemble the adult stage of its ancestors. Appearance of pharyngeal gill slits, yolk sac and the appearances of tail in human embryos are some of the examples.
Question 47.
Biogenetic law is not universal – justify.
Answer:
The biogenetic law is not universal and it is now thought that animals do not recapitulate the adult stage of any ancestors. The human embryo recapitulates the embryonic history and not the adult history of the organisms.
Question 48.
How macro molecules like DNA and RNA play their crucial role in evolutionary history?
Answer:
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of molecules such as DNA, RNA and proteins across generations. It uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in the changes of molecules.
One of the most useful advancement in the development of molecular biology is proteins and other molecules that control life processes are conserved among species. A slight change that occurs over time in these conserved molecules (DNA, RNA and protein) are often called molecular clocks. Molecules that have been used to study evolution are cytochrome (respiratory pathway) and rRNA (protein synthesis).
Question 49.
Explain the principles of Lamarckian theory.
Answer:
- The theory of use and disuse – Organs that are used often will increase in size and those that are not used will degenerate. Neck in giraffe is an example of use and absence of limbs in snakes is an example for disuse theory.
- The theory of inheritance of acquired characters – Characters that are developed during ’ the life time of an organism are called acquired characters and these are then inherited.
Question 50.
Write a note on Mutation theory.
Answer:
Hugo de Vries put forth the Mutation theory. Mutations are sudden random changes that occur in an organism that is not heritable. De Vries carried out his experiments in the Evening Primrose plant (Oenothera lamarckiana) and observed variations in them due to mutation. According to de Vries, sudden and large variations were responsible for the origin of new species whereas Lamarck and Darwin believed in gradual accumulation of all variations as the causative factors in the origin of new species.
Question 51.
What do you mean by “adaptive radiation”? Give example.
Answer:
The evolutionary process which produces new species diverged from a single ancestral form becomes adapted to newly invaded habitats is called adaptive radiation. Adaptive radiations are best exemplified in closely related groups that have evolved in relatively short time. Darwin’s finches and Australian marsupials are best examples for adaptive radiation.
Question 52.
Darwins finches are the classical examples studied for adaptive radation. Explain.
Answer:
Darwin’s finches are the birds whose common ancestor arrived on the Galapagos about 2 million year ago. During that time, Darwin’s finches have evolved into 14 recognized species differing in body size, beak shape and feeding behavior. Changes in the size and form of the beak have enabled different species to utilize different food resources such as insects, seeds and nectar from cactus flowers and blood from iguanas, all driven by Natural selection. Genetic variation in the ALX1 gene in the DNA of Darwin finches is associated with variation in the beak shape. Mild mutation in the ALX1 gene leads to phenotypic change in the shape of the beak of the Darwin finches.
Question 53.
What is micro evolution?
Answer:
Microevolution (evolution on a small scale) refers to the changes in allele frequencies within a population. Allele frequencies in a population may change due to four fundamental forces of evolution such as natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and gene flow.
Question 54.
Name the major types of Natural Selection.
Answer:
- Stabilising Selection
- Directional Selection
- Disruptive Selection
Question 55.
What do you mean by gene flow?
Answer:
Movement of genes through gametes or movement of individuals in (immigration) and out (emigration) of a population is referred to as gene flow. Organisms and gametes that enter the population may have new alleles or may bring in existing alleles but in different proportions than those already in the population. Gene flow can be a strong agent of evolution.
Question 56.
Give an account on Genetic drift. Mention its impact over a population.
Answer:
Genetic drift is a mechanism of evolution in which allele frequencies of a population change over generation due to chance (sampling error). Genetic drift occurs in all population sizes, but its effects are strong in a small population. It may result in a loss of some alleles (including beneficial ones) and fixation of other alleles. Genetic drift can have major effects, when the population is reduced in size by natural disaster due to bottle neck effect or when a small group of population splits from the main population to form a new colony due to founder’s effect.
Question 57.
State Hardy – Weinberg equilibrium.
Answer:
The allele frequencies in a population are stable and are constant from generation to generation in the absence of gene flow, genetic drift, mutation, recombination and natural selection.
Question 58.
Write in brief about the characters of Australian ape man.
Answer:
Australopithecus lived in East African grasslands about 5 mya and was called the Australian ape man. He was about 1.5 meters tall with bipedal locomotion, omnivorous, semi erect, and lived in caves. Low forehead, brow ridges over the eyes, protruding face, lack of chin, low brain capacity of about 350 – 450 cc, human like dentition, lumbar curve in the vertebral column were his distinguishing features.
Question 59.
Who is Cro-Magnon?
Answer:
Cro-Magnon was one of the most talked forms of modem human found from the rocks of Cro-Magnon, France and is considered as the ancestor of modem Europeans. They were not only adapted to various environmental conditions, but were also known for their cave paintings, figures on floors and walls.
5 – Mark Questions
Question 60.
Explain Oparin – Haldane hypothesis on evolution.
Answer:
According to the theory of chemical evolution primitive organisms in the primordial environment of the Earth evolved spontaneously from inorganic substances and physical forces such as lightning, UV radiations, volcanic activities, etc. Oparin (1924) suggested that the organic compounds could have undergone a series of reactions leading to more molecules. He proposed that the molecules formed colloidal aggregates or ‘coacervates’ in an aqueous environment. The coacervates were able to absorb and assimilate organic compounds from the environment. Haldane (1929) proposed that the primordial sea served as a vast chemical laboratory powered by solar energy.
The atmosphere was oxygen free and the combination of CO2, NH2 and UV radiations gave rise to organic compounds. The sea became a ‘hot’ dilute soup containing large populations of organic monomers and polymers. They envisaged that groups of monomers and polymers acquired lipid membranes and further developed into the first living cell. Haldane coined the term prebiotic soup and this became the powerful symbol of the Oparin-Haldane view on the origin of life (1924-1929). Oparin and Haldane independently suggested that if the primitive atmosphere was reducing – and if there was appropriate supply of energy such as lightning or UV light then a wide range of organic compounds can be synthesized.
Question 61.
How Urey – Miller’s experiment supports the origin of life?
Answer:
Urey and Miller (1953), paved way for understanding the possible synthesis of organic compounds that led to the appearance of living organisms is depicted in the Figure In their experiment, a mixture of gases was allowed to circulate over electric discharge from an tungsten electrode. A small flask was kept boiling and the steam emanating from it was made to mix with the mixture of gases (ammonia, methane and hydrogen) in the large chamber that was connected condensed to form water which ran down the ‘U’ tube.
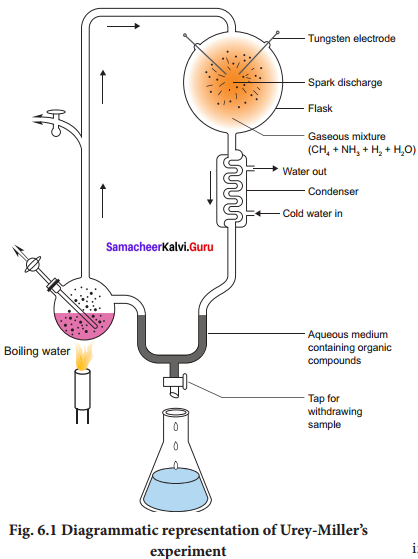
Experiment was conducted continuously for a week and the liquid was analysed. Glycine, alanine, beta alanine and aspartic acid were identified. Thus Miller’s experiments had an insight as to the possibility of abiogenetic synthesis of large amount of variety of organic compounds in nature from a mixture of sample gases in which the only source of carbon was methane. Later in similar experiments, formation of all types of amino acids, and nitrogen bases were noticed.
Question 62.
Give a detailed account of Modern Synthetic Theory.
Answer:
Sewell Wright, Fisher, Mayer, Huxley, Dobzhansky, Simpson and Haeckel explained Natural Selection in the light of Post-Darwinian discoveries. According to this theory gene mutations, chromosomal mutations, genetic recombinations, natural selection and reproductive isolation are the five basic factors involved in the process of organic evolution.
- Gene mutation refers to the changes in the structure of the gene. It is also called gene/ point mutation. It alters the phenotype of an organism and produces variations in their off +springs.
- Chromosomal mutation refers to the changes in the structure of chromosomes due to deletion, addition, duplication, inversion or translocation. This too alters the phenotype of an organism and produces variations in their offspring.
- Genetic recombination is due to crossing over of genes during meiosis. This brings about genetic variations in the individuals of the same species and leads to heritable variations.
- Natural selection does not produce any genetic variations but once such variations occur it favours some genetic changes while rejecting others (driving force of evolution).
- Reproductive isolation helps in preventing interbreeding between related organisms
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HO’ts) Questions
Question 1.
Name the connecting link for the following groups of organisms.
- Annelida and Arthropoda
- Reptiles and Aves
- Pisces and Amphibians
- Reptiles and Mammals
Answer:
- Peripatus
- Archeopteryx
- Lung fish
- Platypus
Question 2.
Point out any four condition under which Hardy Weinberg’s equilibrium is not attained.
Answer:
- Selected mating
- Flow of genes (either by immigration or emmigration)
- Occurance of mutation
- Definite population size
Question 3.
Why are analogous structures a result of convergent evolution?
Answer:
Analogous structures are not anatomically similar though they perform same function.
Question 4.
Organs which are of no use to the organism is called as vestige. Name any four vestigal organs that can be noticed in your body.
Answer:
Wisdom teeth, Mammae in male, Body hair and Coccyx.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter Wise Solutions PDF will help you to clear all doubts. Learn perfectly by using Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chapter 6 Evolution Questions and Answers Bio Zoology Solutions PDF. Leave us a comment to clear your queries. Get instant updates by bookmarking our site. Get the best learning with the effective and excellent step by step Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Guide.