Get Tamilnadu Board Class 12 Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter wise Study Material to score good marks in the exam. Various chapters with subtopics are explained clearly in Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology Solutions Material. All the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology Book Solutions Chapter 3 Reproductive Health Questions, answers, Notes, Guide, Pdf along with the explanations are provided by the subject experts. Students can easily learn Tamilnadu Board Class 12 Chapter wise Bio Zoology with the help of the step by step guide provided on our site. Learn all the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology concepts to attempt the exam with more confidence. Read all the concepts of Tamilnadu Board Solutions for Class 12 Bio Zoology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 3 Reproductive Health
Whether you want to become an expert in Bio Zoology or to get good marks in the exam, you have one and only solution is practicing with Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter wise Solutions. Strengthen your weakness by learning the Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health Questions and Answers on our site. You can learn directly online on our website or learn offline by downloading Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter wise material. Save your time and read Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Subject at your comfort level.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Reproductive Health Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is correct regarding HIV, hepatitis B, gonorrhoea and trichomoniasis?
(a) Gonorrhoea is a STD whereas others are not.
(b) Trichomoniasis is a viral disease whereas others are bacterial.
(c) HIV is a pathogen whereas others are diseases.
(d) Hepatitis B is eradicated completely whereas others are not.
Answer:
(c) HIV is a pathogen whereas others are diseases.
Question 2.
Which one of the following groups includes sexually transmitted diseases caused by bacteria . only?
(a) Syphilis, gonorrhoea and candidiasis
(b) Syphilis, chlamydiasis and gonorrhoea
(c) Syphilis, gonorrhoea and trichomoniasis
(d) Syphilis, trichomoniasis and pediculosis
Answer:
(b) Syphilis, chlamydiasis and gonorrhoea
Question 3.
Identify the correct statements from the following:
(a) Chlamydiasis is a viral disease.
(b) Gonorrhoea is caused by a spirochaete bacterium, Treponema palladium.
(c) The incubation period for syphilis is 2 to 14 days in males and 7 to 21 days in females.
(d) Both syphilis and gonorrhoea are easily cured with antibiotics.
Answer:
(d) Both syphilis and gonorrhoea are easily cured with antibiotics.
Question 4.
A contraceptive pill prevents ovulation by
(a) blocking fallopian tube
(b) inhibiting release of FSH and LH
(c) stimulating release of FSH and LH
(d) causing immediate degeneration of released ovum.
Answer:
(b) inhibiting release of FSH and LH
Question 5.
The approach which does not give the defined action of contraceptive is

Answer:
(b) Vasectomy – Prevents spermatogenesis
Question 6.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults are made of rubber and are inserted into the female reproductive tract to cover the cervix before coitus.
Statement 2: They are chemical barriers of conception and are reusable.
(a) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
(b) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
(c) Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Answer:
(c) Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
Question 7.
Match column I with column II and select the correct the correct option from option the code given below
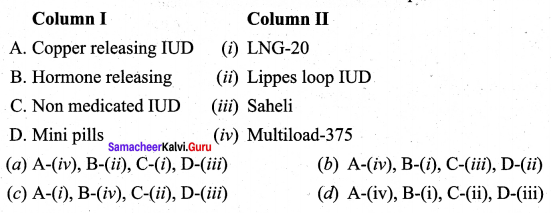
Answer:
(d) A – (iv), B – (i), C – (ii), D – (iii)
Question 8.
Select the incorrect action of hormonal contraceptive pills from the following
(a) Inhibition of spermatogenesis.
(b) Inhibition of ovulation.
(c) Changes in cervical mucus impairing its ability to allow passage and transport of sperms.
(d) Alteration in uterine endometrium to make it unsuitable for implantation.
Answer:
(a) Inhibition of spermatogenesis.
Question 9.
What is amniocentesis? Why a statutory ban is imposed on this technique?
Answer:
Amniocentesis is a prenatal technique used to detect any chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus and it is being often misused to determine the sex of the foetus. Once the sex of the foetus is known, there may be a chance of female foeticide. Hence, a statutory ban on amniocentesis is imposed
Question 10.
Select the correct term from the bracket and complete the given branching tree
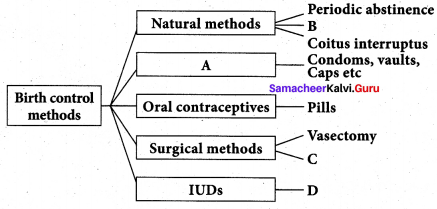
(Barriers, Lactational amonerrhoea, Tubectomy, CuT)
Answer:
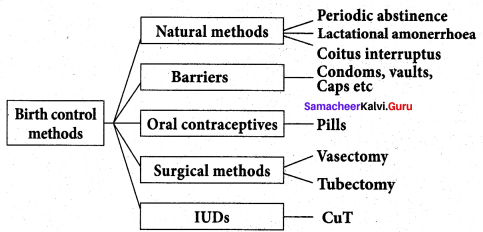
Question 11.
Correct the following statements
- Transfer of an ovum collected from donor into the fallopian tube is called ZIFT.
- Transfering of an embryo with more than 8 blastomeres into uterus is called GIFT,
- Multiload 375 is a hormone releasing IUD.
Answer:
- Transfer of 8 celled blastomere collected from donor into the fallopian tube is called ZIFT.
- Transfering of an embryo with more than 8 blastomeres into uterus is called IUT.
- Multiload 375 is a copper releasing IUD.
Question 12.
Which method do you suggest the couple to have a baby, if the male partner fails to inseminate the female or due to very low sperm count in the ejaculate?
Answer:
Micro-testicular sperm extraction (TESE):
Microsurgical sperm retrieval from the testicle involves a small midline incision in the scrotum, through which one or both testicles can be seen. Under the microscope, the seminiferous tubules are dilated and small amount of testicular tissue in areas of active sperm production are removed and improved for sperm yield compared to traditional biopsy techniques.
Question 13.
Expand the following: (a) ZIFT (b) ICSI
Answer:
Zygote intra-fallopian transfer Intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection
Question 14.
What are the strategies to be implemented in India to attain total reproductive health?
Answer:
- Creating awareness and providing medical assistance to build a healthy society.
- Introducing sex education in schools to provide information about adolescence and adolescence related changes.
- Educating couples and those in the marriageable age groups about the available birth control methods and family planning norms.
- Creating awareness about care for pregnant women, post-natal care of mother and child and the importance of breast feeding.
- Encouraging and supporting governmental and non-governmental agencies to identify new methods and/or to improve upon the existing methods of birth control.
Question 15.
Differentiate foeticide and infanticide.
Answer:
Female foeticide refers to ‘aborting the female in the mother’s womb’.
Female infanticide is ‘killing the female child after her birth’.
Question 16.
Describe the major STDs and their symptoms.
Answer:
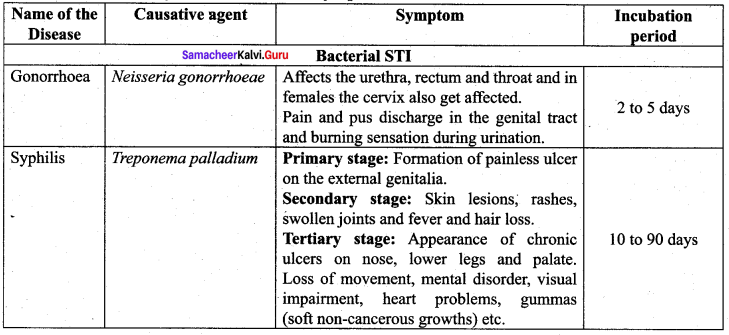
Cervical cancer:
Cervical cancer is caused by a sexually transmitted virus called Human Papilloma virus (HPV). HPV may cause abnormal growth of cervical cells or cervical dysplasia. The most common symptoms and signs of cervical cancer are pelvic pain, increased vaginal discharge and abnormal vaginal bleeding. The risk factors for cervical cancer include
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Prolonged use of contraceptive pills
Cervical cancer can be diagnosed by a Papanicolaou smear (PAP smear) combined with an HPV test. X-Ray, CT scan, MRI and a PET scan may also be used to determine the stage of cancer. The treatment options for cervical cancer include radiation therapy, surgery and chemotherapy.
Modem screening techniques can detect precancerous changes in the cervix. Therefore screening is recommended for women above 30 years once in a year. Cervical cancer can be prevented with vaccination. Primary prevention begins with HPV vaccination of girls aged 9-13 years, before they become sexually active. Modification in lifestyle can also help in preventing cervical cancer. Healthy diet, avoiding tobacco usage, preventing early marriages, practicing monogamy and regular exercise minimize the risk of cervical cancer.
Question 17.
How are STDs transmitted?
Answer:
Sexually transmitted diseases (STD) are called as Sexually transmitted infections (STI). Normally STI are transmitted from person to person during intimate sexual contact with an infected partner. Infections like Hepatitis-B and HIV are transmitted sexually as well as by sharing of infusion needles, surgical instruments, etc with infected people, blood transfusion or from infected mother to baby.
Question 18.
Write the preventive measures of STDs.
Answer:
Prevention of STDs:
- Avoid sex with unknown partner/ multiple partners
- use condoms
- In case of doubt, consult a doctor for diagnosis and get complete treatment.
Question 19.
The procedure of GIFT involves the transfer of female gametes into the fallopain tube, can gametes be transferred to the uterus to achieve the same result? Explain.
Answer:
Gamete intra-fallopian transfer (GIFT): Transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the fallopian tube. In this the eggs are collected from the ovaries and placed with the sperms in one of the fallopian tubes. The zygote travels toward the uterus and gets implanted in the inner lining of the uterus.
Question 20.
Amniocentesis, the foetal sex determination test, is banned in our country. Is it necessary? Comment.
Answer:
Amniocentesis is a prenatal technique used to detect any chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus and it is being often misused to determine the sex of the foetus. Once the sex of ‘ the foetus is known, there may be a chance of female foeticide. Hence, a statutory ban on amniocentesis is imposed.
Question 21.
Open Book Assessment ‘Healthy reproduction, legally checked birth control measures and proper family planning programmes are essential for the survival of mankind’ Justify.
Answer:
Reproductive health and proper family planning programmes are highly essential for survival of mankind. Reproductive health refers to the state of physical, psycological and social well being merely in absence of illness in all matter related to reproductive system and its proper functioning. Family planning has the following health and social benefits.
- Protecting the health of women by reducing frequent pregnancies.
- Reducing abortions.
- Providing stable population growth.
- Assuming the infants well being by providing adequate time lapse between successive pregnancies.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Reproductive Health Additional Questions and Answers
1 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is Not a natural contraceptive?
(a) Rhythm method
(b) Lactational amenorrhoea
(c) Progestasert
(d) Continuous abstinence
Answer:
(c) Progestasert
Question 2.
Identify the fungal STD(s)
(i) Trichomoniasis
(ii) Genital herps
(iii) Candidiasis
(a) Only (i)
(b) Only (z’zz)
(c) Only (zv)
Answer:
(A) Only (iii)
Question 3.
Match the following.

Answer:
(a) – iii, (b) – i, (c) – iv, (d) – ii
Question 4.
Pick out the incorrect statement regarding the character of an good contraceptive.
(a) It should be user friendly
(b) should not affect sexual drive
(c) side effects must be least
(d) should not be easily available
Answer:
(d) should not be easily available
Question 5.
Select the proper hormonal composition of oral contraceptive pills
(a) FSH & Prolactin (b) Prolactin & TSH
(c) TSH & FSH (d) FSH & LH
Answer:
(d) FSH & LH
Question 6.
Assertion (A): IUD’s are inserted in the ovary.
Reason (R): IUD’s Increases phagocytosis of the sperm.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) Both A and R are incorrect
(c) A is correct R is incorrect
(d) A is incorrect R is correct
Answer:
(d) A is incorrect R is correct
Question 7.
Identify the mismatched pair.

Answer:
(c) Candidias (iii) Albugo candida
Question 8.
In India, family planning programme was initiated in
(a) 1961
(b) 1981
(c) 1951
(d) 1971
Answer:
(c) 1951
Question 9.
Assertion (A): Amniocentesis helps to diagnose the chromosomal aberrations in foetus. Reason (R): Amniocentesis is legalized is our country.
(a) Both A and R are wrong
(b) A is right and R is wrong
(c) R explains A
(d) A is wrong R is right
Answer:
(b) A is right and R is wrong
Question 10.
Legalized marriageable age of female in India is
(a) 19 years
(b) 20 years
(c) 18 years
(d) 21 years
Answer:
(c) 18 years
Question 11.
Identify the correct statement.
(a) Lactational amenorrhea is a permanent birth control method
(b) Condoms are made of polyethylene glycol and lambskin
(c) LNG -20 is a copper – releasing IUD
(d) Diaphragm covers the cervix there by preventing sperm entry
Answer:
(d) Diaphragm covers the cervix there by preventing sperm entry
Question 12.
According to WHO, India is the largest HIV affected country.
(a) first
(b) second
(c) third
(d) seventh
Answer:
(e) third
Question 13.
Identify the correct statement.
(a) MTP is the voluntary killing of infant.
(b) MTP is legalized in India from 1974.
(c) Performing MTP during second trimester is more risky.
(d) It is a surgical – based abortion.
Answer:
(c) Performing MTP during second trimester is more risky.
Question 14.
Saheli, contains a non-steroidal preparation called
Answer:
Centchroman
Question 15.
The average foetal heart beat rate is between beats per minute.
Answer:
120-160
Question 16.
World AIDS day is observed on
Answer:
11th July
Question 17.
Indian Government legalized MTP in
Answer:
1971
Question 18.
In chorionic villus sampling test, the tissue sample is taken from
(a) amniotic fluid
(b) placental tissue
(c) Intestinal villi
(d) foetal liver
Answer:
(b) placental tissue
Question 19.
In ZIFT technique, the zygote is transferred at the stage of
(a) 16 blastomere
(b) morula
(c) 12 blastomere
(d) 8 blastomere
Answer:
(d) 8 blastomere
Question 20.
Given below are the basic steps in IVF treatment cycle. Select the proper sequence.
(i) Ovarian stimulation
(ii)Egg retrieval
(iii) fertilization
(iv) Embryo culture
(v) Embryo transfer
(a) (ii) → (ii) → (v) → (i) → (iii)
(b) (i) → (iii) → (ii) → (v) → (iv)
(c) (i) → (ii) → (ii) → (iv) → (v)
(d) (ii) → (i) → (iii) → (v) → (iv)
Answer:
(c) (i) → (ii) → (ii) → (iv) → (v)
Question 21.
Enactment of _____ banned the identification of sex and to prevent the prenatal abortion.
(a) POGSOAct
(b) POTAAct
(c) PCPNDTAct
(d) GOONDAAct
Answer:
(c) PCPNDT Act
Question 22.
Which is NOT a national health care programme?
(a) Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan
(b) Pradhan Mantri Fiscal BhimaYojana
(c) RMNCH + A approach
(d) Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram
Answer:
(b) Pradhan Mantri Fiscal Bhima Yoj ana
Question 23.
______ is Known as anti-sterility vitamin.
Answer:
Vitamin-E
2 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
Name any four national level health care programmes run by Indian Government.
Answer:
- Janani Suraksha Yojana
- Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram
- RMNCH+A Programme
- Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan
Question 2.
Comment on ‘Saheli’
Answer:
Saheli is an oral contraceptive pill provided by Central Drug Research Institute in Lucknow, – India. It contains a non-steroidal hormone preparation called centchroman.
Question 3.
What is Mayer – Rokitansky Syndrome?
Answer:
All women are bom with ovaries, but some do not have functional uterus. This condition is called Mayer-Rokitansky syndrome.
Question 4.
Point out any four STD’s caused by viruses.
Answer:
- Genital herpes
- Hepatitis-B
- Genital warts
- AIDS
Question 5.
Define Surrogacy.
Answer:
Surrogacy is a method of assisted reproduction or agreement whereby a woman agrees to carry a pregnancy for another person, who will become the newborn child’s parent after birth. Through In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), embryos are created in a lab and are transferred into the surrogate mother’s uterus.
Question 6.
Name the causative organism of
- Syphilis
- Genital warts
Answer:
- Syphilis is caused by Treponema palladium
- Genital warts caused by Human Papilloma vims.
Question 7.
Define Infertility.
Answer:
Inability to conceive or produce children even after unprotected sexual cohabitation is called infertility. That is, the inability of a man to produce sufficient numbers or quality of sperm to impregnate a woman or inability of a woman to become pregnant or maintain a pregnancy.
Question 8.
Expand the acronyms:
- GIFT
- ICSI
Answer:
- GIFT – Gamete Intra – Fallopian Transfer.
- ICSI – Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection.
Question 9.
What is amniocentesis?
Answer:
Amniocentesis involves taking a small sample of the amniotic fluid that surrounds the foetus to diagnose for chromosomal abnormalities.
Question 10.
How copper IUD’s provide contraception?
Answer:
Copper IUD’s release free copper and copper salts into the uterus and suppress the sperm motility. They remain in uterus for 5-10 years.
Eg: NovaT, Cu T-380.
Question 11.
What do you mean by the term – coitus interruptus?
Answer:
Coitus interruptus is a oldest family planning method, where the male partner withdraws his penis before ejaculation, there by preventing the deposition of semen into vagina.
Question 12.
What is MTP?
Answer:
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) : Medical method of abortion is a voluntary or intentional termination of pregnancy in a non-surgical or non-invasive way. Early medical termination is extremely safe upto 12 weeks (the first trimester) of pregnancy and generally ,has no impact on a women’s fertility. Abortion during the second trimester is more risky as the foetus becomes intimately associated with the maternal tissue.
Question 13.
Which type of women are benefited by In Vitro Fertilization?
Answer:
IVF is used to treat women with blocked, damaged or absent fallopian tubes.
3 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
What are the steps taken by Government to overcome population explosion?
Answer:
To overcome the problem of population explosion, birth control is the only available solution.
People should be motivated to have smaller families by using various contraceptive devices. Advertisements by the Government in the media as well as posters/bills, etc., with a slogan Naam iruvar namakku iruvar (we two, ours two) and Naam iruvar namakku oruvar (we two, ours one) have also motivated to control population growth in Tamil Nadu. Statutory rising of marriageable age of the female to 18 years and that of males to 21 years and incentives given to pouples with small families are the other measures taken to control population growth in our country.
Question 2.
Lactational amenorrhoea – Comment.
Answer:
Menstrual cycles resume as early as 6 to 8 weeks from parturition. However, the reappearance of normal ovarian cycles may be delayed for six months during breastfeeding. This delay in ovarian cycles is called lactational amenorrhoea. It serves as a natural, but an unreliable form of birth control.
Question 3.
Write a note on sterilization procedure in the male.
Answer:
Vasectomy is the surgical procedure for male sterilisation. In this procedure, both vas deferens are cut and tied through a small incision on the scrotum to prevent the entry of sperm into the urethra. Vasectomy prevents sperm from heading off to penis as the discharge has no sperms in it.
Question 4.
Define Tubectomy.
Answer:
Tubectomy is the surgical sterilisation in women. In this procedure, a small portion of both fallopian tubes are cut and tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through vagina. This prevents fertilization as well as the entry of the egg into the uterus.
Question 5.
Complete the table by filling the gaps.
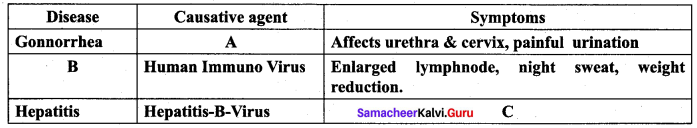
Answer:
A – Neisseria Gonorrhoea
B – AIDS
C- Jaundice
Question 6.
List various natural methods of birth control.
Answer:
- Periodic abstinence
- Coitus interruptus
- Lactational amenorrhea
Question 7.
What does ICSI stands for? Describe the technique.
Answer:
ICSI stands for Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection. In this method, a sperm is carefully injected into the cytoplasm of the egg and the zygote formed is allowed to divide till 8 celled stage and transferred to uterus. Fertilization occurs in 75-85% of eggs injected with sperm.
Question 8.
How LNG-20 act as contraceptive?
Answer:
LNG-20 is a Intra Uterine System of contraceptive method. It increases the viscosity of cervical mucus and thereby preventing the sperms from entering the cervix.
Question 9.
MTP is legalized in our country. Yes or No? Why?
Answer:
Yes. Government oflndia legalized MTP in 1971 for medical necessity and social consequences ’with certain restrictions like sex discrimination and illegal female foeticides to avoid its misuse. MTP performed illegally by unqualified quacks is unsafe and could be fatal. MTP of the first conception may have serious psychological consequences
Question 10.
Write the hormonal composition of oral contraceptive pills. Also explain their action mode.
Answer:
Oral contraceptive pills are enriched with synthetic progesterone and oestrogen hormones. These pills prevent the ovulation by inhibiting the secretion of LH and FSH hormones.
Question 11.
Suggest some methods to help infertile couples to have children.
Answer:
- Invitro fertilisation
- Zygote intra-fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
- Gamete intra-fallopian transfer (GIFT)
- Surrogacy
Question 12.
What are the characteristics of a good contraceptive?
Answer:
An ideal contraceptive should be user friendly, easily available, with least side effects and should not interfere with sexual drive.
Question 13.
Write is a note on foetoscope.
Answer:
Foetoscope is used to monitor the foetal heart rate and other functions during late pregnancy and labour. The average foetal heart rate is between 120 and 160 beats per minute. An abnormal foetal heart rate or pattern may mean that the foetus is not getting enough oxygen and it indicates other problems. A hand-held doppler device is often used during prenatal visits to count the foetal heart rate. During labour, continuous electronic foetal monitoring is often used.
Question 14.
How the technique of amniocentesis is performed?
Answer:
Amniocentesis is generally performed in a pregnant woman between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy by inserting a long, thin needle through the abdomen into the amniotic sac to withdraw a small sample of amniotic fluid. The amniotic fluid contains cells shed from the foetus.
Question 15.
Mention the role of prolactin in lactational amenorrhoea.
Answer:
Suckling by the baby during breast-feeding stimulates the pituitary to secrete increased prolactin hormone in order to increase milk production. This high prolactin concentration in the mother’s blood may prevent menstrual cycle by suppressing the release of GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone) from hypothalamus and gonadotropin secretion from the pituitary.
Question 16.
Name any one
- fungal STI
- Bacterial STI
- Protozoan STI
Answer:
- Fungal STI – Candidiasis
- Bacterial STI -Gonorrhoea
- Protozoan STI – Trichomoniasis
Question 17.
Why ultrasonography is performed for a carrying women?
Answer:
Ultrasonography is usually performed in the first trimester for dating, determination of the number of foetuses, and for assessment of early pregnancy complications.
Question 18.
Suggest any two simple precautions to avoid contracting RTFs.
Answer:
- Avoiding coitus with unknown/multiple partners.
- Use of condoms during coitus.
Question 19.
Name the most effective long-acting reversible contraceptive methods.
Answer:
Intrauterine devices and contraceptive implants.
5 – Mark Question
Question 1.
Give an detailed account on various natural methods of contraception.
Answer:
Natural method is used to prevent meeting of sperm with ovum, i.e., Rhythm method (safe period), coitus interruptus, continuous abstinence and lactational amenorrhoea.
a. Periodic abstinence/rhythm method: Ovulation occurs at about the 14th day of the menstrual cycle. Ovum survives for about two days and sperm remains alive for about 72 hours in the female reproductive tract. Coitus is to be avoided during this time.
b. Continuous abstinence is the simplest and most reliable way to avoid pregnancy is not to have coitus for a defined period that facilitates conception.
c. Coitus interruptus is the oldest family planning method. The male partner withdraws his penis before ejaculation, thereby preventing deposition of semen into the vagina.
d. Lactational amenorrhoea : Menstrual cycles resume as early as 6 to 8 weeks from parturition. However, the reappearance of normal ovarian cycles may be delayed for six months during breast-feeding. This delay in ovarian cycles is called lactational amenorrhoea. It serves as a natural, but an unreliable form of birth control.
Suckling by the baby during breast-feeding stimulates the pituitary to secrete increased prolactin hormone in order to increase milk production. This high prolactin concentration in the mother’s blood may prevent menstrual cycle by suppressing the release of GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone) from hypothalamus and gonadotropin secretion from the pituitary.
Question 2.
What are IUD’s? Explain its way of functioning. Also describe their types.
Answer:
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) are inserted by medical experts in the uterus through the vagina. These devices are available as copper releasing IUDs, hormone releasing IUDs and non- medicated IUDs. IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperm within the uterus. IUDs are the ideal contraceptives for females who want to delay pregnancy.
It is one of the popular methods of contraception in India and has a success rate of 95 to 99%. Copper releasing IUDs differ from each other by the amount of copper. Copper IUDs such as Cu T-380 A, Nova T, Cu 7, Cu T 380 Ag, Multiload 375, etc. release free copper and copper salts into the uterus and suppress sperm motility. They can remain in the uterus for five to ten years. Hormone-releasing IUDs such as Progestasert and LNG – 20 are often called as intrauterine systems (IUS). They increase the viscosity of the cervical mucus and thereby prevent sperms from entering the cervix. Non-medicated IUDs are made of plastic or stainless steel. Lippes loop is a double S-shaped plastic device.
Question 3.
Write in detail about cervical cancer.
Answer:
Cervical cancer is caused by a sexually transmitted virus called Human Papilloma virus (HPV). HPV may cause abnormal growth of cervical cells or cervical dysplasia.
The most common symptoms and signs of cervical cancer are pelvic pain, increased vaginal discharge and abnormal vaginal bleeding. The risk factors for cervical cancer include
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Prolonged use of contraceptive pills
Cervical cancer can be diagnosed by a Papanicolaou smear (PAP smear) combined with an HPV test. X-Ray, CT scan, MRI and a PET scan may also be used to determine the stage of cancer. The treatment options for cervical cancer include radiation therapy, surgery and chemotherapy. Modem screening techniques can detect precancerous changes in the cervix. Therefore screening is recommended for women above 30 years once in a year.
Cervical cancer can be prevented with vaccination. Primary prevention begins with HPV vaccination of girls aged 9-13 years, before they become sexually active. Modification in lifestyle can also help in preventing cervical cancer. Healthy diet, avoiding tobacco usage, preventing early marriages, practicing monogamy and regular exercise minimize the risk of cervical cancer.
Question 4.
List out the causes of fertility in human.
Answer:
Causes for male infertility:
- Undescended tests and swollen veins in scrotum
- Underdeveloped testes
- Tight clothing increases the temperature in scrotum and affect sperm production.
- Autoimmune response against own sperm.
- Usage of alcohol, tobacco, marijuana drugs etc.
Causes for female infertility:
- Malformation of cervix or fallopian tubes.
- Inadequate nutrition at puberty.
- Low body fat (anorexia = psychological eating disorder due to fear of gaining weight)
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), uterine disorders, endometriosis.
- underdeveloped ovaries.
- Developing antibodies against sperm.
Common Causes for both the sexes:
- Tumours in pituitary or sex organs
- Inherited mutation of hormone synthesizing genes
- Long term stress
- Ingestion of toxins (Cadmium) & drugs
- Injuries to gonads
- Ageing
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
Dr. Sheela is a famous Gynaecologist at Poes garden. However illegally she performed amniocentesis for several pregnant illiterates and did MTP if identified as female foetus, on request. Under which act will she get arrested, if a complaint is filed against her.
Answer:
Dr. Sheela will be be arrested under PCPNDT Act – preconception and prenatal diagnostic technique Act-1994.
Question 2.
Identify the picture and describe the surgical procedure.
Answer:
The picture describes tubectomy.
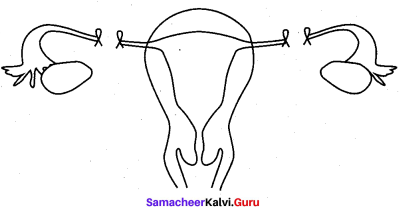
- Tubectomy is the surgical sterilization in woman.
- In this a portion of oviduct is cut and tied through vagina or minor incision in abdomen.
- It prevents fertilization and also the entry of egg to uterus.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter Wise Solutions PDF will help you to clear all doubts. Learn perfectly by using Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chapter 3 Reproductive Health Questions and Answers Bio Zoology Solutions PDF. Leave us a comment to clear your queries. Get instant updates by bookmarking our site. Get the best learning with the effective and excellent step by step Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Guide.