Students can download 12th Business Maths Chapter 1 Applications of Matrices and Determinants Ex 1.4 Questions and Answers, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Applications of Matrices and Determinants Ex 1.4
Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
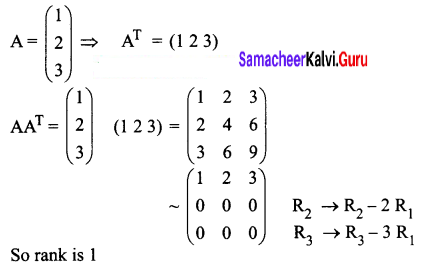
If A = (1 2 3), then the rank of AAT is ______
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 1
Answer:
(d) 1
Hint:
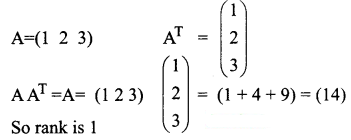
Question 2.
The rank of m × n matrix whose elements are unity is _________
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) m
(d) n
Answer:
(b) 1
Hint:
All the rows except the first row can be made zero
Question 3.
If 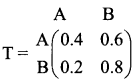 is a transition probability matrix, then at equilibrium A is equal to
is a transition probability matrix, then at equilibrium A is equal to
(a) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
(b) \(\frac{1}{5}\)
(c) \(\frac{1}{6}\)
(d) \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Answer:
(a) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Hint:

Question 4.
If A = \(\left(\begin{array}{ll}
2 & 0 \\
0 & 8
\end{array}\right)\) then ρ(A) is _______
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) n
Answer:
(c) 2
Hint:
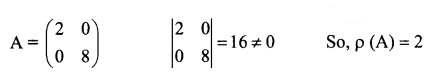
Question 5.
The rank of the matrix \(\left(\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 2 & 3 \\
1 & 4 & 9
\end{array}\right)\) is _____
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer:
(d) 3
Hint:
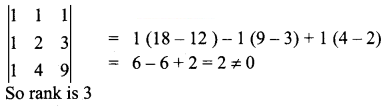
Question 6.
The rank of the unit matrix of order n is _______
(a) n – 1
(b) n
(c) n + 1
(d) n2
Answer:
(b) n
Hint:
Unit matrix of order n is in echelon form with n non-zero rows
Question 7.
If ρ(A) = r then which of the following is correct?
(a) all the minors of order r which does not vanish
(b) A has at least one minor of order r which does not vanish
(c) A has at least one (r + 1) order minor which vanishes
(d) all (r + 1) and higher-order minors should not vanish
Answer:
(b) A has at least one minor of order r which does not vanish
Question 8.
If A = \(\left(\begin{array}{l}
1 \\
2 \\
3
\end{array}\right)\) then the rank of AAT is _______
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer:
(b) 1
Hint:
Question 9.
If the rank of the matrix \(\left(\begin{array}{ccc}
\lambda & -1 & 0 \\
0 & \lambda & -1 \\
-1 & 0 & \lambda
\end{array}\right)\) is 2. Then λ is _______
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) only real number
Answer:
(a) 1
Hint:
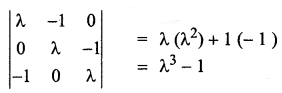
Since rank is 2, the third order minor should vanish.
λ3 – 1 = 0
⇒ λ = 1
Question 10.
The rank of the diagonal matrix 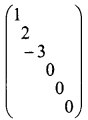
is _______
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 3
Hint:
There are only three non-zero rows as the matrix is in echelon form.
Question 11.
If 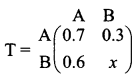 is a transition probability matrix, then the value of x is
is a transition probability matrix, then the value of x is
(a) 0.2
(b) 0.3
(c) 0.4
(d) 0.7
Answer:
(c) 0.4
Hint:
x = 1 – 0.6 = 0.4
Question 12.
Which of the following is not an elementary transformation?
(a) Ri ↔ Rj
(b) Ri → 2Ri + 2Cj
(c) Ri → 2Ri – 4Rj
(d) Ci → Ci + 5Cj
Answer:
(b) Ri → 2Ri + 2Cj
Hint:
Since rows and columns cannot be taken together.
Question 13.
If ρ(A) = ρ(A, B), then the system is _______
(a) Consistent and has infinitely many solutions
(b) Consistent and has unique solutions
(c) consistent
(d) inconsistent
Answer:
(c) consistent
Question 14.
If ρ(A) = ρ(A, B) = the number of unknowns, then the system is _______
(a) Consistent and has infinitely many solutions
(b) Consistent and has unique solutions
(c) inconsistent
(d) consistent
Answer:
(i) Consistent and has unique solutions
Question 15.
If ρ(A) ≠ ρ(A, B), then the system is ________
(a) Consistent and has infinitely many solutions
(b) Consistent and has unique solutions
(c) inconsistent
(d) consistent
Answer:
(c) inconsistent
Question 16.
In a transition probability matrix, all the entries are greater than or equal to _______
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 0
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) 0
Question 17.
If the number of variables in a non- homogeneous system AX = B is n, then the system possesses a unique solution only when _______
(a) ρ(A) = ρ(A, B) > n
(b) ρ(A) = ρ(A, B) = n
(c) ρ(A) = ρ(A, B) < n
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) ρ(A) = ρ(A, B) = n
Question 18.
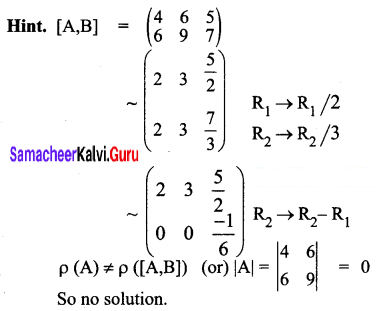
The system of equations 4x + 6y = 5, 6x + 9y = 7 has ________
(a) a unique solution
(b) no solution
(c) infinitely many solutions
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) no solution
Question 19.
For the system of equations x + 2y + 3z = 1, 2x + y + 3z = 2, 5x + 5y + 9z = 4 _______
(a) there is only one solution
(b) there exists infinitely many solutions
(c) there is no solution
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) there is only one solution
Hint:
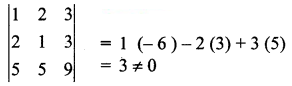
By Cramer’s rule, there is only one solution
Question 20.
If |A| ≠ 0, then A is _______
(a) non- singular matrix
(b) singular matrix
(c) zero matrix
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) non-singular matrix
Question 21.
The system of linear equations x + y + z = 2, 2x + y – z = 3, 3x + 2y + k = 4 has unique solution, if k is not equal to ______
(a) 4
(b) 0
(c) -4
(d) 1
Answer:
(b) 0
Hint:
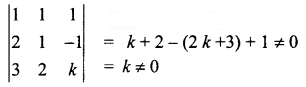
Question 22.
Cramer’s rule is applicable only to get an unique solution when ______
(a) Δz ≠ 0
(b) Δx ≠ 0
(c) Δ ≠ 0
(d) Δy ≠ 0
Answer:
(c) Δ ≠ 0
Question 23.
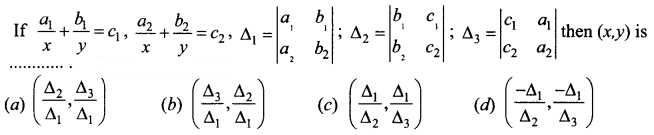
Answer:
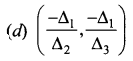
Hint:
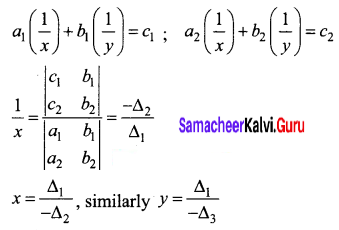
Question 24.
|An×n| = 3 |adj A| = 243 then the value n is _______
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 1
Answer:
(b) 5
Hint:
|adj A| = |A|n-1, n is order of matrix
243 = 3n-1
34 = 3n-1
n = 5
Question 25.
Rank of a null matrix is ______
(a) 0
(b) -1
(c) ∞
(d) 1
Answer:
(a) 0