You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Applications of Matrices and Determinants Ex 1.1
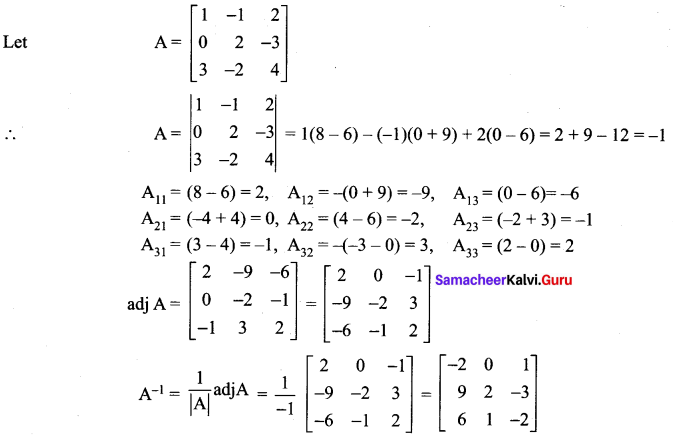
12th Maths Exercise 1.1 Answers Question 1.
Find the adjoint of the following:
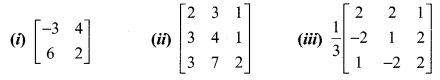
Solution:

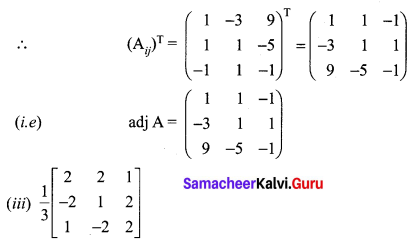
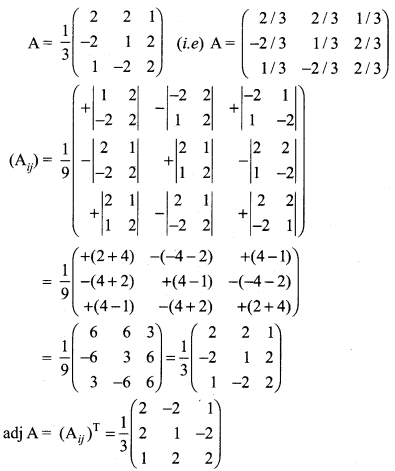
Exercise 1.1 Class 12 Maths State Board Question 2.
Find the inverse (if it exists) of the following:
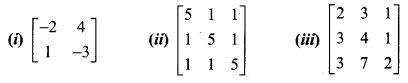
Solution:
For a matrix A, \(\mathrm{A}^{-1}=\frac{1}{|\mathrm{A}|}(\mathrm{adj} \mathrm{A})\). Where |A| ≠ 0. If |A| = 0 then A is called a singular matrix and so \(\mathrm{A}^{-1}\) does not exist.

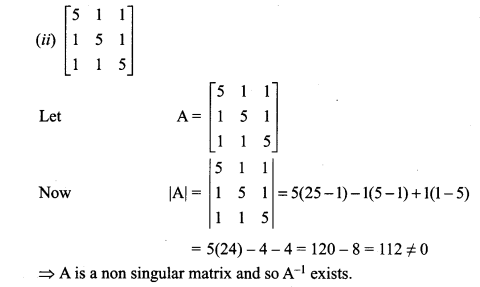
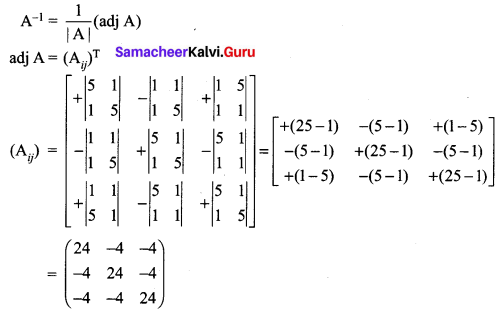
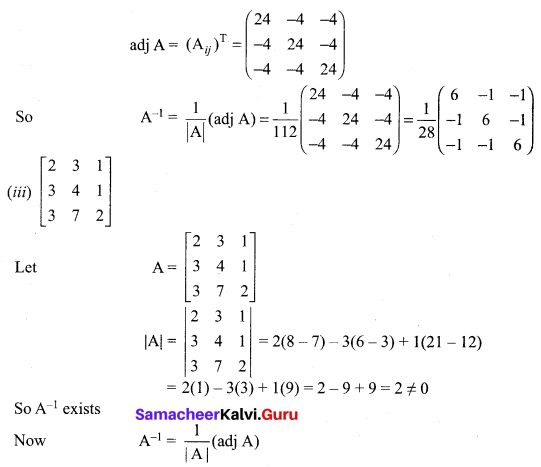
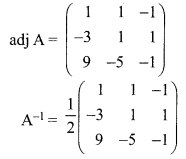
12th Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 3.
If F(α) = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{\cos \alpha} & {0} & {\sin \alpha} \\ {0} & {1} & {0} \\ {-\sin \alpha} & {0} & {\cos \alpha}\end{array}\right]\) show that \([\mathrm{F}(\alpha)]^{-1}=\mathrm{F}(-\alpha)\)
Solution:
Let A = F (α)
So \([\mathrm{F}(\alpha)]^{-1}=\mathrm{A}^{-1}\)
Now
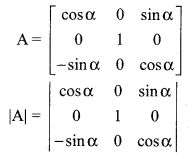

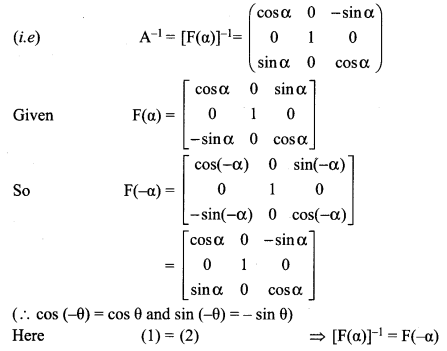
12th Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 4.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{5} & {3} \\ {-1} & {-2}\end{array}\right]\) show that A2 – 3A – 7I2 = O2. Hence find A-1.
Solution:
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{5} & {3} \\ {-1} & {-2}\end{array}\right]\)
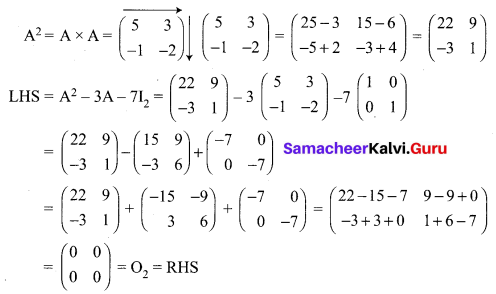
To Find A-1
Now we have proved that A2 – 3A – 7I2 = O2
Post multiply by A-1 we get
A – 3I – 7A-1 = O2
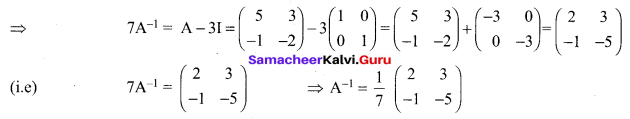
12th Maths 1.1 Exercise Question 5.
If \(\mathbf{A}=\frac{1}{9}\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{-8} & {1} & {4} \\ {4} & {4} & {7} \\ {1} & {-8} & {4}\end{array}\right]\) prove that A-1 = AT
Solution:
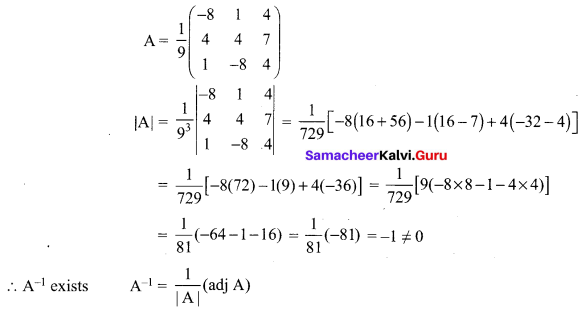
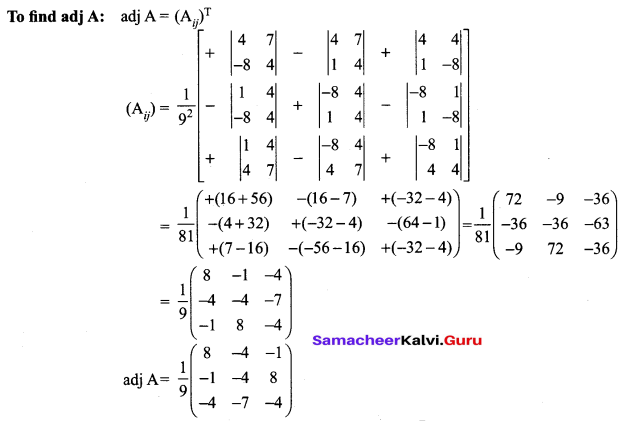
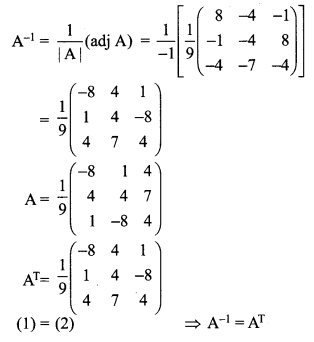
12 Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 6.
If \(\mathbf{A}=\left[\begin{array}{rr}{8} & {-4} \\ {-5} & {3}\end{array}\right]\), verify that A(adj A) = (adj A)A = |A| I2
Solution:

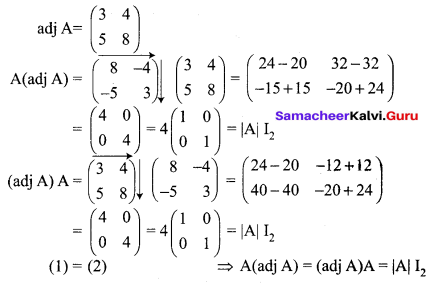
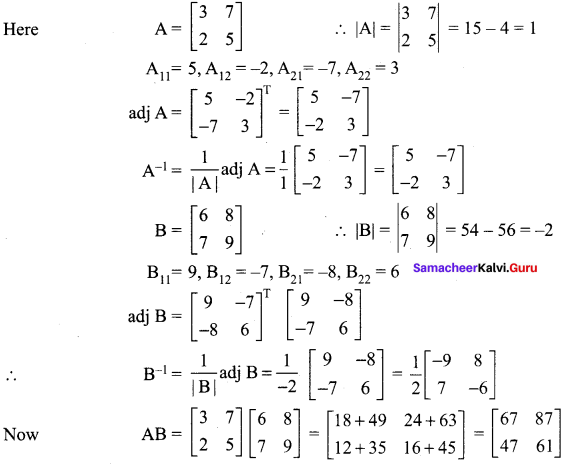
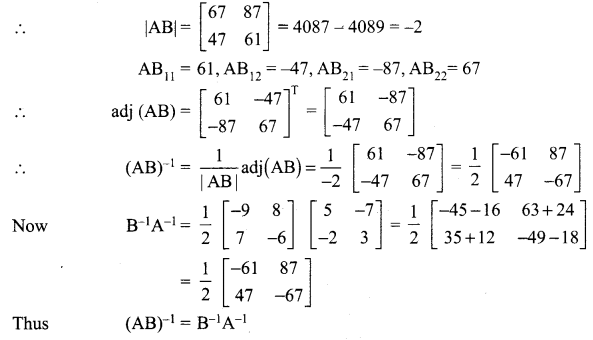
12th Maths 1st Chapter Exercise 1.1 Question 7.
If \(\mathbf{A}=\left[\begin{array}{ll}{3} & {2} \\ {7} & {5}\end{array}\right]\), and \(\mathbf{B}=\left[\begin{array}{cc}{-1} & {-3} \\ {5} & {2}\end{array}\right]\) verify that (AB)-1 = B-1 A-1.
Solution:
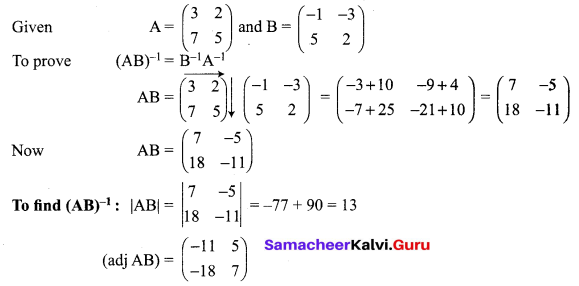
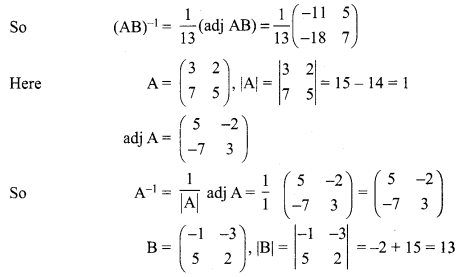
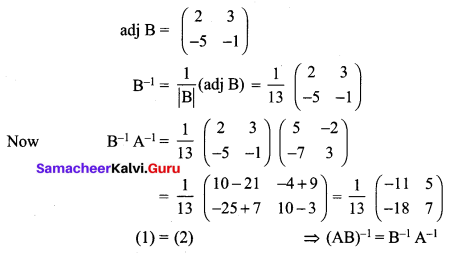
12th Maths Application Of Matrices And Determinants Question 8.
If adj (A) = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{2} & {-4} & {2} \\ {-3} & {12} & {-7} \\ {-2} & {0} & {2}\end{array}\right]\) find A
Solution:
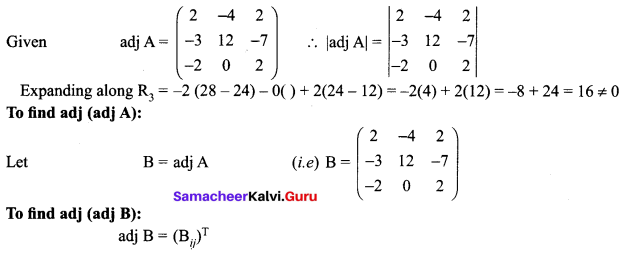
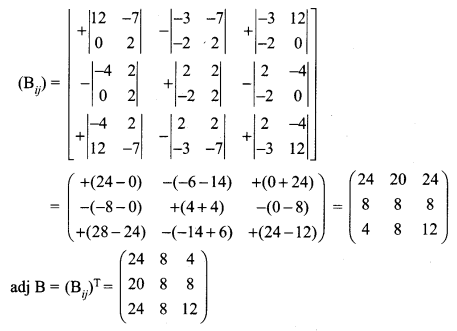
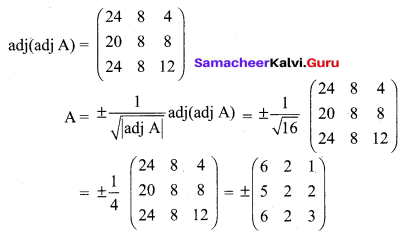
12th Maths Ex 1.1 Question 9.
If adj(A) = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{0} & {-2} & {0} \\ {6} & {2} & {-6} \\ {-3} & {0} & {6}\end{array}\right]\) find A-1
Solution:
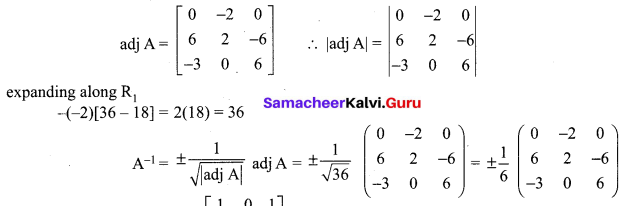
12th Exercise 1.1 Question 10.
Find adj(adj(A)) if adj A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{1} & {0} & {1} \\ {0} & {2} & {0} \\ {-1} & {0} & {1}\end{array}\right]\)
Solution:
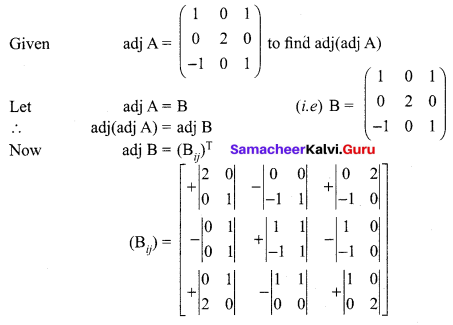
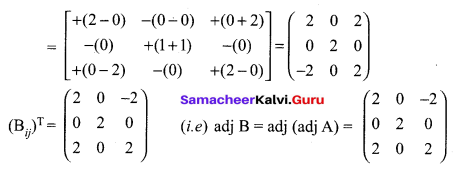
12th Maths Exercise 1.1 Answers In Tamil Medium Question 11.

Solution:
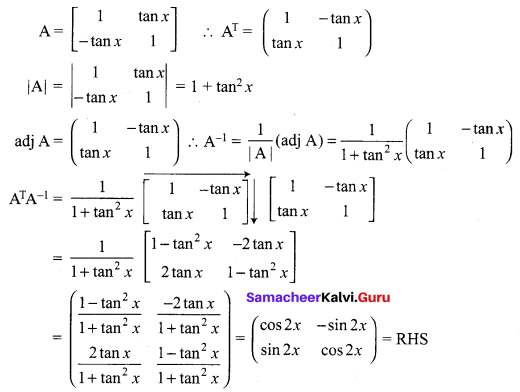
12th Maths 1st Chapter Question 12.
Find the matrix A for which A \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{5} & {3} \\ {-1} & {-2}\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{cc}{14} & {7} \\ {7} & {7}\end{array}\right]\)
Solution:
Given A \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{5} & {3} \\ {-1} & {-2}\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{cc}{14} & {7} \\ {7} & {7}\end{array}\right]\)
Let \(\mathrm{B}=\left(\begin{array}{cc}{5} & {3} \\ {-1} & {-2}\end{array}\right) \text { and } \mathrm{C}=\left(\begin{array}{cc}{14} & {7} \\ {7} & {7}\end{array}\right)\)
Given AB = C, To find A
Now AB = C
Post multiply by B-1 on both sides
ABB-1 = CB-1 (i.e) A (BB-1) = CB-1
⇒ A(I) = CB-1 (i.e) A = CB-1
To find B-1:
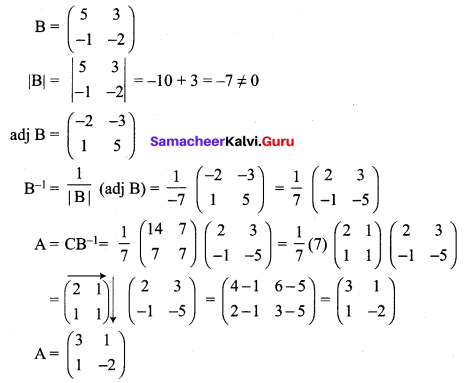
12th Maths 1.1 Question 13.
Given \(\mathbf{A}=\left[\begin{array}{cc}{1} & {-1} \\ {2} & {0}\end{array}\right], \mathbf{B}=\left[\begin{array}{cc}{3} & {-2} \\ {1} & {1}\end{array}\right] \text { and } \mathbf{C}\left[\begin{array}{ll}{1} & {1} \\ {2} & {2}\end{array}\right]\), find a matrix X such that AXB = C.
Solution:
A × B = C
Pre multiply by A-1 and post multiply by B-1 we get
A-1 A × BB-1 = A-1CB-1 (i.e) X = A-1CB-1
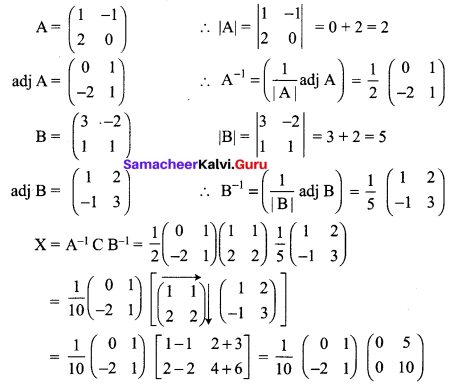
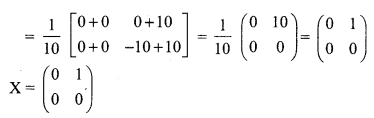
12 Maths Samacheer Kalvi Solutions Question 14.

Solution:
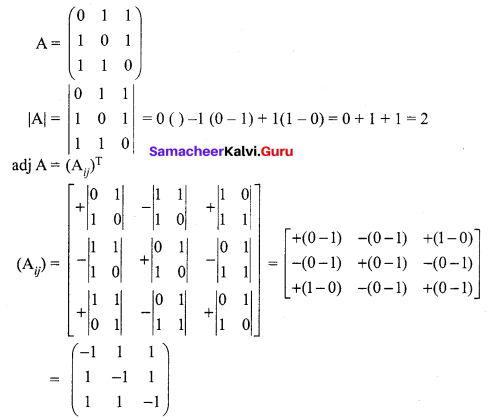
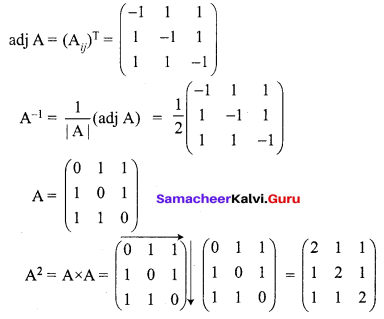
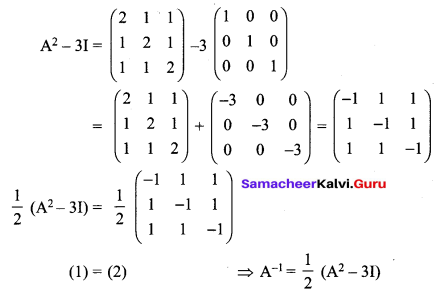
12th Maths Exercise 1.1 5th Sum Question 15.
Decrypt the received encoded message \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{2} & {-3}\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{ll}{20} & {4}\end{array}\right]\) with the encryption matrix \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{-1} & {-1} \\ {2} & {1}\end{array}\right]\) and the decryption matrix as its inverse, where the system of codes are described by the numbers 1-26 to the letters A- Z respectively, and the number 0 to a blank space.
Solution:
Let the encoding matrix be \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{-1} & {-1} \\ {2} & {1}\end{array}\right]\)
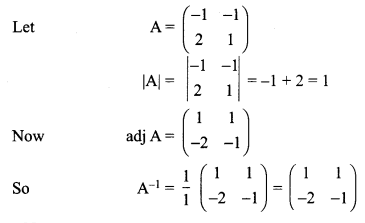
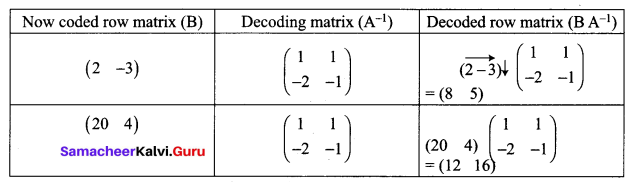
So the sequence of decoded matrices is [8 5], [12 16].
Thus the receivers read this message as HELP.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Applications of Matrices and Determinants Ex 1.1 Additional Problems
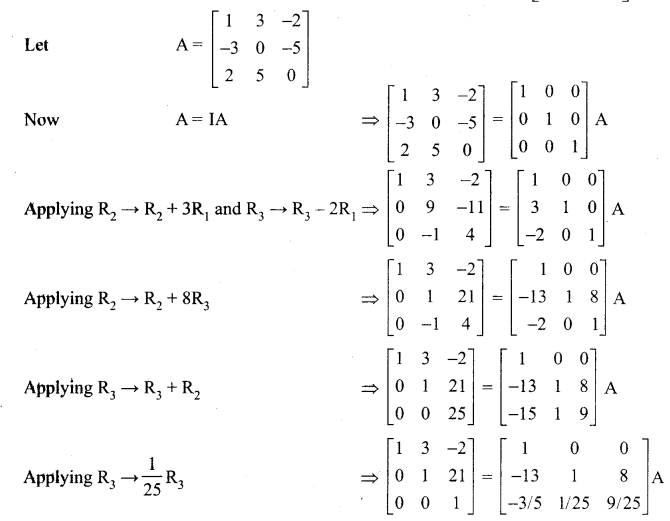
12th Maths Chapter 1 Question 1.
Using elementary transformations find the inverse of the following matrix 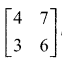
Solution:
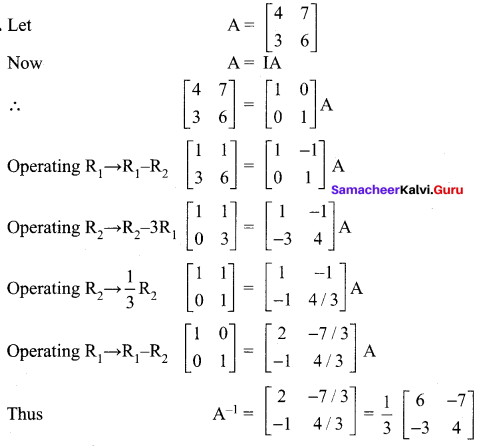
12th Maths Guide Question 2.
Using elementary transformations find the inverse of the matrix 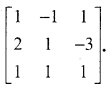
Solution:
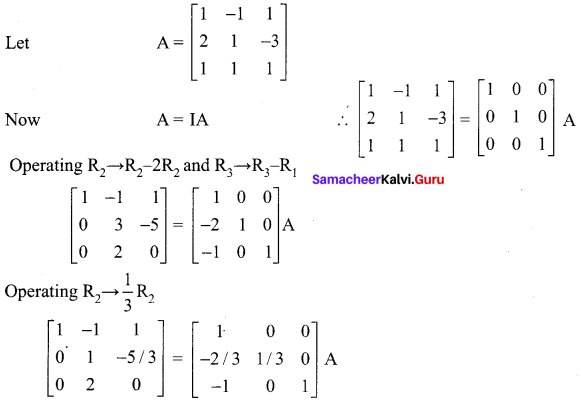
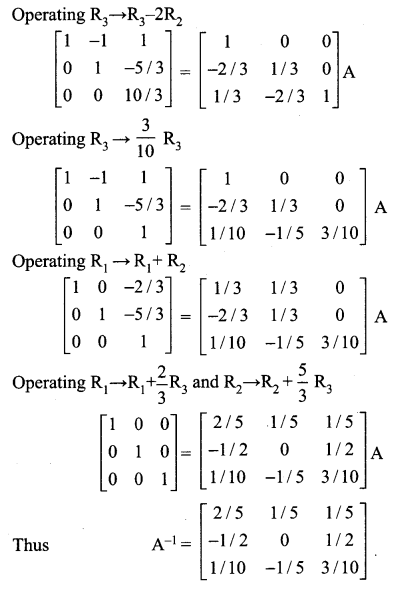
12th Maths Solutions Samacheer Kalvi Question 3.
Using elementary transformation find the inverse of the matrix 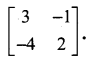
Solution:
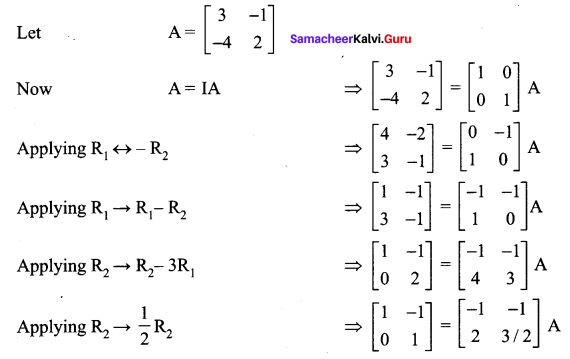
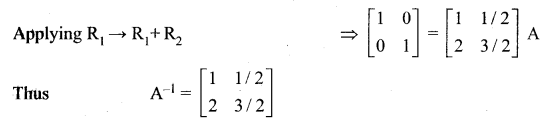
12 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 4.
Using elementary transformations find the inverse of the matrix 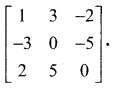
Solution:

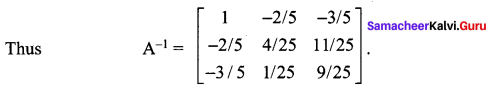
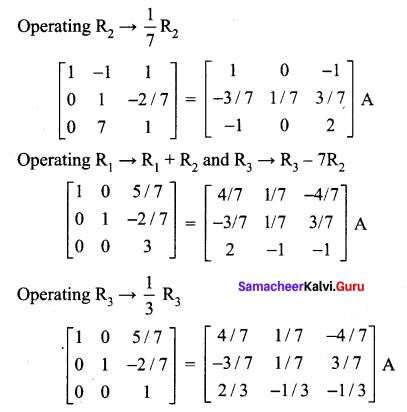
12th Maths Exercise 1.1 Solutions Question 5.
Using elementary transformation, find the inverse of the following matrix 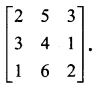
Solution:
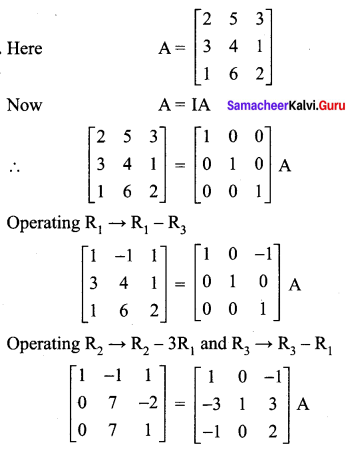
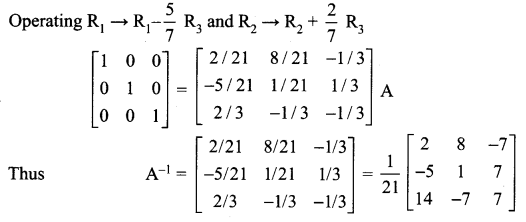
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Question 6.

Solution:

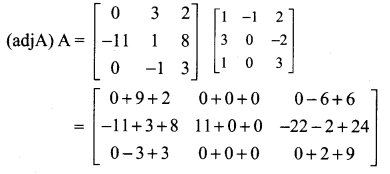
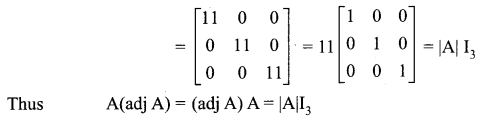
Samacheer Kalvi 12 Maths Solutions Question 7.
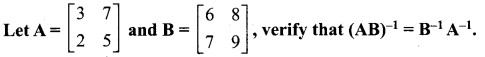
Solution:
12 Maths Solutions Samacheer Kalvi Question 8.
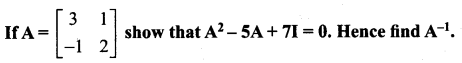
Solution:
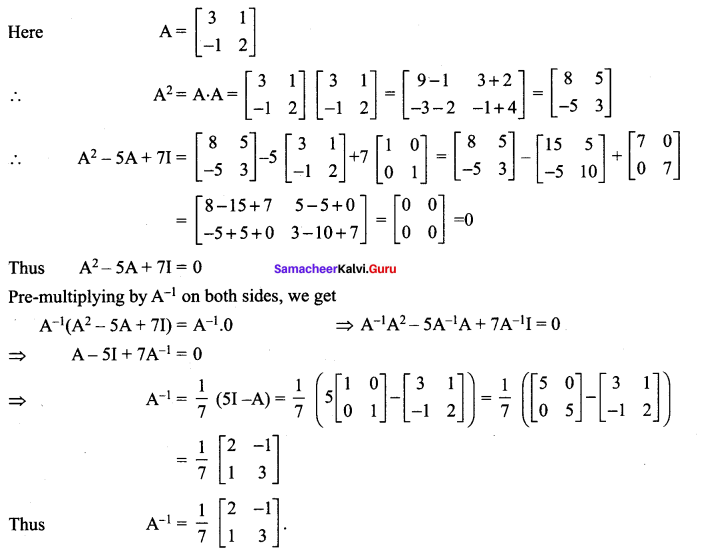
Question 9.
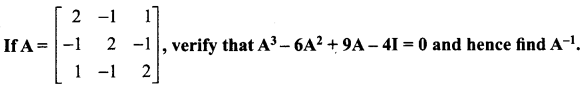
Solution:
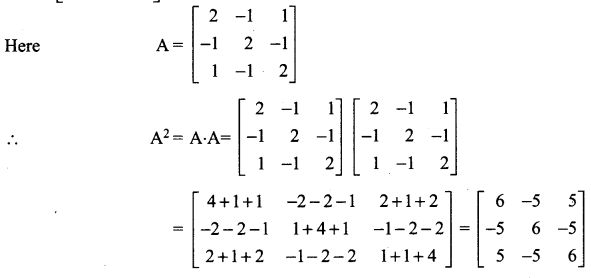
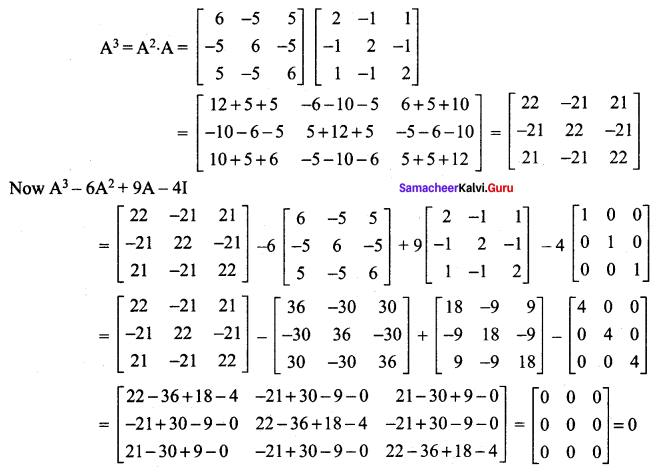

Question 10.
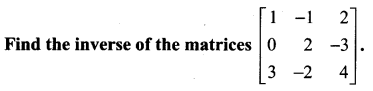
Solution: