Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 2 கலப்பு எண்கள் Ex 2.7 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
TN Board 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 கலப்பு எண்கள் Ex 2.7
கேள்வி 1.
கீழ்காணும் கலப்பெண்களின் வடிவினைக் காண்க.
(i) 2+i2\(\sqrt{3}\)
(ii) 3-i\(\sqrt{3}\)
(iii) -2-i2
(iv) \(\frac{i-1}{\cos \frac{\pi}{3}+i \sin \frac{\pi}{3}}\)
தீர்வு:
(i) 2 +i2\(\sqrt{3}\)
2+i 2\(\sqrt{3}\) = x + iy = r (cos θ + i sin θ) என்க
r = எண் மதிப்பு = \(\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{2^{2}+(2 \sqrt{3})^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{4+12}\) = \(\sqrt{16}\) = 4
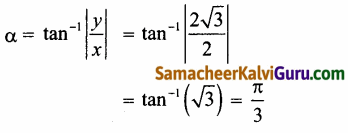
2 + i2\(\sqrt{3}\) என்ற கலப்பெண் முதலாம் கால் பகுதியில் அமைவதால் [x, y இரண்டும் மிகை) அதன் முதன்மை வீச்சு
θ = α = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
அதன் துருவ வடிவம் 2 +i2\(\sqrt{3}\)
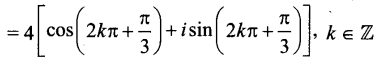
![]()
(ii) 3 – i\(\sqrt{3}\)
x + iy = 3 – i\(\sqrt{3}\) என்க.
= r (cos θ + i sin θ)
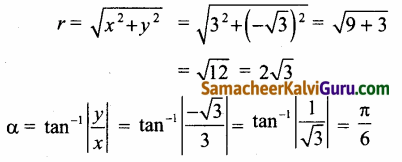
3 – i\(\sqrt{3}\) என்ற கலப்பெண் நான்காம் கால்பகுதியில் அமைவதால்,
[∵ x → + ve, y → – ve]
அதன் முதன்மை வீச்சு θ = -α
⇒ θ = \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
∴ துருவ வடிவம்
3-i\(\sqrt{3}\) = 2\(\sqrt{3}\)
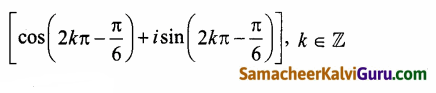
(iii) – 2 – i2
x + iy = -2- 2i = r (cos θ + i sin θ) என்க
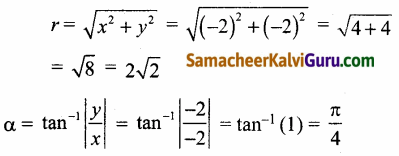
-2 – 2i என்ற கலப்பெண் மூன்றாம் கால்பகுதியின் அமைவதால்
[x குறை y குறை]
அதன் முதன்மை வீச்சு θ = α – π
⇒ θ = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)-π=\(\frac{\pi-4 \pi}{4}\)=\(-\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)
அதன் துருவ வடிவம்
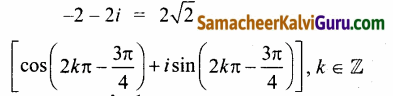
(iv) 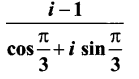
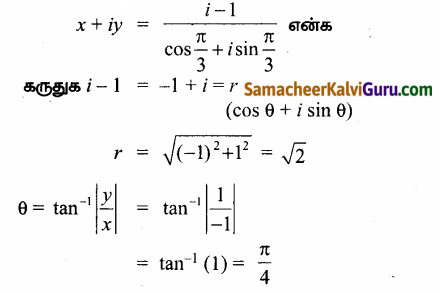
(-1 + i) என்ற கலப்பெண் II-ம் கால் பகுதியில்
அமைவதால் [x → குறை y → மிகை)
அதன் முதன்மை வீச்சு θ = π – \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) = \(-\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)
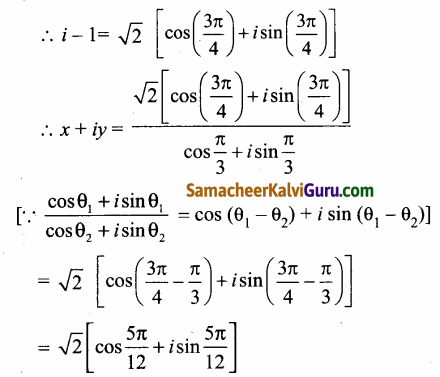
எனவே துருவ வடிவம்
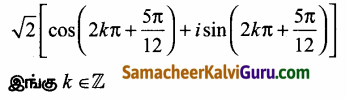
![]()
கேள்வி 2.
பின்வருவனவற்றை செவ்வக வடிவில் எழுதுக.
(i) (cos \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + i sin\(\frac{\pi}{6}\))(cos \(\frac{\pi}{12}\) + isin \(\frac{\pi}{12}\))
(ii) 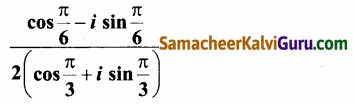
தீர்வு:
(i) (cos \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + i sin\(\frac{\pi}{6}\))(cos \(\frac{\pi}{12}\) + isin \(\frac{\pi}{12}\))
[ ∵ (cos θ1 + i sin θ1) (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
= cos (θ1 + θ2) +i sin (θ1 + θ2)
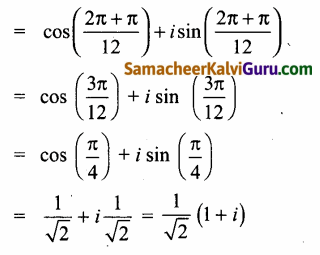
(ii) 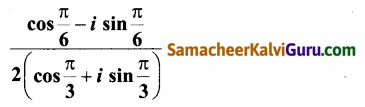
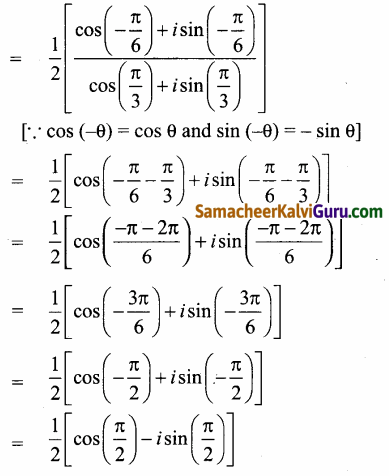
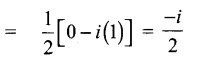
கேள்வி 3.
(x1 + iy1) (x2 + iy2) …… (xn + iyn) = a + ib எனில்,
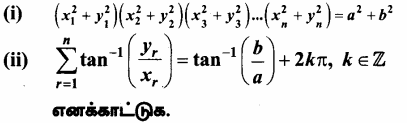
தீர்வு:
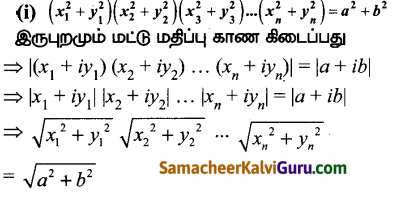
இருபுறமும் மட்டு மதிப்பு காண கிடைப்பது
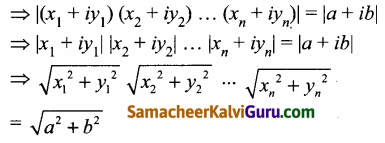
இருபுறமும் வர்க்கப்படுத்த கிடைப்பது,
![]()
(ii) 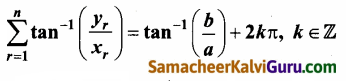
(x1 + iy1)(x2 + iy1) …. (xn + iyn) = a + ib
arg((x1 + iy1)(x2 + iy2)…….(xn + iyn)) = arg(a + ib)
⇒ arg(x1 + iy1) + arg(x2 + iy2) + ….. + arg(xn + iyn) = arg(a + ib)
(∵ arg(z1z2….zn) = arg z1 + arg z2 + … + arg zn)
⇒ tan-1\(\left(\frac{y_{1}}{x_{1}}\right)\) + tan-1\(\left(\frac{y_{2}}{x_{2}}\right)\) + ….. + tan-1\(\left(\frac{y_{n}}{x_{n}}\right)\)
= tan-1\(\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)\) + 2kπ k∈ℤ
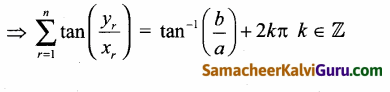
![]()
கேள்வி 4.

தீர்வு:
![]()
அதாவது \(\frac{1+z}{1-z}\) = cos 2θ + i sin 2θ
⇒ \(\frac{1+x+i y}{1-x-i y}\) = cos 2θ + i sin 2θ …… (1)
மட்டு மதிப்பு காண கிடைப்பது,
\(\frac{1+x+i y}{1-x-i y}\) = |cos 2θ + i sin2θ| ⇒ |\(\frac{1+x+i y}{1-x-i y}\)|
= \(\sqrt{\cos ^{2} 2 \theta+\sin ^{2} 2 \theta}\) = 1
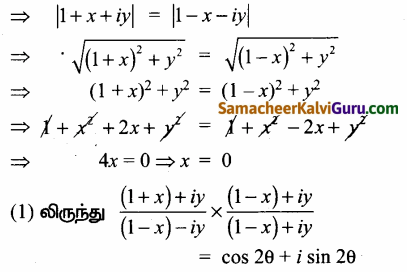
கற்பனை பகுதியை தனியாக எடுக்க கிடைப்பது
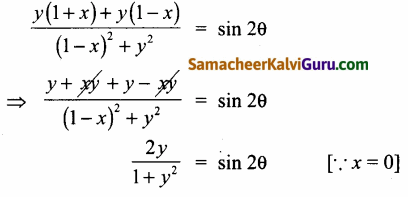
⇒ \(\frac{2 \tan \theta}{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}\) = sin 2θ
∴ y ஆனது tan 8 ற்கு சமமாக இருக்க வேண்டும்.
⇒ y = tan θ
∴ z = 0 + i tan θ = z ⇒ tan θ
![]()
கேள்வி 5.
cos α + cos β + cos γ = sin α + sin β + sin γ = 0, எனில்,
(i) cos 3α + cos 3β + cos 3γ = 3 cos (α + β + γ) மற்றும்
(ii) sin 3γ + sin 3β + sin 3γ= 3 sin (α + β + γ) என நிறுவுக.
தீர்வு:
(i) cos 3α + cos 3β + cos 3γ = 3 cos (α + β + γ)
கொடுக்கப்பட்ட cos α + cos β + cos γ = sin α +sin β + sin γ = 0
⇒ (cos α + cos β + cos γ) + i (sin α + sin β+ sin γ)=0
⇒ (cos α + i sin α) + (cos β + i sin β) + (cos γ + i sin γ) = 0
⇒ a + b + c = 0 இங்கு a = cos α + i sin α, b = cos β + i sin β, c = cos γ + i sin γ
a + b + c = 0, எனில் a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc.
∴ (cos α + i sin α)3 + (cos β + i sin β)3 + (cos γ + i sin γ)3 = 3[(cos α + i sin α) + (cos β + i sin β) + (cos γ + i sin γ)]
டி மாய்வரின் தேற்றப்படி,
⇒ cos 3α + i sin 3α + cos 3β + i sin 3β + cos 3γ + i sin 3γ
⇒ 3 [(cos (α + β + γ) + i sin (α + β + γ)]
⇒ (cos 3α + cos 3β + cos 3γ) + i [sin 3α + sin 3β + sin 3γ)]
= 3 [(cos (α + β + γ) + i sin (α + β + γ)]
மெய் மற்றும் கற்பனை பகுதிகளை சமப்படுத்த கிடைப்பது
cos 3α + cos 3β + cos 3γ = 3 cos (α + β + γ)
மற்றும் sin 3α + sin 3β + sin 3γ = 3sin (α + β + γ) எனவே நிரூபிக்கப்பட்டது.
![]()
கேள்வி 6.
z = x + iy மற்றும் arg \(\left(\frac{z-i}{z+2}\right)\) = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) எனில்,
x2 + y2 + 3x – 3y + 2 = 0 எனக்காட்டுக.
தீர்வு:
கொடுக்கப்பட்ட z =x + iy மற்றும்
arg \(\left(\frac{z-i}{z+2}\right)\) = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
⇒ arg (z – i) – arg(z + 2) = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
⇒ arg (x + iy – i) – arg(x + iy + 2) = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
⇒ arg (x + i(y – 1)) – arg((x + 2) + iy) = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
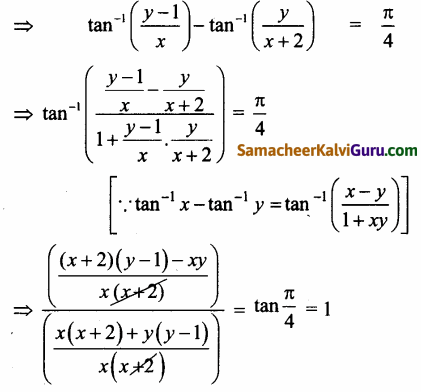
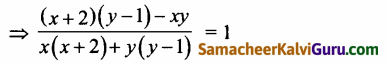
⇒ -x + 2y – 2 = x2 + 2x + y2 – y
⇒ x2 + 2x + y2 – y + x – 2y + 2 = 0
⇒ x2 + y2 + 3x – 3y + 2 = 0
எனவே நிரூபிக்கப்பட்டது.